
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119472780
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 60P
In Fig. 12-69, a package of mass m hangs from a short cord that is tied to the wall via cord 1 and to the ceiling via cord 2. Cord 1 is at angle ϕ = 40° with the horizontal; cord 2 is at angle θ. (a) For what value of θ is the tension in cord 2 minimized? (b) In terms of mg, what is the minimum tension in cord 2?
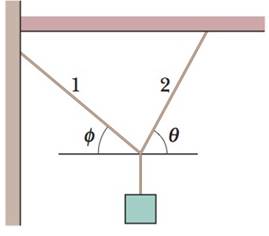
Figure 12-69 Problem 60.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Is work function of a metals surface related to surface energy and surface tension? What is the need to the work function component in the math of tension of metal surfaces that cannot be provided by existing equations of surface energy and surface tension? What are the key differences in each parameter and variables that allow for a differentiation of each function? What has a more significant meaning work function, surface tension or surface energy? Are there real differences and meaning? Please clarify and if possible provide examples . Does surface tension dependant on thickness of a metal or type of metal surface all having the same thickness? Clearly temperature has a profound change on surface tension what other variables besides temperature are key to surface tension. What if any is there a connection between crystal structure of the element and surface energy and tension? This is NOT a Assignment Question!!!
The cylindrical beam of a 12.7-mW laser is 0.920 cm in diameter. What is the rms value of the electric field?
V/m
Consider a rubber rod that has been rubbed with fur to give the rod a net negative charge, and a glass rod that has been rubbed with silk to give it a net positive charge. After being charged by contact by the fur and silk...?
a. Both rods have less mass
b. the rubber rod has more mass and the glass rod has less mass
c. both rods have more mass
d. the masses of both rods are unchanged
e. the rubber rod has less mass and the glass rod has mroe mass
Chapter 12 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
Ch. 12 - Figure 12-15 shows three situations in which the...Ch. 12 - In Fig, 12-16, a rigid beam is attached to two...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-17 shows four overhead views of rotating...Ch. 12 - A ladder leans against a frictionless wall but is...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-18 shows a mobile of toy penguins...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-19 shows an overhead view of a uniform...Ch. 12 - Prob. 7QCh. 12 - Three piatas hang from the stationary assembly of...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-22, a vertical rend is hinged at its...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-23 shows a horizontal block that is...
Ch. 12 - The table gives the initial lengths of three reds...Ch. 12 - A physical therapist gone wild has constructed the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 1PCh. 12 - An automobile with a mass of 1360 kg has 3.05 m...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-26, a uniform sphere of mass m =...Ch. 12 - An archers bow is drawn at its midpoint until the...Ch. 12 - ILWA rope of negligible mass is stretched...Ch. 12 - A scaffold of mass 60 kg and Length 5.0 m is...Ch. 12 - A 75 kg window cleaner uses a 10 kg ladder that is...Ch. 12 - A physics Brady Bunch, whose weights in newtons...Ch. 12 - SSMA meter stick balances horizontally on a...Ch. 12 - GO The system in Fig. 12-28 is in equilibrium,...Ch. 12 - SSMFigure 12-29 shows a diver of weight 580 N...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-30, trying to gel his car out of mud, a...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-31 shows the anatomical structures in...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-32, a horizontal scaffold, of length...Ch. 12 - ILWForces F1, F2 and F3 act on the structure of...Ch. 12 - A uniform cubical crate is 0.750 m on each side...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-34, a uniform beam of weight 500 N and...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-35, horizontal scaffold 2, with...Ch. 12 - To crack a certain nut in a nutcracker, forces...Ch. 12 - A bowler holds a bowling ball M = 7.2 kg in the...Ch. 12 - ILWThe system in Fig. 12-38 is in equilibrium. A...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig-12-39, a 55 kg rock climber is in a...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-40, one end of a uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-41, a climber with a weight of 533.8...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWIn Fig. 12-42, what magnitude of constant...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-43, a climber leans out against a...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-44, a 15 kg block is held in place...