
a.
Journalize the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the stockholders’ equity transactions in the books of Incorporation G.
Transaction on January 5:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| January | 5 | Dividends | 560,000 | |||
| Dividends Payable | 560,000 | |||||
| (Record declaration of dividends) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Dividends is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the dividends are declared, stockholders’ equity is decreased, and a decrease in equity account is debited.
- Dividends Payable is a liability account. Since the liability to pay dividends increased, liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the amount of cash dividends on common stock.
Transaction on February 18:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| February | 18 | Dividends Payable | 560,000 | |||
| Cash | 560,000 | |||||
| (Record payment of cash dividends) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Dividends Payable is a liability account. Since the liability to pay dividends has been paid off, liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because cash is paid as dividends, and a decrease in assets should be credited.
Transaction on April 20:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| April | 20 | 10,000 | ||||
| Cash | 10,000 | |||||
| (Record reacquisition of common stock as treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the issued shares are bought back, the stockholders’ equity decreases, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because cash is paid as dividends, and a decrease in assets should be credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cash paid.
Transaction on May 25:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| May | 25 | Cash | 6,000 | |||
| Treasury Stock | 5,000 | |||||
| Additional Paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock | 1,000 | |||||
| (Record sale of treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because cash is received on sale of reacquired shares, and an increase in assets should be debited.
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since reacquired shares of treasury stock are sold, the value of treasury stock is reduced. The treasury stock which was debited previously, is now credited to reduce its balance.
- Additional Paid-In Capital–Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since treasury stock is sold for a price more than its purchase price, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cash received.
Compute treasury stock value.
Compute additional paid-in capital value.
Transaction on June 15:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| June | 15 | 307,725 | ||||
| Stock Dividends to Be Distributed | 27,975 | |||||
| Additional Paid-in Capital: Stock Dividends | 279,750 | |||||
| (Record declaration of stock dividends) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the dividends are declared, stockholders’ equity is decreased, and a decrease in equity account is debited.
- Stock Dividends to Be Distributed is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is declared to be distributed as stock dividends at par value, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
- Additional Paid-in Capital: Stock Dividends is a stockholders’ equity account. Since the stock is issued in excess of par value, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute the number of shares to be distributed as stock dividends.
Compute amount of retained earnings distributable for stock dividends (Refer to Equation (1) for stock dividend shares value).
Compute the amount of stock dividends to be distributed (Refer to Equation (1) for stock dividend shares value).
Compute additional paid-in capital (Refer to Equations (2) and (3) for retained earnings and stock dividends to be distributed value).
Transaction on June 30:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| June | 30 | Stock Dividends to Be Distributed | 27,975 | |||
| Common Stock | 27,975 | |||||
| (Record distribution of stock dividends) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Stock Dividends to Be Distributed is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is issued due to declaration of stock dividends, the value is transferred to common stock, the equity value is decreased. A decrease in equity is debited.
- Common Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since common stock is issued, equity value is increased. An increase in equity is credited.
Note: Refer to Equation (3) for value and computation of stock dividends distributable value.
Transaction on August 12:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| August | 12 | Cash | 2,925 | |||
| Additional Paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock | 75 | |||||
| Treasury Stock | 3,000 | |||||
| (Record sale of treasury stock) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because cash is received on sale of reacquired shares, and an increase in assets should be debited.
- Additional Paid-In Capital–Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since treasury stock is sold for a price less than its purchase price, equity value is decreased. A decrease in equity is debited.
- Treasury Stock is a stockholders’ equity account. Since reacquired shares of treasury stock are sold, the value of treasury stock is reduced. The treasury stock which was debited previously, is now credited to reduce its balance.
Working Notes:
Compute cash received.
Compute treasury stock value.
Compute additional paid-in capital value.
Transaction on December 31 (closing net income):
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Income Summary | 1,750,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | 1,750,000 | |||||
| (Record net income being closed to Retained Earnings account) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Income Summary is a temporary account used to close the net balance of revenue and expense accounts. Since the net income is closed to Retained Earnings account, the Retained Earnings is credited and Income Summary account is debited.
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since revenues are transferred to the account, the value increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Transaction on December 31 (closing dividends):
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2018 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Income Summary | 560,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | 560,000 | |||||
| (Record dividends being closed to Retained Earnings account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Retained Earnings is a stockholders’ equity account. Since dividends are transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Income Summary is a temporary account used to close the net balance of revenue and expense accounts. Since the dividends (expense) are closed to Retained Earnings account, the Retained Earnings is debited and Income Summary account is credited.
b.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the
b.
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ equity section: The section of balance sheet which reports the changes in stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock, during the year is referred to as stockholders’ equity section.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet for Incorporation G at December 31, 2018.
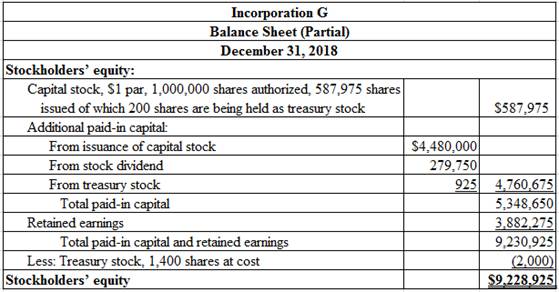
Table (10)
Working Notes:
Compute the number of shares issued as at December 31, 2018.
Compute number of shares in treasury stock.
Refer to transaction on June 1 for value of additional paid-in capital from stock dividend.
Compute additional paid-in capital from treasury stock.
Note: Refer to the working notes of the transactions on May 25 and August 12 for both the values.
Compute amount of retained earnings (Refer to the working notes of transactions on February 18 and June 15 for value of cash and stock dividends).
| Incorporation G | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2018 | ||
| Retained earnings, January 1, 2018 | $3,000,000 | |
| Add: Net income | 1,750,000 | |
| 4,750,000 | ||
| Less: | ||
| Cash dividends | $560,000 | |
| Stock dividends | 307,725 | (867,725) |
| Retained earnings, December 31, 2018 | $3,882,275 | |
Table (11)
Thus, the total stockholders’ equity of Incorporation G is $9,228,925.
c.
Compute the amount of legal cash dividend per share according to the given condition.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Cash dividends: This is the amount of cash distributed to stockholders by a company out of its earnings, according to their proportion of shares held in the company stock.
Compute the amount of legal cash dividend per share of Incorporation G in 2018.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, December 31, 2018 | $3,882,275 |
| Less: Restriction of retained earnings for treasury stock | 2,000 |
| Unrestricted retained earnings | 3,880,275 |
| Number of outstanding common shares | ÷ 5887,775 shares |
| Maximum legal cash dividend per common share | $6.60 |
Table (12)
Note: Refer to working notes of Part (b) for the value of retained earnings ending balance, and number of outstanding shares at the end of 2018.
Thus, the legal cash dividend per common share of Incorporation G for the year ended December 31, 2018 is $6.60.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Ironside Inc. paid $560 in dividends and $640 in interest this past year. Common stock increased by $270 and retained earnings decreased by $150. What is the net income for the year? a. $560 b. $390 c. $410 d. $610 HELParrow_forwardCalculate the net profit.arrow_forwardCash conversion cycle????arrow_forward
- General accountingarrow_forwardGeneral Accountingarrow_forwardEverett Corporation, a company that produces and sells a single product, has provided its contribution format income statement for October: Sales (8,200 units): $452,600 • Variable expenses: $280,200 • Contribution margin: $172,400 Fixed expenses: $115,750 • Net operating income: $56,650 If Everett Corporation sells 9,000 units instead of 8,200 units, what will be its net operating income? A. $69,250 B. $73,800 C. $76,300 D. $80,400arrow_forward
- Eagle Parts Co. uses direct labor hours in its predetermined overhead rate. At the beginning of the year, the estimated direct labor hours were 13,000 hours, and the total estimated manufacturing overhead was $315,000. At the end of the year, actual direct labor hours were 12,600 hours, and actual manufacturing overhead was $309,000. Find overhead at the end of the year. Helparrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardWhat it likely to be the price of the stock? General accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





