
Mechanics of Materials
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780137605460
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Pearson Education (US)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.9, Problem 132P
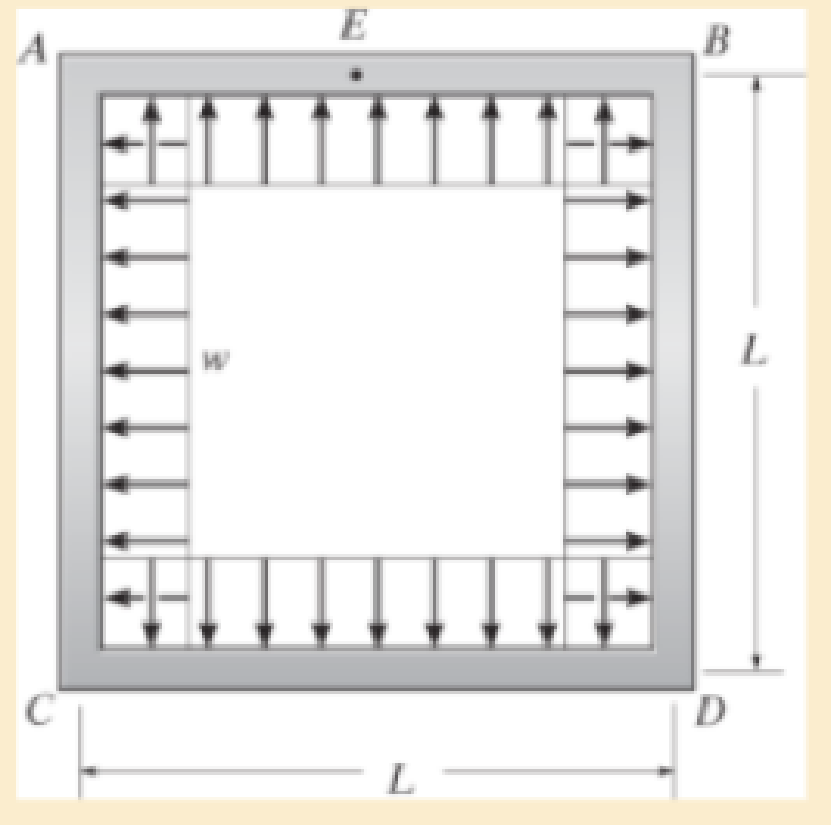
Determine the moment developed in each corner. Neglect the deflection due to axial load. El is constant.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.
An experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is
expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual
water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm)
is measured.
Problem (20): Given the value of APm/Lm [kPa/m], and assuming pressure coefficient similitude, calculate the
drop in the pressure per unit length of the water main (APP/Lp) in [Pa/m].
Givens:
AP M/L m = 590.637 kPa/m
meen
Answers:
( 1 ) 59.369 Pa/m
( 2 )
73.83 Pa/m
(3)
95.443 Pa/m
( 4 ) 44.444 Pa/m
*******
Find the reaction force in y if Ain = 0.169 m^2, Aout = 0.143 m^2, p_in = 0.552 atm, Q = 0.367 m^3/s, α = 31.72 degrees. The pipe is flat on the ground so do not factor in weight of the pipe and fluid.
Chapter 12 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of end A of the cantilevered...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the slope of the simply supported beam...Ch. 12.2 - An L2 steel strap having a thickness of 0.125 in....Ch. 12.2 - The L2 steel blade of the band saw wraps around...Ch. 12.2 - A picture is taken of a man performing a pole...Ch. 12.2 - A torque wrench is used to tighten the nut on a...
Ch. 12.2 - The pipe can be assumed roller supported at its...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve for...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum deflection of the solid...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the equations of the elastic curve using...Ch. 12.3 - The shaft supports the two pulley loads shown....Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve, the...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve and...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 45PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 46PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 47PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 48PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection of end A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at A of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 11FPCh. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the simply...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope and deflection at C. El is...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 54PCh. 12.4 - The composite simply supported steel shaft is...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the maximum deflection of the...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 60PCh. 12.4 - Determine the slope at A and the maximum...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the displacement of the 20-mm-diameter...Ch. 12.4 - The two force components act on the tire of the...Ch. 12.4 - Determine the slope at B and deflection at C. El...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 79PCh. 12.5 - The W10 15 cantilevered beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A992...Ch. 12.5 - The W14 43 simply supported beam is made of A-36...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, B, and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B,...Ch. 12.7 - The beam has a constant E1I1 and is supported by...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the reaction at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the fixed support A and...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller B. EI is...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reaction at the roller support B if...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the journal bearing...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the reactions at the supports, then draw...Ch. 12.9 - The rim on the flywheel has a thickness t, width...Ch. 12.9 - Determine the moment developed in each corner....Ch. 12 - Determine the equation of the elastic curve. Use...Ch. 12 - Draw the bending-moment diagram for the shaft and...Ch. 12 - Determine the moment reactions at the supports A...Ch. 12 - Specify the slope at A and the maximum deflection....Ch. 12 - Determine the maximum deflection between the...Ch. 12 - Determine the slope at B and the deflection at C....Ch. 12 - Determine the reactions, then draw the shear and...Ch. 12 - El is constant.Ch. 12 - Using the method of superposition, determine the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the reaction force in x if Ain = 0.301 m^2, Aout = 0.177 m^2, p_in = 1.338 atm, Q = 0.669 m^3/s, and α = 37.183 degreesarrow_forwardProblem 5: Three-Force Equilibrium A structural connection at point O is in equilibrium under the action of three forces. • • . Member A applies a force of 9 kN vertically upward along the y-axis. Member B applies an unknown force F at the angle shown. Member C applies an unknown force T along its length at an angle shown. Determine the magnitudes of forces F and T required for equilibrium, assuming 0 = 90° y 9 kN Aarrow_forwardProblem 19: Determine the force in members HG, HE, and DE of the truss, and state if the members are in tension or compression. 4 ft K J I H G B C D E F -3 ft -3 ft 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft- 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lb 1500 lbarrow_forward
- Problem 14: Determine the reactions at the pin A, and the tension in cord. Neglect the thickness of the beam. F1=26kN F2 13 12 80° -2m 3marrow_forwardProblem 22: Determine the force in members GF, FC, and CD of the bridge truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. F 15 ft B D -40 ft 40 ft -40 ft 40 ft- 5 k 10 k 15 k 30 ft Earrow_forwardProblem 20: Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG. After the truss is sectioned use a single equation of equilibrium for the calculation of each force. State if the members are in tension or compression. 5 kN 4 kN 4 kN 3 kN 2 kN B D E F 3 m -5 m- -5 m- 5 m 5 m-arrow_forward
- An experimental setup is being built to study the flow in a large water main (i.e., a large pipe). The water main is expected to convey a discharge (Qp). The experimental tube will be built at a length scale of 1/20 of the actual water main. After building the experimental setup, the pressure drop per unit length in the model tube (APm/Lm) is measured. Problem (19): Given the value of Qp [m³/s], and assuming Reynolds number similitude between the water main and experimental tube, calculate the flow rate in the model tube (Qm) in [lit/s]. = 30.015 m^3/sarrow_forwardProblem 11: The lamp has a weight of 15 lb and is supported by the six cords connected together as shown. Determine the tension in each cord and the angle 0 for equilibrium. Cord BC is horizontal. E 30° B 60° Aarrow_forwardProblem 10: If the bucket weighs 50 lb, determine the tension developed in each of the wires. B $30° 5 E D 130°arrow_forward
- Problem 3: Four-Force Equilibrium Knowing the forces in members A and C, determine the force of B and D, assuming the system is in equilibrium. A structural joint is held in equilibrium by four forces acting along different members. • Member A applies a force of 4 kN at an angle of 60° above the positive x-axis. • Member C applies a force of 2 kN horizontally to the left along the x-axis. • Member B applies an unknown force along the horizontal direction. • Member D applies an unknown force at an angle of 45° above the negative x-axis. Determine the forces in members B and D, assuming the system is in static equilibrium. 4 kN 2 kN C 45° A D 60° FB Barrow_forwardProblem 18: Determine the force in each member of the truss. State if the members are in tension or compression. 3 ft 3 ft 3 ft B D 4 ft 4 ft. 130 lb Earrow_forwardProblem 16: Determine the force in each of the member of the truss and state if the members are in tension or compression. Set P₁ = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. 2 m G F E A A 1 m B 2 m 1 m P1 Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Solids: Lesson 53 - Slope and Deflection of Beams Intro; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I7lTq68JRmY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY