
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134382593
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12.2, Problem 1PP
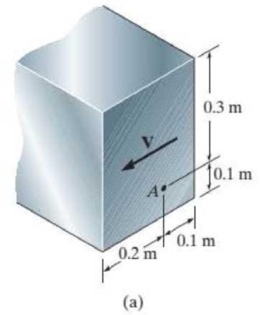
In each case, calculate the value of Q and t that are used in the shear formula for finding the shear stress at A. Also, show how the shear stress acts on a differential volume element located at point A.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
##2# Superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical energy. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 Mpa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 90%
Design the simplified power plant schematic
Analyze it on the basis of the attached figure
Determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant
### Dados in the attached images
### To make a conclusion for a report of an experiment on rockets, in which the openrocket software was used for the construction and modeling of two rockets: one one-stage and one two-stage.
First rocket (single-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 100 m/s and a maximum height of 500 m
The second rocket (two-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 50 m/s and a maximum height of 250 m
To make a simplified conclusion, taking into account the efficiency of the software in the study of rockets
Determine the coefficients of polynomial for the polynomial function of Cam profile based on
the boundary conditions shown in the figure.
S
a
3
4
5
C₁
(+)
Ꮎ
В
s = q + q { + c f * + q € * + q ( +c+c+c
6
Ꮎ
+C5
+C
β
В
В
0
cam angle 0
B
7
(
Chapter 12 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Ch. 12.2 - In each case, calculate the value of Q and t that...Ch. 12.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 2FPCh. 12.2 - Determine the absolute maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 12.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =...Ch. 12.2 - If the beam is made from four plates and subjected...Ch. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V = 30kN,...
Ch. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - The wood beam has an allowable shear stress of...Ch. 12.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 12.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the largest shear force V that the...Ch. 12.2 - If the applied shear force V = 18 kip, determine...Ch. 12.2 - The overhang beam is subjected to the uniform...Ch. 12.2 - The beam is made from a polymer and is subjected...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the strut if...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum shear force V that the strut...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 15PCh. 12.2 - Plot the shear-stress distribution over the cross...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 17PCh. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the length of the cantilevered beam so...Ch. 12.2 - If the beam is made from wood having an allowable...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the largest intensity w of the...Ch. 12.2 - If w = 800 lb/ft, determine the absolute maximum...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the shear stress at point B on the web...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...Ch. 12.2 - Railroad tics must be designed to resist large...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 27PCh. 12.2 - Prob. 28PCh. 12.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the T-beam...Ch. 12.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the T-beam...Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 31PCh. 12.3 - The two identical boards are bolted together to...Ch. 12.3 - Two identical 20-mm-thick plates are bolted to the...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 8FPCh. 12.3 - Prob. 9FPCh. 12.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is constructed from two boards fastened...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards. If it...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 36PCh. 12.3 - The double T-beam is fabricated by welding the...Ch. 12.3 - The beam is constructed from three boards....Ch. 12.3 - A beam is constructed from three boards bolted...Ch. 12.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 41PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 42PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 43PCh. 12.3 - The box beam is constructed from four boards that...Ch. 12.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 12.3 - The member consists of two plastic channel strips...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 47PCh. 12.3 - Prob. 48PCh. 12 - The beam is fabricated from four boards nailed...Ch. 12 - Prob. 2RPCh. 12 - Prob. 3RPCh. 12 - Prob. 4RPCh. 12 - Prob. 5RPCh. 12 - Prob. 6RPCh. 12 - Prob. 7RPCh. 12 - The member consists of two triangular plastic...Ch. 12 - If the pipe is subjected to a shear of V = 15 kip,...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ### Superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical energy. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 Mpa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 90% Design the simplified power plant schematic Analyze it on the basis of the attached figure Determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant ### Dados in the attached imagesarrow_forwardThe machine below forms metal plates through the application of force. Two toggles (ABC and DEF) transfer forces from the central hydraulic cylinder (H) to the plates that will be formed. The toggles then push bar G to the right, which then presses a plate (p) into the cavity, thus shaping it. In this case, the plate becomes a section of a sphere. If the hydraulic cylinder can produce a maximum force of F = 10 kN, then what is the maximum P value (i.e. Pmax) that can be applied to the plate when θ = 35°? Also, what are the compressive forces in the toggle rods in that situation? Finally, what happens to Pmax and the forces in the rods as θ decreases in magnitude?arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the minimum force P needed to prevent the 20 kg uniform rod AB from sliding. The contact surface at A is smooth, whereas the coefficient of static friction between the rod and the floor is μs = 0.3.arrow_forward
- Determine the magnitudes of the reactions at the fixed support at A.arrow_forwardLet Hill frame H = {i-hat_r, i-hat_θ, i-hat_h} be the orbit frame of the LMO satellite. These base vectors are generally defined as:i-hat_r = r_LM / |r_LM|, i-hat_theta = i-hat_h X i-hat_r, i-hat_h = r_LM X r-dot_LMO /( | r_LM X r-dot_LMO | ) How would you: • Determine an analytic expressions for [HN]arrow_forwardDe Moivre’s Theoremarrow_forward
- hand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forwardDetermine the shear flow qqq for the given profile when the shear forces acting at the torsional center are Qy=30Q_y = 30Qy=30 kN and Qz=20Q_z = 20Qz=20 kN. Also, calculate qmaxq_{\max}qmax and τmax\tau_{\max}τmax. Given:Iy=10.5×106I_y = 10.5 \times 10^6Iy=10.5×106 mm4^44,Iz=20.8×106I_z = 20.8 \times 10^6Iz=20.8×106 mm4^44,Iyz=6×106I_{yz} = 6 \times 10^6Iyz=6×106 mm4^44. Additional parameters:αy=0.5714\alpha_y = 0.5714αy=0.5714,αz=0.2885\alpha_z = 0.2885αz=0.2885,γ=1.1974\gamma = 1.1974γ=1.1974. (Check hint: τmax\tau_{\max}τmax should be approximately 30 MPa.)arrow_forwardhand-written solutions only, please.arrow_forward
- In the bending of a U-profile beam, the load path passes through the torsional center C, causing a moment of 25 kNm at the cross-section under consideration. Additionally, the beam is subjected to an axial tensile force of 100 kN at the centroid. Determine the maximum absolute normal stress.(Check hint: approximately 350 MPa, but where?)arrow_forward### Make an introduction to a report of a rocket study project, in the OpenRocket software, where the project consists of the simulation of single-stage and two-stage rockets, estimating the values of the exhaust velocities of the engines used, as well as obtaining the graphs of "altitude", "mass ratio x t", "thrust x t" and "ψ × t".arrow_forwardA 6305 ball bearing is subjected to a steady 5000-N radial load and a 2000-N thrust load and uses a very clean lubricant throughout its life. If the inner race angular velocity is 500 rpm find The equivalent radial load the L10 life and the L50 lifearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Torsion; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1YTKedLQOa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY