
1.
Calculate the cash payback period for the given proposals.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Cash payback method:
Cash payback period is the expected time period which is required to recover the cost of investment. It is one of the capital investment method used by the management to evaluate the long-term investment (fixed assets) of the business.
The cash payback period for the given proposals is as follows:
Proposal A:
Initial investment=$680,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal A | ||||
| Year | Net | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 200,000 | 200,000 | ||
| 2 | 200,000 | 400,000 | ||
| 3 | 200,000 | 600,000 | ||
| 6 months (1) | 80,000 | 680,000 | ||
Table (1)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal A is 3 years and 6 months.
Working note:
1. Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
Proposal B:
Initial investment=$320,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal B | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 90,000 | 90,000 | ||
| 2 | 90,000 | 180,000 | ||
| 3 | 70,000 | 250,000 | ||
| 4 | 70,000 | 320,000 | ||
Table (2)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal B is 4 years.
Proposal C:
Initial investment=$108,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal C | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 55,000 | 55,000 | ||
| 2 | 53,000 | 108,000 | ||
Table (3)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal C is 2 years.
Proposal D:
Initial investment=$400,000
| Cash payback period of Proposal D | ||||
| Year | Net cash flows | Cumulative net cash flows | ||
| 1 | 180,000 | 180,000 | ||
| 2 | 180,000 | 360,000 | ||
| 3 months (2) | 40,000 | 400,000 | ||
Table (4)
Hence, the cash payback period of proposal D is 2 years and 3 months.
Working note:
2. Calculate the no. of months in the cash payback period:
2.
Calculate the average
2.
Explanation of Solution
Average rate of return method:
Average rate of return is the amount of income which is earned over the life of the investment. It is used to measure the average income as a percent of the average investment of the business, and it is also known as the accounting rate of return.
The average rate of return is computed as follows:
The average rate of return for the given proposals is as follows:
Proposal A:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal A is 14.1%.
Proposal B:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal B is 2.5%.
Proposal C:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal C is 52.6%.
Proposal D:
Hence, the average rate of return for Proposal D is 30.0%.
3.
Indicate the proposals which should be accepted for further analysis, and which should be rejected.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The proposals which should be accepted for further analysis, and which should be rejected is as follows:
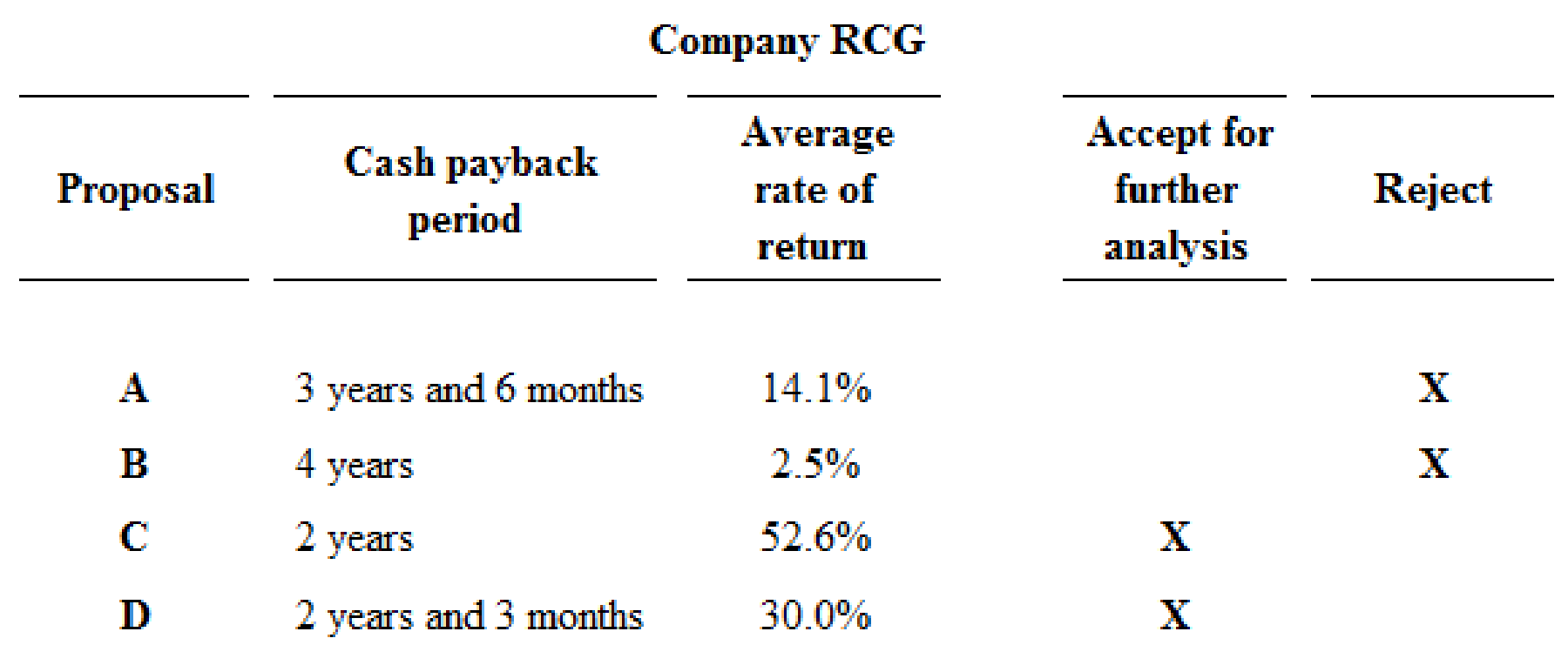
Figure (1)
Proposals A and B are rejected, because proposal A and B fails to meet the required maximum cash back period of 3 years, and they has less rate of return than the other proposals. Hence, Proposals C and D are preferable.
4.
Calculate the
4.
Explanation of Solution
Net present value method:
Net present value method is the method which is used to compare the initial
Calculate the net present value of the proposals which has 12% rate of return as follows:
Proposal C:
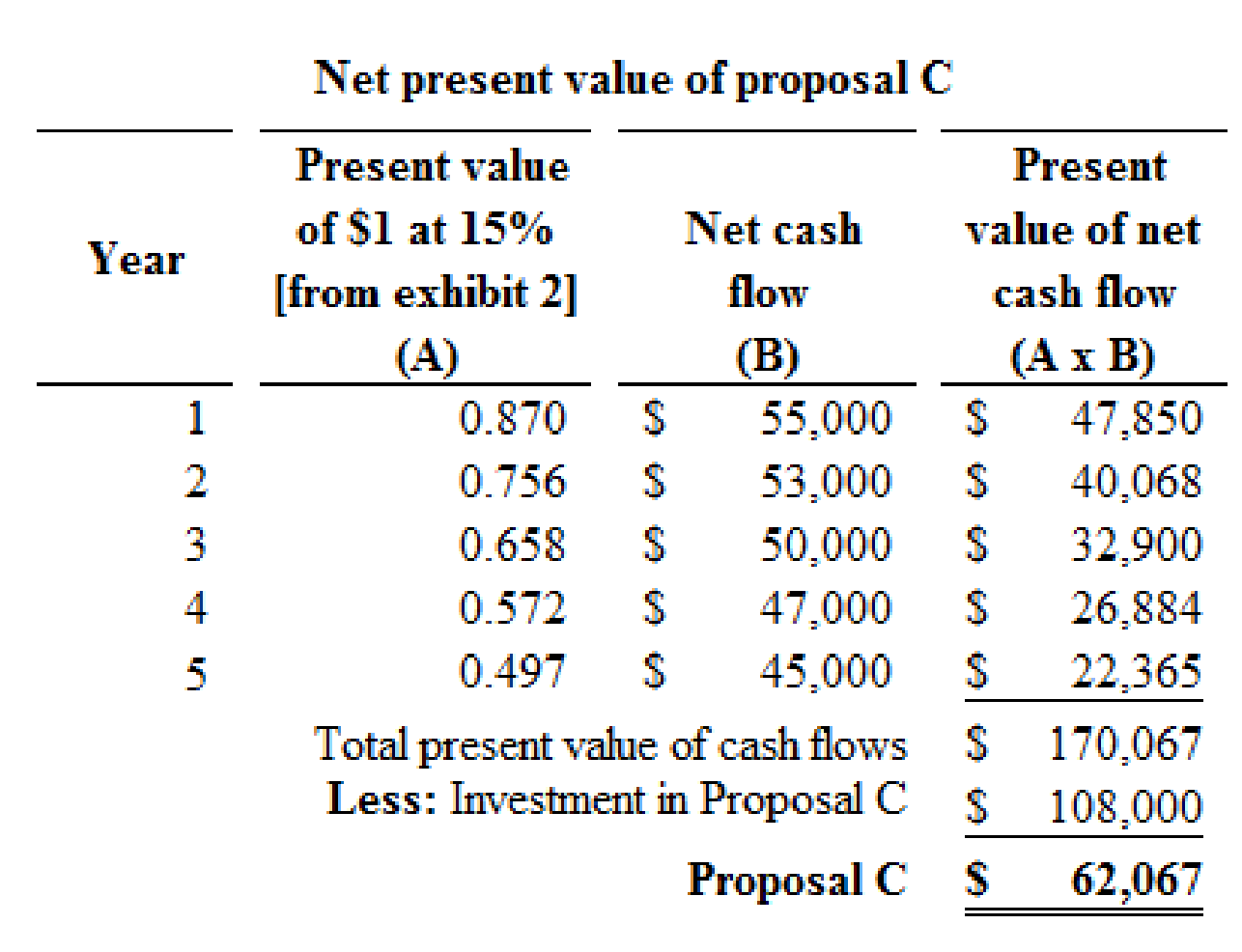
Figure (2)
Hence, the net present value of proposal C is $62,067.
Proposal D:
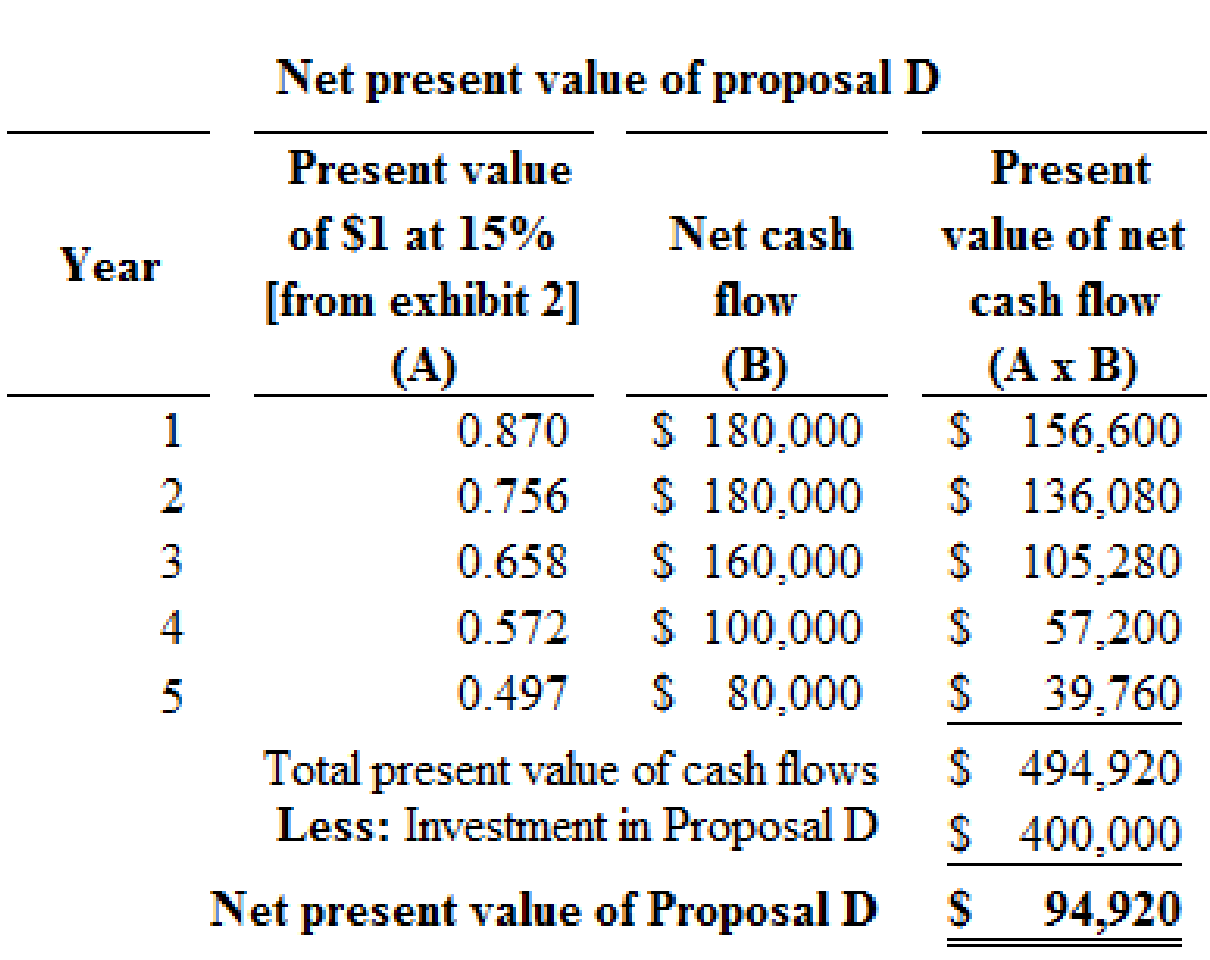
Figure (3)
Hence, the net present value of proposal D is $94,920.
5.
Calculate the present value index for each proposal.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Present value index:
Present value index is a technique, which is used to rank the proposals of the business. It is used by the management when the business has more investment proposals, and limited fund.
The present value index for each proposal is as follows:
Proposal C:
Calculate the present value index for proposal C:
Hence, the present value index for proposal C is 1.575.
Proposal D:
Calculate the present value index for proposal D:
Hence, the present value index for proposal D is 1.237.
6.
Rank the proposal from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value of net cash flows.
6.
Explanation of Solution
Present value index:
Present value index is a technique, which is used to rank the proposals of the business. It is used by the management when the business has more investment proposals, and limited fund.
The present value index is computed as follows:
Proposals are arranged by rank is as follows:
| Proposals | Net present value | Rank |
| Proposal D | $ 94,920 | 1 |
| Proposal C | $ 62,067 | 2 |
Table (5)
7.
Rank the proposal from most attractive to least attractive, based on the present value of index.
7.
Explanation of Solution
Present value index:
Present value index is a technique, which is used to rank the proposals of the business. It is used by the management when the business has more investment proposals, and limited fund.
The present value index is computed as follows:
Proposals are arranged by rank is as follows:
| Proposals | Present value index | Rank |
| Proposal C | 1.57 | 1 |
| Proposal D | 1.24 | 2 |
Table (6)
8.
Analyze the proposal which is favor to investment, and comment on the relative attractiveness of the proposals based on the rank.
8.
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of net present value:
The net present value of Proposal C is $62,067, and Proposal D is $94,920. In this case, the net present value of proposal D is more than the net present value of proposal C. Hence, investment in Proposal D is preferable.
On the basis of present value index:
The present value index of Proposal C is 1.57, and the present value index of Proposal D is 1.24. In this case, Proposal C has the favorable present value index, because the present value index of Proposal C (1.57) is more than Proposal D (1.24). Thus, the investment in Proposal C is preferable (favorable).
Every business tries to get maximum profit with minimum investment. Hence, the cost of investment in Proposal C is less than the proposal D. Thus, investment in Proposal C is preferable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Arden Manufacturing uses a process costing system. Beginning inventory for June consisted of 2,400 units that were 55% completed. 14,500 units were started during June. On June 30, the inventory consisted of 1,200 units that were 40% completed. How many units were completed during the period?arrow_forwardThe total assets are?arrow_forwardProvide answerarrow_forward
- How does reciprocal accounting differ from standard intercompany accounting? a. Mutual transactions simultaneously affect both entities' records b. One entity records the transaction first c. Transactions are recorded at year-end only d. Each entity keeps independent recordsarrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Can you demonstrate the accurate method for solving this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardKahlo Industries uses a predetermined factory overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. For October, Kahlo's budgeted overhead was $180,000 based on a budgeted volume of 15,000 direct labor-hours. Actual overhead amounted to $192,000, with actual direct labor-hours totaling 14,200. Required: What was over- or underapplied manufacturing overhead in October?arrow_forwardWhat is the total equity for Orion tools at year end ?arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardThe financial statements of Isabella Corporation report net sales of $840,000 and accounts receivable of $175,000 and $135,000 at the beginning and end of the year, respectively. What is the average collection period for accounts receivable in days?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





