
1.
Prepare the given transactions in the cash receipts journal and verify the total column and rule the column and use the general journal to record the sales returns and allowances.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Cash Receipts Journal: It is a special book where only cash receipts transactions that are received from customers, merchandise sales and service made in cash and collection of accounts receivable are recorded.
The following are the some examples of transactions that would be recorded in the Other Accounts credit column of the cash receipts journal:
- • Cash received as interest on notes payable
- • Interest revenue received from debtors
- • Cash receipts from bank loans
- • Cash receipts for capital investments
Prepare the given transactions in the cash receipts journal and verify the total column and rule the column and use the general journal to record the sales returns and allowances:
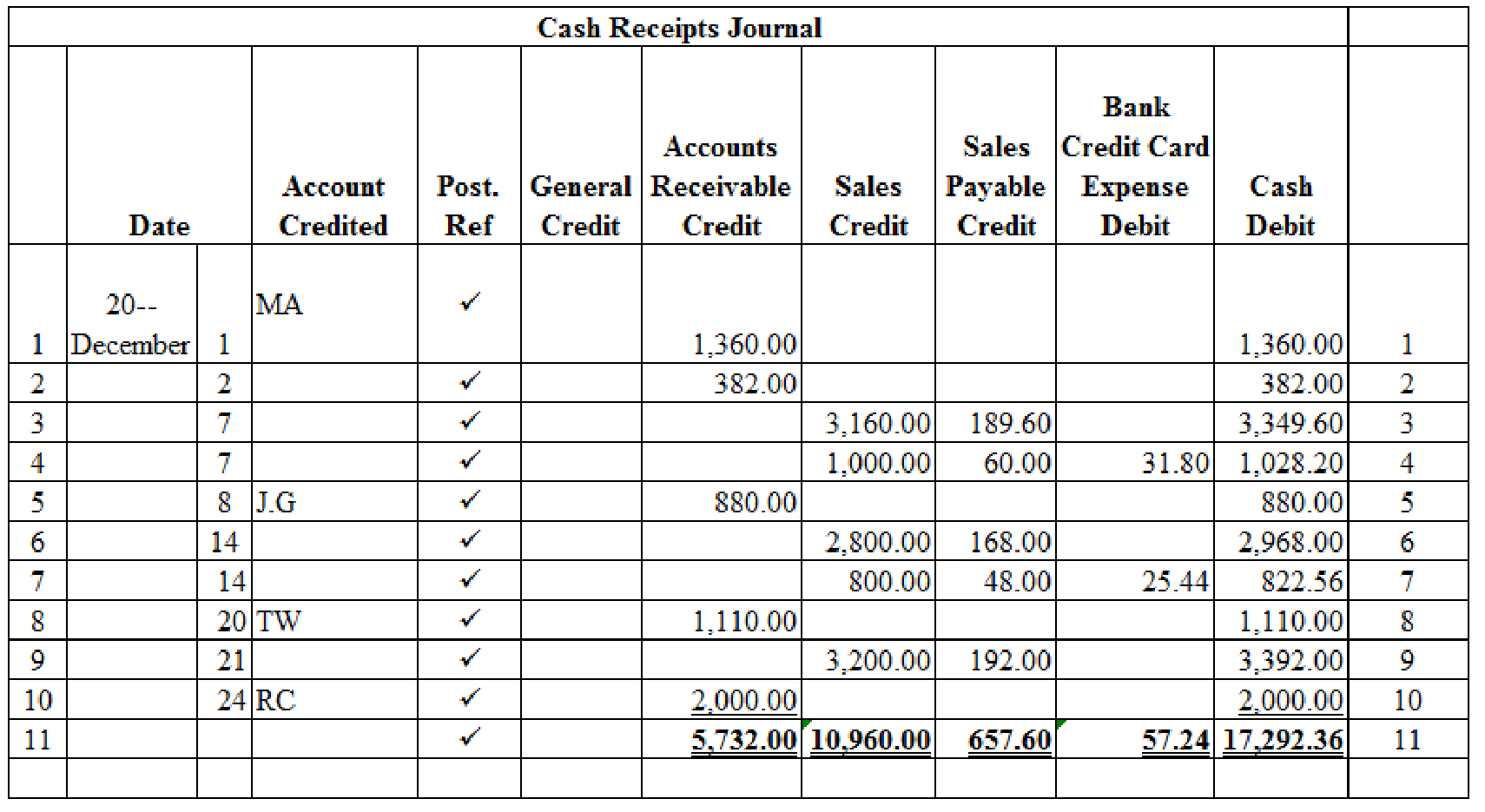
Table (1)
Verification of total debit and credit column:
Working note 1:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 7th December:
Working note 2:
Calculate the amount of bank credit card expense on dated 7th December:
Working note 3:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 7th December:
Working note 4:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 14th December:
Working note 5:
Calculate the amount of bank credit card expense on dated 14th December:
Working note 6:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 14th December:
Working note 7:
Calculate the amount of cash on dated 21st December:
Use the general journal to record the sales returns and allowances:
General Journal: It is a book where all the monetary transactions are recorded in the form of journal entries on the date of their occurrence in a chronological order.
Transaction on December 11:
| General Journal | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 11 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 401.1 | 60.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | 231 | 3.60 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable, MA | 122/✓ | 63.60 | ||||
| (To record the merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- ■ Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account, and contra-revenue accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Sales Tax Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased due to returns, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable, MA is an asset account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be received has decreased, asset account is decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working note 1:
Compute the sales tax payable amount.
Working note 2:
Compute the accounts receivable amount.
Transaction on December 21:
| General Journal | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 21 | Sales Returns and Allowances | 401.1 | 22.00 | ||
| Sales Tax Payable | 231 | 1.32 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable, A Manufacturing | 122/✓ | 23.32 | ||||
| (To record the merchandise returned) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- ■ Sales Returns and Allowances is a contra-revenue account, and contra-revenue accounts decrease the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- ■ Sales Tax Payable is a liability account. Since the payable decreased due to returns, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- ■ Accounts Receivable, A Manufacturing is an asset account. Since inventory is returned, amount to be received has decreased, asset account is decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working note 1:
Compute the sales tax payable amount.
Working note 2:
Compute the accounts receivable amount;
2.
Post the prepared journal to the general ledger, and to the accounts receivable ledger.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Posting transactions: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting the transactions.
Post the prepared journals to the general ledger:
| ACCOUNT Cash ACCOUNT NO. 101 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 9,862.00 | |||
| 31 | CR10 | 17,292.36 | 27,154.36 | ||||
Table (4)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Receivable ACCOUNT NO. 122 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 9,352.00 | |||
| 11 | J8 | 63.60 | 9,288.40 | ||||
| 21 | J8 | 23.32 | 9,265.08 | ||||
| 31 | CR10 | 5,732.00 | 3,533.08 | ||||
Table (5)
| ACCOUNT Sales Tax Payable ACCOUNT NO. 231 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 11 | J8 | 3.60 | 3.60 | |||
| 21 | J8 | 1.32 | 4.92 | ||||
| 31 | CR10 | 657.60 | 652.68 | ||||
Table (6)
| ACCOUNT Sales ACCOUNT NO. 401 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 31 | CR10 | 10,960.00 | 10,960.00 | |||
Table (7)
| ACCOUNT Sales Returns and Allowances ACCOUNT NO. 401.1 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 11 | J8 | 60.00 | 60.00 | |||
| 21 | J8 | 22.00 | 82.00 | ||||
Table (8)
| ACCOUNT Bank Credit Card Expense ACCOUNT NO. 513 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 20-- | |||||||
| December | 31 | CR10 | 57.24 | 57.24 | |||
Table (9)
Post the journals to the accounts receivable ledger.
| NAME MA | ||||||
| ADDRESS 233 W 11th Avenue, D, Mi 59500-1154 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 2,480.00 | ||
| 1 | CR10 | 1,360.00 | 1,120.00 | |||
| 11 | J8 | 63.60 | 1,056.40 | |||
Table (10)
| NAME A Manufacturing | ||||||
| ADDRESS 284 W 88 Street, D, Mi 59522-1168 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 982.00 | ||
| 2 | CR10 | 382.00 | 600.00 | |||
| 21 | J8 | 23.32 | 576.68 | |||
Table (11)
| NAME JG | ||||||
| ADDRESS P.O. Box 864, D, Mi 59552-0864 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 880.00 | ||
| 8 | CR10 | 880.00 | 0 | |||
Table (12)
| NAME TW | ||||||
| ADDRESS 100 N w S Street., D, Mi 59210-1337 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 1,810.00 | ||
| 20 | CR10 | 1,110.00 | 700.00 | |||
Table (13)
| NAME RC | ||||||
| ADDRESS 11312 Fourteenth Avenue South, D, Mi 59221-1142 | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20-- | ||||||
| December | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,200.00 | ||
| 24 | CR10 | 2,000.00 | 1,200.00 | |||
Table (14)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapter 1-15 (Looseleaf)
- Grunewald Industries sells on terms of 3/10, net 40. Gross sales last year were $4,161,000 and accounts receivable averaged $370,500. Half of Grunewald's customers paid on the 10th day and took discounts. What are the nominal and effective costs of trade credit to Grunewald's non-discount customers? (Hint:Calculate daily sales based on a 365-day year, calculate the average receivables for discount customers, and then find the DSO for the non-discount customers.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to two decimal places. Effective cost of trade credit =arrow_forwardprovide solutionarrow_forwardWhat is the estimate of the overheads if 16,000 square meters are to be cleanedarrow_forward
- Kindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardWhat was cost of goods manufactured for the period?arrow_forwardDuring September, 8,500 units were produced. The standard quantity of material allowed per unit was 9 pounds at a standard cost of $5.50 per pound. If there was an unfavorable usage variance of $18,975 for September, what amount must be the actual quantity of materials used?arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning