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-45, suppose the length L of the...Ch. 12 - A door has a height of 2.1 m along a y axis that...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-46, a 50.0 kg uniform square sign,...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-47, a nonuniform bar is suspended at...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-48, the driver of a car on a horizontal...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-49a shows a vertical uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-45, a thin horizontal bar AB of...Ch. 12 - SSM WWWA cubical box is filled with sand and...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-50 shows a 70 kg climber hanging by only...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-51, a uniform plank, with a length L...Ch. 12 - In Fig, 12-52, uniform beams A and B are attached...Ch. 12 - For the stepladder shown in Fig. 12-53, sides AC...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-54a shows a horizontal uniform beam of...Ch. 12 - A crate, in the form of a cube with edge lengths...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-7 and the associated sample problem,...Ch. 12 - SSM ILWA horizontal aluminum rod 4.8 cm in...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-55 shows the stressstrain curve for a...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-56, a lead brick rests horizontally on...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-57 shows an approximate plot of stress...Ch. 12 - A tunnel of length L = 150 m, height H = 7.2 m,...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-59 shows the stress versus strain plot...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-60, a 103kg uniform log hangs by two...Ch. 12 - GO Figure 12-61 represents an insect caught at the...Ch. 12 - GO Figure 12-62 is an overhead view of a rigid rod...Ch. 12 - After a fall, a 95 kg rock climber finds himself...Ch. 12 - SSMIn Fig 12-63, a rectangular slab of slate rests...Ch. 12 - A uniform ladder whose length is 5.0 m and whose...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-64, block A mass 10 kg is in...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-65a shows a uniform ramp between two...Ch. 12 - GO In Fig. 12-66, a 10 kg sphere is supported on a...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-67a, a uniform 40.0 kg beam is centered...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-68, an 817 kg construction bucket...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-69, a package of mass m hangs from a...Ch. 12 - ILWThe force F in Fig. 12-70 keeps the 6.40 kg...Ch. 12 - A mine elevator is supported by a single steel...Ch. 12 - Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 64PCh. 12 - In Fig. 12-73, a uniform beam with a weight of 60...Ch. 12 - A uniform beam is 5.0 m long and has a mass of 53...Ch. 12 - A solid copper cube has an edge length of 85.5 cm....Ch. 12 - A construction worker attempts to lift a uniform...Ch. 12 - SSM In Fig. 12-76, a uniform rod of mass m is...Ch. 12 - A 73 kg man stands on a level bridge of length L....Ch. 12 - SSMA uniform cube of side length 8.0 cm rests cm a...Ch. 12 - The system in Fig. 12-77 is in equilibrium. The...Ch. 12 - SSMA uniform ladder is 10 m long and weighs 200 N....Ch. 12 - A pan balance is made up of a rigid, massless rod...Ch. 12 - The rigid square frame in Fig. 12-79 consists of...Ch. 12 - A gymnast with mass 46.0 stands on the end of a...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-81 shows a 300 kg cylinder that is...Ch. 12 - In Fig. 12-82, a uniform beam of length 12.0 m is...Ch. 12 - Four bricks of length L, identical and uniform,...Ch. 12 - A cylindrical aluminum rod, with an initial length...Ch. 12 - Prob. 81PCh. 12 - If the square beam in Fig. 12-6a and the...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-84 shows a stationary arrangement of two...Ch. 12 - A makeshift swing is constructed by makings loop...Ch. 12 - Figure 12-85a shows details of a finger in the...Ch. 12 - A trap door in a ceiling is 0.91 m square, has a...Ch. 12 - A particle is acted on by forces given, in...Ch. 12 - The leaning Tower of Pisa is 59.1 m high and 7.44...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. The number of stars in the Milky Way G...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Describe several distinguishing features of thoracic vertebrae.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Define histology.
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
1.1 Write a one-sentence definition for each of the following:
a. chemistry
b. chemical
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Static Equilibrium: concept; Author: Jennifer Cash;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0BIgFKVnlBU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY