
Connect Online Access 1-Semester for Organic Chemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260475609
Author: SMITH, Janice
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Higher Education (us)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.6, Problem 14P
Draw the products of each reaction.
a. 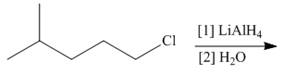 b.
b. 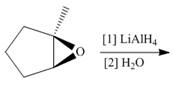
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Explain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.
Briefly describe a nucleophilic addition.
Is nucleophilic acyl substitution an SN1 or SN2 reaction?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Connect Online Access 1-Semester for Organic Chemistry
Ch. 12.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 12.3 - Problem 12.2 What alkane is formed when each...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 12.3 - Compound Molecular formula before...Ch. 12.4 - Problem 12.8 Draw the products formed when...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 9PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 12.5 - Problem 12.11 (a) Draw the structure of a compound...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 13PCh. 12.6 - Problem 12.14 Draw the products of each...Ch. 12.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 12.8 - Problem 12.16 Draw all stereoisomers formed when...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 17PCh. 12.9 - Problem 12.18 Draw the products formed when both...Ch. 12.10 - Problem 12.19 Draw the products formed when each...Ch. 12.10 - Prob. 20PCh. 12.10 - Prob. 21PCh. 12.11 - Problem 12.22 Draw the products formed when each...Ch. 12.11 - Prob. 23PCh. 12.12 - Problem 12.24 Draw the organic products in each of...Ch. 12.13 - Prob. 25PCh. 12 - 12.29 Draw the products formed when A is treated...Ch. 12 - Prob. 30PCh. 12 - Prob. 31PCh. 12 - Prob. 32PCh. 12 - Prob. 33PCh. 12 - Draw the organic products formed when cyclopentene...Ch. 12 - Draw the organic products formed when allylic...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Prob. 40PCh. 12 - Prob. 41PCh. 12 - What alkene is needed to synthesize each 1,2-diol...Ch. 12 - 12.48 Draw the products formed in each oxidative...Ch. 12 - What alkene or alkyne yields each set of products...Ch. 12 - Prob. 47PCh. 12 - Prob. 48PCh. 12 - Prob. 49PCh. 12 - Prob. 50PCh. 12 - 12.57 Draw the product of each asymmetric...Ch. 12 - 12.60 Identify A in the following reaction...Ch. 12 - Prob. 58PCh. 12 - 12.62 It is sometimes necessary to isomerize a cis...Ch. 12 - 12.63 Devise a synthesis of each compound from...Ch. 12 - Prob. 61P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
6. How can you use the features found in each chapter?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Why is it unlikely that two neighboring water molecules would be arranged like this?
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Why are mutants used as test organisms in the Ames test?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. NH2 F3C CF3 NH OMe NH2-NH2, ACOH Aarrow_forwardPhotochemical smog is formed in part by the action of light on nitrogen dioxide. The wavelength of radiation absorbed by NO2 in this reaction is 197 nm.(a) Draw the Lewis structure of NO2 and sketch its π molecular orbitals.(b) When 1.56 mJ of energy is absorbed by 3.0 L of air at 20 °C and 0.91 atm, all the NO2 molecules in this sample dissociate by the reaction shown. Assume that each absorbed photon leads to the dissociation (into NO and O) of one NO2 molecule. What is the proportion, in parts per million, of NO2 molecules in this sample? Assume that the sample behaves ideally.arrow_forwardCorrect each molecule in the drawing area below so that it has the skeletal ("line") structure it would have if it were dissolved in a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HCI. If there are no changes to be made, check the No changes box under the drawing area. No changes. HO Explanation Check NH, 2 W O :□ G ©2025 M unter Accessibilityarrow_forward
- An expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forward
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY