
To test: the null hypothesis and show that it is rejected at the
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
Concept Involved:
In order to decide whether the presumed hypothesis for data sample stands accurate for the entire population or not we use the hypothesis testing.
The critical value from Table A.4, using degrees of freedom of
The values of two qualitative variables are connected and denoted in a contingency table.
This table consists of rows and column. The variables in each row and each column of the table represent a category. The number of rows of contingency table is represented by letter ‘r’ and number of column of contingency table is represented by letter ‘c’.
The formula to find the number of degree of freedom of contingency table is
Calculation:
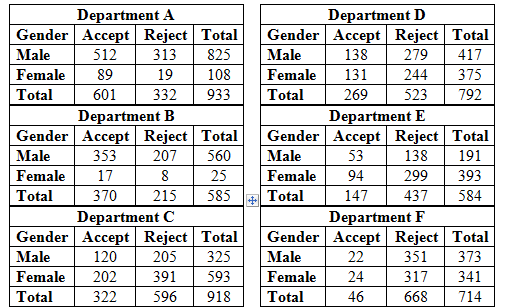
For department A:
| Department A | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 512 | 313 | 825 |
| Female | 89 | 19 | 108 |
| Total | 601 | 332 | 933 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department A The row total is 825, the column total is 601, and the grand total is 933. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department A The row total is 825, the column total is 332, and the grand total is 933. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department A The row total is 108, the column total is 601, and the grand total is 933. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department A The row total is 108, the column total is 332, and the grand total is 933. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department A The observed frequency is 512 and expected frequency is 531.43 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department A The observed frequency is 313 and expected frequency is 293.57 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department A The observed frequency is 89 and expected frequency is 69.57 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department A The observed frequency is 19 and expected frequency is 38.43 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department A, % of male accepted =
For department B:
| Department B | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 353 | 207 | 560 |
| Female | 17 | 8 | 25 |
| Total | 370 | 215 | 585 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department B The row total is 560, the column total is 370, and the grand total is 585. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department B The row total is 560, the column total is 215, and the grand total is 585. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department B The row total is 25, the column total is 370, and the grand total is 585. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department B The row total is 25, the column total is 215, and the grand total is 585. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department B The observed frequency is 353 and expected frequency is 354.19 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department B The observed frequency is 207 and expected frequency is 205.81 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department B The observed frequency is 17 and expected frequency is 15.81 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department B The observed frequency is 8 and expected frequency is 9.19 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department B, % of male accepted =
For department C:
| Department C | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 120 | 205 | 325 |
| Female | 202 | 391 | 593 |
| Total | 322 | 596 | 918 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department C The row total is 325, the column total is 322, and the grand total is 918. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department C The row total is 325, the column total is 596, and the grand total is918. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department C The row total is 593, the column total is 322, and the grand total is 918. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department C The row total is 593, the column total is 596, and the grand total is 918. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department C The observed frequency is 120 and expected frequency is 114 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department C The observed frequency is 205 and expected frequency is 211 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department C The observed frequency is 202 and expected frequency is 208 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department C The observed frequency is 391 and expected frequency is 385 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department C, % of male accepted =
For department D:
| Department D | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 138 | 279 | 417 |
| Female | 131 | 244 | 375 |
| Total | 269 | 523 | 792 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department D The row total is 417, the column total is 269, and the grand total is 792. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department D The row total is 417, the column total is 523, and the grand total is792. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department D The row total is 375, the column total is 269, and the grand total is 792. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department D The row total is 375, the column total is 523, and the grand total is 792. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department D The observed frequency is 138 and expected frequency is 141.63 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department D The observed frequency is 279 and expected frequency is 275.37 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department D The observed frequency is 131 and expected frequency is 127.37 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department D The observed frequency is 244 and expected frequency is 247.63 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department D, % of male accepted =
For department E:
| Department E | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 53 | 138 | 191 |
| Female | 94 | 299 | 393 |
| Total | 147 | 437 | 584 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department E The row total is 191, the column total is 147, and the grand total is 584. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department E The row total is 191, the column total is 437, and the grand total is584. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department E The row total is 393, the column total is 147, and the grand total is 584. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department E The row total is 393, the column total is 437, and the grand total is 584. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department E The observed frequency is 53 and expected frequency is 48.08 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department E The observed frequency is 138 and expected frequency is 142.92 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department E The observed frequency is 94 and expected frequency is 98.92 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department E The observed frequency is 299 and expected frequency is 294.08 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department E, % of male accepted =
For department F:
| Department F | |||
| Gender | Accept | Reject | Total |
| Male | 22 | 351 | 373 |
| Female | 24 | 317 | 341 |
| Total | 46 | 668 | 714 |
| Finding the expected frequency for the cell corresponding to: | The expected frequency |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department F The row total is 373, the column total is 46, and the grand total is 714. | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department F The row total is 373, the column total is 668, and the grand total is714. | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department F The row total is 341, the column total is 46, and the grand total is 714. | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department F The row total is 341, the column total is 668, and the grand total is 714. |
| Finding the value of the chi-square corresponding to: | |
| Number of male applicants acceptedin department F The observed frequency is 22 and expected frequency is 24.03 | |
| Number of male applicants rejectedin department F The observed frequency is 351 and expected frequency is 348.97 | |
| Number of female applicantsaccepted in department F The observed frequency is 24 and expected frequency is 21.97 | |
| Number of female applicantsrejected in department F The observed frequency is 317 and expected frequency is 319.03 |
To compute the test statistics, we use the observed frequencies and expected frequency:
In department E, % of male accepted =
Here r represents the number of rows and c represents the number of columns.
For all the contingency table
| Degrees of freedom | Table A.4 Critical Values for the chi-square Distribution | |||||||||
| 0.995 | 0.99 | 0.975 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.01 | 0.005 | |
| 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 2.706 | 3.841 | 5.024 | 6.635 | 7.879 |
| 2 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.051 | 0.103 | 0.211 | 4.605 | 5.991 | 7.378 | 9.210 | 10.597 |
| 3 | 0.072 | 0.115 | 0.216 | 0.352 | 0.584 | 6.251 | 7.815 | 9.348 | 11.345 | 12.838 |
| 4 | 0.207 | 0.297 | 0.484 | 0.711 | 1.064 | 7.779 | 9.488 | 11.143 | 13.277 | 14.860 |
| 5 | 0.412 | 0.554 | 0.831 | 1.145 | 1.610 | 9.236 | 11.070 | 12.833 | 15.086 | 16.750 |
The critical value is same for all the contingency table.
Conclusion:
For department A:
Test statistic: 17.25; Critical value: 6.635.
For department B:
Test statistic: 0.25; Critical value: 6.635.
For department C:
Test statistic: 0.75; Critical value: 6.635.
For department D:
Test statistic: 0.30; Critical value: 6.635.
For department E:
Test statistic: 1.00; Critical value: 6.635.
For department F:
Test statistic: 0.39; Critical value: 6.635.
In departmentA, 82.4% of the women were accepted, but only 62.1% of themen were accepted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Elementary Statistics
- A firm paid its first annual dividend yesterday in the amount of $.15 per share. The company plans to double the dividend in each of the next 3 years. Starting in Year 4, the firm plans to pay $1.50 per share indefinitely. What is one share of this stock worth today if the market rate of return on similar securities is 13.8 percent? Multiple Choice $11.79 $8.92 $10.77 $11.02 $10.26arrow_forwardSuppose the random variable X is normally distributed with mean 80 and standard deviation 16. Find following probabilities. Find ‘b’ such that P(X ≥ b) = 0.975. Find the probability using a normal distribution table AND using ti-83 calculator. SHOW ALL STEPS PLEASE.arrow_forwardSuppose the random variable X is normally distributed with mean 80 and standard deviation 16. Find following probabilities. Equation: P(85 ≤ X ≤ 102). Find the probability using a normal distribution table AND using ti-83 calculator. SHOW ALL STEPS PLEASE.arrow_forward
- Data set is Bachelor Degree's Conferred by Race and Ethnicity.arrow_forward4. Vons, a large supermarket in Grover Beach, California, is con- sidering extending its store hours from 7:00 am to midnight, seven days a week, to 6:00 am to midnight. Discuss the sam- pling bias in the following sampling strategies:arrow_forward3. Natalie Min is an undergraduate in the Haas School of Busi- ness at Berkeley. She wishes to pursue an MBA from Berkeley and wants to know the profile of other students who are likely to apply to the Berkeley MBA program. In particular, she wants to know the GPA of students with whom she might be compet- ing. She randomly surveys 40 students from her accounting class for the analysis. Discuss in detail whether or not Natalie's analysis is based on a representative sample.arrow_forward
- See data attached. SoftBus Company sells PC equipment and customized software to small companies to help them manage their day-to-day business activities. Although SoftBus spends time with all customers to understand their needs, the customers are eventually on their own to use the equipment and software intelligently. To understand its customers better, SoftBus recently sent questionnaires to a large number of prospective customers. Key personnel—those who would be using the software—were asked to fill out the questionnaire. SoftBus received 82 usable responses, as shown in the file. You can assume that these employees represent a random sample of all of SoftBus's prospective customers. SoftBus believes it can afford to spend much less time with customers who own PCs and score at least 4 on PC Knowledge. Let's call these the "PC-savvy" customers. On the other hand, SoftBus believes it will have to spend a lot of time with customers who do not own a PC and score 2 or less on PC…arrow_forwardSee data attached. SoftBus Company sells PC equipment and customized software to small companies to help them manage their day-to-day business activities. Although SoftBus spends time with all customers to understand their needs, the customers are eventually on their own to use the equipment and software intelligently. To understand its customers better, SoftBus recently sent questionnaires to a large number of prospective customers. Key personnel—those who would be using the software—were asked to fill out the questionnaire. SoftBus received 82 usable responses, as shown in the file. You can assume that these employees represent a random sample of all of SoftBus's prospective customers. SoftBus believes it can afford to spend much less time with customers who own PCs and score at least 4 on PC Knowledge. Let's call these the "PC-savvy" customers. On the other hand, SoftBus believes it will have to spend a lot of time with customers who do not own a PC and score 2 or less on PC…arrow_forwardWho is the better student, relative to his or her classmates? Here’s all the information you ever wanted to knowarrow_forward
- 3. A bag of Skittles contains five colors: red, orange, green, yellow, and purple. The probabilities of choosing each color are shown in the chart below. What is the probability of choosing first a red, then a purple, and then a green Skittle, replacing the candies in between picks? Color Probability Red 0.2299 Green 0.1908 Orange 0.2168 Yellow 0.1889 Purple 0.1736arrow_forwardName: Quiz A 5.3-5.4 Sex Female Male Total Happy 90 46 136 Healthy 20 13 33 Rich 10 31 41 Famous 0 8 8 Total 120 98 218 Use the following scenario for questions 1 & 2. One question on the Census at School survey asks students if they would prefer to be happy, healthy, rich, or famous. Students may only choose one of these responses. The two-way table summarizes the responses of 218 high school students from the United States by sex. Preferred status 1. Define event F as a female student and event R as rich. a. Find b. Find or c. Find and 2. Define event F as a female student and event R as rich. a. Find b. Find c. Using your results from a and b, are these events (female student and rich) independent? Use the following scenario for questions 3 & 4. At the end of a 5k race, runners are offered a donut or a banana. The event planner examined each runner's race bib and noted whether Age Less than 30 years old At least 30 years old Total Choice Donut Banana 52 54 106 5 72 77 Total 57 126…arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



