
The concept of trade-off,
Explanation of Solution
According to the question an independent supermarket owner has a store and builds another in the neighboring town. But there is single owner to supervise both the stores. As the owner has limited time (resource), there will be scarcity of time and he has to make trade-off between the time to be given to store 1 and the time to be given to store 2. The opportunity cost of giving time to store 2 is the time he could give to store 1.
Now considering the production of good 1 as sale of store 1 and production of good 2 as sale of store 2
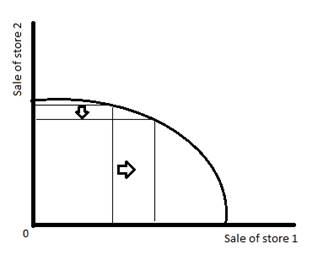
The above given PPC shows sale of store 1 the on x-axis and sale of store 2 on the y-axis. If the owner wants to increase the sale of store 1 then he has to decrease the time given to store 2 as shown by the arrows.
Introduction:
Trade-off: it refers to sacrificing one good or service in order to buy or produce another good or service. In other words, choosing one option over the other.
Scarcity: it is the problem that arises because of limited resources and unlimited wants for those resources.
Opportunity cost : it refers to the cost of the next best alternative forgone in order to do what have been chosen.
Production possibility curve: this curve shows the maximum possible combinations of two goods that can be produced using given resources.
Chapter 1 Solutions
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student Edition
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
- 1. Based on the video, answer the following questions. • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? Based on the video. • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? Based on the video. • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? Based on the video. • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? Based on the video. • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Based on the video. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forward1. Answer the following questions based on the reference video below: • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Discuss. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forwardExplain the importance of differential calculus within economics and business analysis. Provide three refernces with your answer. They can be from websites or a journals.arrow_forward
- Analyze the graph below, showing the Gross Federal Debt as a percentage of GDP for the United States (1939-2019). Which of the following is correct? FRED Gross Federal Debt as Percent of Gross Domestic Product Percent of GDP 120 110 100 60 50 40 90 30 1940 1950 1960 1970 Shaded areas indicate US recessions 1980 1990 2000 2010 1000 Sources: OMD, St. Louis Fed myfred/g/U In 2019, the Federal Government of the United States had an accumulated debt/GDP higher than 100%, meaning that the amount of debt accumulated over time is higher than the value of all goods and services produced in that year. The debt/GDP is always positive during this period, so the Federal Government of the United States incurred in budget deficits every year since 1939. From the mid-40s until the mid-70s, the debt/DGP was decreasing, meaning that the Federal Government of the United States was running a budget surplus every year during those three decades. During the second half of the 1970s, the Federal Government…arrow_forwardAn imaginary country estimates that their economy can be approximated by the AD/AS model below. How can this government act to move the equilibrium to potential GDP? LRAS Price Level P Y Real GDP E SRAS AD The AD/AS model shows that a contractionary fiscal policy is suitable, but the choice of increasing taxes, decreasing government expenditure or doing both simultaneously is mostly political The AD/AS model shows that increasing taxes is the best fiscal policy available. The AD/AS model shows that decreasing government expenditure is the best fiscal policy available. The AD/AS model shows that an expansionary fiscal policy capable of shifting the AD curve to the potential GDP level would decrease Real GDP but increase inflationary pressuresarrow_forwardQuestion 1 Coursology Consider the four policies bellow. Classify them as either fiscal or monetary policy: I. The United States Government promoting tax cuts for small businesses to prevent a wave of bankruptcies during the COVID-19 pandemic II. The Congress approving a higher budget for the Affordable Health Care Act (also known as Obamacare) III. The Federal Reserve increasing the required reserves for commercial banks aiming to control the rise of inflation IV. President Joe Biden approving a new round of stimulus checks for households I. fiscal, II. fiscal, III. monetary, IV. fiscal I. fiscal, II. monetary, III. monetary, IV. monetary I. monetary, II. fiscal, III. fiscal, IV. fiscal I. monetary, II. monetary, III. fiscal, IV. monetaryarrow_forward
- Consider the following supply and demand schedule of wooden tables.a. Draw the corresponding graphs for supply and demand.b. Using the data, obtain the corresponding supply and demand functions. c. Find the market-clearing price and quantity. Price (Thousand s USD Supply Demand 2 96 1104 196 1906 296 2708 396 35010 496 43012 596 51014 696 59016 796 67018 896 75020…arrow_forwardConsider a firm with the following production function Q=5000L-2L2.a. Find the maximum production level.b. How many units of labour are needed at that point. c. Obtain the function of marginal product of labour (MRL) d. Graph the production function and the MRL.arrow_forwardExercise 4A firm has the following total cost function TC=100q-5q2+0.5q3. Find the average cost function.arrow_forward
- A firm has the following demand function P=200 − 2Q and the average costof AC= 100/Q + 3Q −20.a. Find the profit function. b. Estimate the marginal cost function. c. Obtain the production that maximizes the profit. d. Evaluate the average cost and the marginal cost at the maximising production level.arrow_forwardRubber: Initial investment: $159,000 Annual cost: $36,000 Annual revenue: $101,000 Salvage value: $12,000 Useful life: 10 years Using the cotermination assumptions, a study period of 6 years, and a MARR of 9%, what is the present worth of the rubber alternative? Assume that the rubber alternative's equipment has a market value of $18,000 at the end of Year 6.arrow_forwardRichard has just opened a new restaurant. Not being good at deserts, he has contracted with Carla to provide pies. Carla’s costs are $10 per pie, and she sells the pies to Richard for $25 each. Richard resells them for $50, and he incurs no costs other than the $25 he pays Carla. Assume Carla’s costs go up to $30 per pie. If courts always award expectation damages, which of the following statements is most likely to be true?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





