
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915389
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.6, Problem 26FP
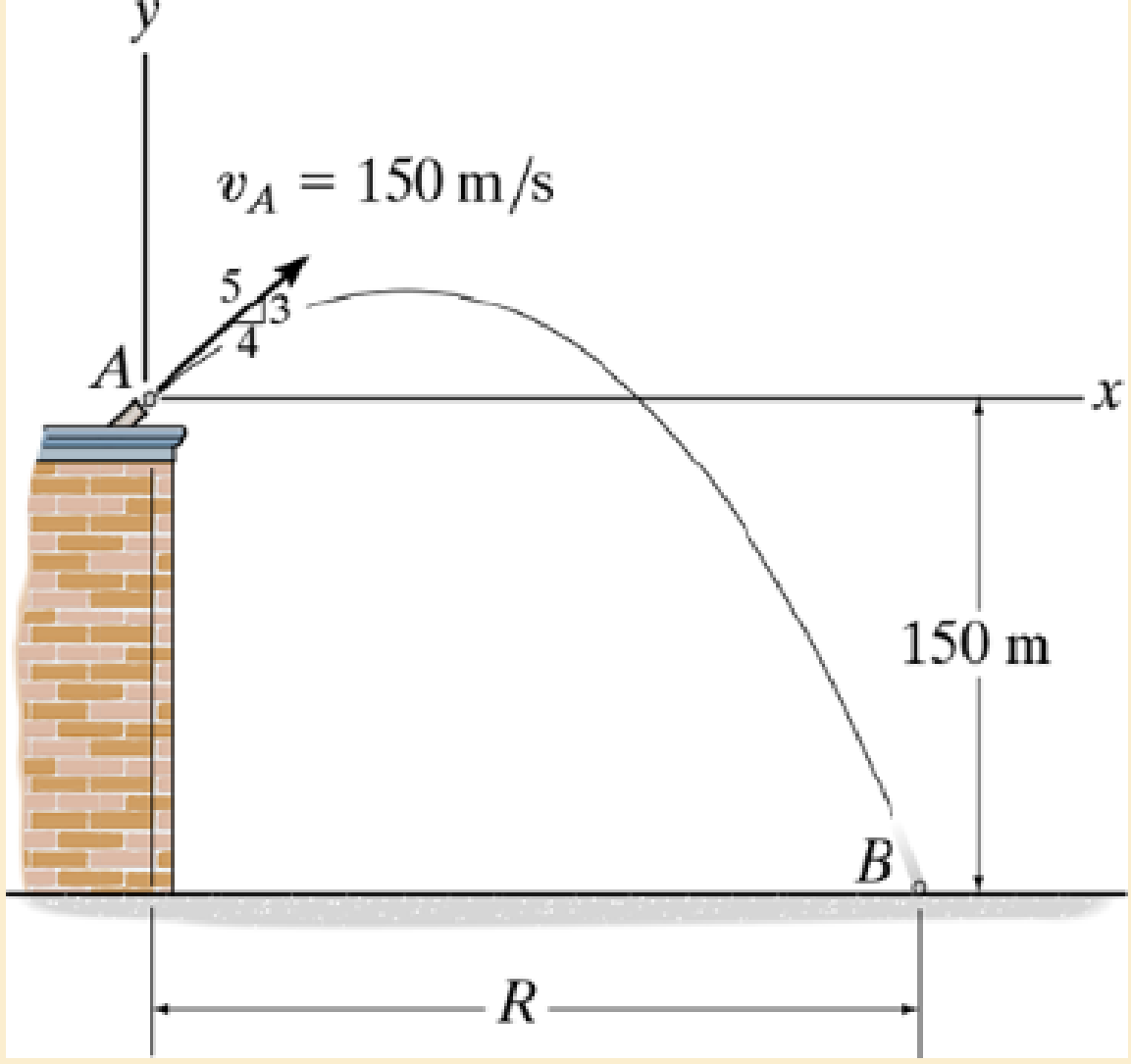
Determine the range R where it strikes the ground at B.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:12
Students have asked these similar questions
2. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of
known functions.
(x + 2)²y" + (x + 2)y' - y = 0 ; Hint: Let: z = x+2
1. Find a power series solution in powers of x.
y" - y' + x²y = 0
3. Find a basis of solutions by the Frobenius method. Try to identify the series as expansions of
known functions.
8x2y" +10xy' + (x 1)y = 0
-
Chapter 12 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 12.2 - a. If s = (2t3) m, where t is in seconds,...Ch. 12.2 - Initially, the car travels along a straight road...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the time of flight when it returns to...Ch. 12.2 - A particle travels along a straight line with a...Ch. 12.2 - A particle travels along a straight line with a...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the time when the velocity of the...Ch. 12.2 - A particle travels along a straight line with an...Ch. 12.2 - A particle moves along a straight line such that...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the acceleration of the particle at s =...Ch. 12.2 - What is the particles velocity when t = 6 s, and...
Ch. 12.2 - If a particle has an initial velocity of v0 = 12...Ch. 12.2 - When t = 1 s, the particle is located 10m to the...Ch. 12.2 - When s =4ft, v = 3ft/s and when s = 10ft, v = 8...Ch. 12.2 - If s = 0 when t = 0, determine the particles...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the position of the particle when t = 6...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the average velocity, the average speed,...Ch. 12.2 - Determine (a) the displacement of the particle...Ch. 12.2 - If s = 1 m and v = 2 m/s when t = 0, determine the...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the particles velocity when s = 2 m, if...Ch. 12.2 - Then in another 5 s it moves from SB to SC = 6 m....Ch. 12.2 - How long will it take to reach a speed of 120...Ch. 12.2 - It takes about 3 s for a driver having 0.1%...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the total distance traveled when t = 10...Ch. 12.2 - If it is subjected to a deceleration of a = kv3,...Ch. 12.2 - Determine how far it travels before it stops. How...Ch. 12.2 - It takes the driver of car A 0.75 s to react (this...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the time needed for the rocket to reach...Ch. 12.2 - Afterwards it travels with a constant velocity for...Ch. 12.2 - If s = 4 ft when t = 0, determine the position of...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the distance traveled in three seconds,...Ch. 12.2 - If the bag is released with the same upward...Ch. 12.2 - If v = 20 m/s when s = 0 and t = 0, determine the...Ch. 12.2 - If v = 0, s = 1 m when t = 0, determine the...Ch. 12.2 - If the body is released from rest at a very high...Ch. 12.2 - At t 0,s 1 m and v = 10 m/s. When t 9 s,...Ch. 12.2 - Initially the particle falls from rest.Ch. 12.2 - Determine the distance between them when t = 4 s...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the height from the ground and the time...Ch. 12.2 - A sphere is fired downwards into a medium with an...Ch. 12.2 - If s = 0 when t = 0, determine the position and...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the elapsed time t 2v0/g from the...Ch. 12.2 - Neglecting air resistance, this acceleration is...Ch. 12.2 - Accounting for the variation of gravitational...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the v t graph for the same time...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the s t and a t graphs during the same...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the a s graph for the same interval.Ch. 12.3 - The sports car travels along a straight road such...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the v t graph for the time interval 0 ...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the s t graph during the time interval...Ch. 12.3 - A freight train starts from rest and travels with...Ch. 12.3 - The s-t graph for a train has been experimentally...Ch. 12.3 - Rocket A accelerates vertically at 20 m/s2 for 12...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the v-t and a-t graphs for the time...Ch. 12.3 - If the position of a particle is defined by s = [2...Ch. 12.3 - It then climbs in a straight line with a uniform...Ch. 12.3 - It can accelerate at 5 ft/s2 and then decelerate...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the total distance the car moves until...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the time t when the jet plane stops....Ch. 12.3 - The acceleration and deceleration that occur are...Ch. 12.3 - Draw the st and at graphs for the particle. When t...Ch. 12.3 - If the rocket starts at s = 0 when v = 0,...Ch. 12.3 - After 30 s the first stage, A, burns out and the...Ch. 12.3 - The flat part of the graph is caused by shifting...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the cars maximum velocity and the time t...Ch. 12.3 - Draw the v-s graph and determine the time needed...Ch. 12.3 - From the data, construct the s-t and a-t graphs...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the total distance the motorcycle...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the motorcycles acceleration and...Ch. 12.3 - Draw the s-t and a-t graphs. Also determine the...Ch. 12.3 - If it is subjected to the decelerations shown,...Ch. 12.3 - Determine the boats speed when s = 50 ft, 100 ft,...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the v-s graph.Ch. 12.3 - After 15 s the first stage A burns out and the...Ch. 12.3 - The speed of a train during the first minute has...Ch. 12.3 - If the elevator maintains a constant upward speed...Ch. 12.3 - Car A accelerates at 4 m/s2 for 10 s and then...Ch. 12.3 - If the position of a particle is defined as s =...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the st and at graphs for the motion....Ch. 12.3 - Draw the vs graph if v = 0 at s = 0.Ch. 12.3 - Determine the speed of the plane when it has...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the s-t and a-s graphs. Also, determine...Ch. 12.3 - Construct the a-s graph.Ch. 12.3 - Determine its acceleration when s = 100 m and when...Ch. 12.6 - Use the chain-rule and find and in terms of x, ...Ch. 12.6 - The particle travels from A to B. Identify the...Ch. 12.6 - The particle travels from A to B. Identify the...Ch. 12.6 - The particle travels from A to B. Identify the...Ch. 12.6 - If the x and y components of a particle's velocity...Ch. 12.6 - If its position along the x axis is x = (8t) m,...Ch. 12.6 - If x = (4t4) m, where t is in seconds, determine...Ch. 12.6 - A particle travels 3long a straight line path y =...Ch. 12.6 - If x = 8 m, vx = 8 m/s, and ax = 4 m/s2 when t = 2...Ch. 12.6 - If the box has x components of velocity and...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the maximum height h it reaches.Ch. 12.6 - The ball is kicked from point A with the initial...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the speed at which the basketball at A...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the range R.Ch. 12.6 - A ball is thrown from A. If it is required to...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the range R where it strikes the ground...Ch. 12.6 - If the velocity of a particle is defined as v(t) =...Ch. 12.6 - If r = 0 when t = 0, determine the displacement of...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the particles position (x, y, z) at t =...Ch. 12.6 - If the particle is at the origin when t = 0,...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the point B(x, y) where the water...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the particles position (x, y, z) when t...Ch. 12.6 - It takes 4 s for it to go from B to C and then 3 s...Ch. 12.6 - It takes 8 s for it to go from B to C and then 10...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the magnitude of the crates velocity and...Ch. 12.6 - If the x component of acceleration is...Ch. 12.6 - If the component of velocity along the x axis is...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the x and y components of its velocity...Ch. 12.6 - If it takes 3 s for it to go from A to C,...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the magnitudes of its velocity and...Ch. 12.6 - If the link moves with a constant speed of 10 m/s,...Ch. 12.6 - If it has a constant speed of 75 ft/s, determine...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the distance the helicopter is from...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the minimum initial velocity v0 and the...Ch. 12.6 - If it takes 1.5 s to travel from A to B, determine...Ch. 12.6 - Neglecting the size of the ball, determine the...Ch. 12.6 - The girl at A can throw a ball at vA = 10 m/s....Ch. 12.6 - If vA = 10 m/s, determine the range R if this...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the point (x, y) where it strikes the...Ch. 12.6 - If it strikes the ground at B having coordinates x...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the distance d to where it will land.Ch. 12.6 - Determine the speed at which it strikes the ground...Ch. 12.6 - Neglecting the size of the ball, determine the...Ch. 12.6 - If he strikes the ground at B, determine his...Ch. 12.6 - If he strikes the ground at B, determine his...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the horizontal velocity vA of a tennis...Ch. 12.6 - If the acceleration varies with time as shown,...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the range R, the maximum height h...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the maximum and minimum speed at which...Ch. 12.6 - Also, what is the corresponding angle A at which...Ch. 12.6 - Also, what is the corresponding angle A at which...Ch. 12.6 - Note that the first dart must be thrown at C( D)...Ch. 12.6 - Determine the time for a particle of water leaving...Ch. 12.6 - The snowmobile is traveling at 10 m/s when it...Ch. 12.6 - Water flows from the hose at vA = 80 ft/s.Ch. 12.6 - When the ball is directly overhead of player B he...Ch. 12.6 - If it takes 1.5 s to travel from A to B, determine...Ch. 12.7 - a. Determine the acceleration at the instant...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when t...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when s...Ch. 12.7 - If the car decelerates uniformly along the curved...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the direction of the crates velocity,...Ch. 12.7 - If the motorcycle has a deceleration of at =...Ch. 12.7 - The car travels up the hill with a speed of v =...Ch. 12.7 - If the acceleration of the automobile is 5 ft/s2,...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the maximum constant speed a race car...Ch. 12.7 - If it then increases its speed along a circular...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the speed of the particle and its normal...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the radius of curvature of the path at...Ch. 12.7 - If its speed is increased by v = (0.05t2) ft/s2,...Ch. 12.7 - If it then starts to increase its speed at v =...Ch. 12.7 - If they are at the positions shown when t = 0,...Ch. 12.7 - At the instant shown, A has a speed of 60ft/sand...Ch. 12.7 - If the acceleration is 2.5 m/s2, determine the...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitudes of its velocity and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the cars acceleration...Ch. 12.7 - If the car passes point A with a speed of 20m/s...Ch. 12.7 - The motorcycle is traveling at 1 m/s when it is at...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitudes of its velocity and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitudes of its velocity and...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the rate of increase in the train's...Ch. 12.7 - If it increases its speed along the circular track...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the time when the magnitude of...Ch. 12.7 - If its speed at t = 0 is 15 ft/s and is increasing...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the boat's acceleration...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitudes of his velocity and...Ch. 12.7 - If it is initially traveling with a speed of 10...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of its acceleration when...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the rate of increase in the planes...Ch. 12.7 - Find the equation of the path, y = f (x), and then...Ch. 12.7 - The motorcycle is traveling at 40 m/s when it is...Ch. 12.7 - If the speed limit is posted at 60 km/h, determine...Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 140PCh. 12.7 - Determine the normal and tangential components of...Ch. 12.7 - Take =150 m.Ch. 12.7 - The motorcycle travels along the elliptical track...Ch. 12.7 - The motorcycle travels along the elliptical track...Ch. 12.7 - If at the instant shown the speed of A begins to...Ch. 12.7 - If the speed of B is increasing by (at)B = 4m/s2,...Ch. 12.7 - Also, specify the direction of flight, measured...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.7 - The train passes point B with a speed of 20 m/s...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.7 - Determine the particles acceleration when it is...Ch. 12.7 - When t = 8 s, determine the coordinate direction...Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 153PCh. 12.7 - If the speed of the crate at A is 15 ft/s, which...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the angular velocity of the radial line...Ch. 12.8 - A ball rolls outward along the radial groove so...Ch. 12.8 - Peg P is driven by the fork link OA along the...Ch. 12.8 - Peg P is driven by the forked link OA along the...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitude of the velocity of the...Ch. 12.8 - At the instant = 45, the athlete is running with...Ch. 12.8 - A particle is moving along a circular path having...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the radial and transverse components of...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the components of its velocity and...Ch. 12.8 - If the propeller has a diameter of 6 ft and is...Ch. 12.8 - Express the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitudes of velocity and...Ch. 12.8 - If a particle moves along a path such that r = (2...Ch. 12.8 - If a particle moves along a path such that r =...Ch. 12.8 - At the instant shown, its angular rate of rotation...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the angular rate of rotation of the...Ch. 12.8 - Calculate this vector, a, in terms of its...Ch. 12.8 - such that its position as a function of time is...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the radial and transverse components of...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the radial and transverse components of...Ch. 12.8 - If it is assumed that the hose lies in a...Ch. 12.8 - Two pin-connected slider blocks, located at B....Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.8 - If the geometry of the fixed rod for a short...Ch. 12.8 - The platform rotates at a constant rate of 6...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the cars radial and transverse...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the cars radial and transverse...Ch. 12.8 - If it maintains a constant speed of v = 35 ft/s,...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the cylindrical components of the...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the maximum and minimum magnitudes of...Ch. 12.8 - The peg is constrained to move in the slots of the...Ch. 12.8 - When = 30, the angular velocity and angular...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the angular rate of rotation of the...Ch. 12.8 - A truck is traveling along the horizontal circular...Ch. 12.8 - Two pin-connected slider blocks, located at B,...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the...Ch. 12.8 - The searchlight on the boat anchored 2000 ft from...Ch. 12.8 - If the car in Prob.12-187 is accelerating at 15...Ch. 12.8 - If = 4 rad/s (constant), determine the radial and...Ch. 12.8 - if the particle has an angular acceleration = 5...Ch. 12.8 - If = (0.5t)rad, where t is in seconds, determine...Ch. 12.8 - Determine the magnitudes of the velocity and...Ch. 12.8 - When t = 0, = 0. Use Simpson's rule with n = 50...Ch. 12.8 - The double collar C is pin connected together such...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of block D if end A of the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of block A if end B of the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of block A if end B of the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of block A if end F of the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of car A if point P on the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of cylinder B if cylinder A...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of car B relative to car A.Ch. 12.10 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the distance between them when t = 4 s.Ch. 12.10 - If B is accelerating at 1200 km/h2 while A...Ch. 12.10 - If the end of the cable at A is pulled down with a...Ch. 12.10 - The motor at D draws in its cable at aD = 5 m/s2....Ch. 12.10 - If BC remains fixed while the plunger P is pushed...Ch. 12.10 - If the end of the cable at A is pulled down with a...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the displacement of the log if the truck...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the constant speed at which the cable at...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the time needed to lift the load 7 m.Ch. 12.10 - If the end A of the cable is moving at vA = 3 m/s,...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the time needed for the load at B to...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity of the block.Ch. 12.10 - If block A of the pulley system is moving downward...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the speed of the block at B.Ch. 12.10 - Determine the speed of block A if the end of the...Ch. 12.10 - The motor draws in the cable at D with a constant...Ch. 12.10 - The pulley at A is attached to the smooth collar...Ch. 12.10 - When sB = 6ft. the end of the cord at B is pulled...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of block B...Ch. 12.10 - Determine how fast the boat approaches the pier at...Ch. 12.10 - If the hydraulic cylinder H draws in rod BC at 2...Ch. 12.10 - The car at B is traveling at 18.5 m/s along the...Ch. 12.10 - When sA = 1.5 m, vB = 6 m/s. Determine the...Ch. 12.10 - If block B is moving down with a velocity vB and...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the velocity and acceleration of the...Ch. 12.10 - If their velocities are vA = 500km/h and vB =...Ch. 12.10 - If B is increasing its speed by 1200mi/h2, while A...Ch. 12.10 - The point of destination is located along the...Ch. 12.10 - If vA = 40ft/s and vB = 30 ft/s. determine the...Ch. 12.10 - An instrument in the car indicates that the wind...Ch. 12.10 - If vA = 10m/s and vB = 15m/s, determine the...Ch. 12.10 - At the same instant, car B is decelerating at 250...Ch. 12.10 - At the instant shown, A has a speed of 90ft/sand...Ch. 12.10 - If raindrops fall vertically at 7 km/h in still...Ch. 12.10 - If B is increasing its velocity by 2 m/s2, while A...Ch. 12.10 - If A is increasing its speed at 4 m/s2, whereas...Ch. 12.10 - Compute the terminal (constant) velocity vr of the...Ch. 12.10 - He wishes to cross the 40-ft-wide river to point...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 12.10 - At the instant the ball is thrown, the player is...Ch. 12.10 - At the instant the ball is thrown, the player is...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the constant speed at which the player...Ch. 12.10 - At this same instant car B travels along the...Ch. 12.10 - If you measured the time it takes for the...Ch. 12.10 - Determine its maximum acceleration and maximum...Ch. 12.10 - Originally s0 = 0.Ch. 12.10 - A projectile, initially at the origin, moves along...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the acceleration when t = 2.5 s, 10 s,...Ch. 12.10 - If it takes 3 s to go from A to B, and then 5 s to...Ch. 12.10 - From a videotape, it was observed that a player...Ch. 12.10 - The truck travels in a circular path having a...Ch. 12.10 - If the car starts from rest when = 0, determine...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the magnitude of the particles...Ch. 12.10 - Determine the time needed for the load at B to...Ch. 12.10 - If their velocities are vA = 600 km/h and vB = 500...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3.1 Discuss the differences between an error and a residual.
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
________ binding is when the compiler binds member function calls at compile time.
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Magic Dates The date June 10, 1960, is special because when we write it in the following format, the month time...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
What major structural changes are introduced into a UHSMC?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
The Social Security Administration maintains an actuarial life table that contains the probability that a perso...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hello I was going over the solution for this probem and I'm a bit confused on the last part. Can you please explain to me 1^4 was used for the Co of the tubular cross section? Thank you!arrow_forwardBlood (HD = 0.45 in large diameter tubes) is forced through hollow fiber tubes that are 20 µm in diameter.Equating the volumetric flowrate expressions from (1) assuming marginal zone theory and (2) using an apparentviscosity for the blood, estimate the marginal zone thickness at this diameter. The viscosity of plasma is 1.2 cParrow_forwardQ2: Find the shear load on bolt A for the connection shown in Figure 2. Dimensions are in mm Fig. 2 24 0-0 0-0 A 180kN (10 Markarrow_forward
- determine the direction and magnitude of angular velocity ω3 of link CD in the four-bar linkage using the relative velocity graphical methodarrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forwardFour-bar linkage mechanism, AB=40mm, BC=60mm, CD=70mm, AD=80mm, =60°, w1=10rad/s. Determine the direction and magnitude of w3 using relative motion graphical method. A B 2 3 77777 477777arrow_forward
- The evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forward(Read image) (Answer given)arrow_forwardProblem (17): water flowing in an open channel of a rectangular cross-section with width (b) transitions from a mild slope to a steep slope (i.e., from subcritical to supercritical flow) with normal water depths of (y₁) and (y2), respectively. Given the values of y₁ [m], y₂ [m], and b [m], calculate the discharge in the channel (Q) in [Lit/s]. Givens: y1 = 4.112 m y2 = 0.387 m b = 0.942 m Answers: ( 1 ) 1880.186 lit/s ( 2 ) 4042.945 lit/s ( 3 ) 2553.11 lit/s ( 4 ) 3130.448 lit/sarrow_forward
- Problem (14): A pump is being used to lift water from an underground tank through a pipe of diameter (d) at discharge (Q). The total head loss until the pump entrance can be calculated as (h₁ = K[V²/2g]), h where (V) is the flow velocity in the pipe. The elevation difference between the pump and tank surface is (h). Given the values of h [cm], d [cm], and K [-], calculate the maximum discharge Q [Lit/s] beyond which cavitation would take place at the pump entrance. Assume Turbulent flow conditions. Givens: h = 120.31 cm d = 14.455 cm K = 8.976 Q Answers: (1) 94.917 lit/s (2) 49.048 lit/s ( 3 ) 80.722 lit/s 68.588 lit/s 4arrow_forwardProblem (13): A pump is being used to lift water from the bottom tank to the top tank in a galvanized iron pipe at a discharge (Q). The length and diameter of the pipe section from the bottom tank to the pump are (L₁) and (d₁), respectively. The length and diameter of the pipe section from the pump to the top tank are (L2) and (d2), respectively. Given the values of Q [L/s], L₁ [m], d₁ [m], L₂ [m], d₂ [m], calculate total head loss due to friction (i.e., major loss) in the pipe (hmajor-loss) in [cm]. Givens: L₁,d₁ Pump L₂,d2 오 0.533 lit/s L1 = 6920.729 m d1 = 1.065 m L2 = 70.946 m d2 0.072 m Answers: (1) 3.069 cm (2) 3.914 cm ( 3 ) 2.519 cm ( 4 ) 1.855 cm TABLE 8.1 Equivalent Roughness for New Pipes Pipe Riveted steel Concrete Wood stave Cast iron Galvanized iron Equivalent Roughness, & Feet Millimeters 0.003-0.03 0.9-9.0 0.001-0.01 0.3-3.0 0.0006-0.003 0.18-0.9 0.00085 0.26 0.0005 0.15 0.045 0.000005 0.0015 0.0 (smooth) 0.0 (smooth) Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.00015 Drawn…arrow_forwardThe flow rate is 12.275 Liters/s and the diameter is 6.266 cm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
moment of inertia; Author: NCERT OFFICIAL;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A4KhJYrt4-s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY