
Concept explainers
The solid-state structure of silicon is shown below.
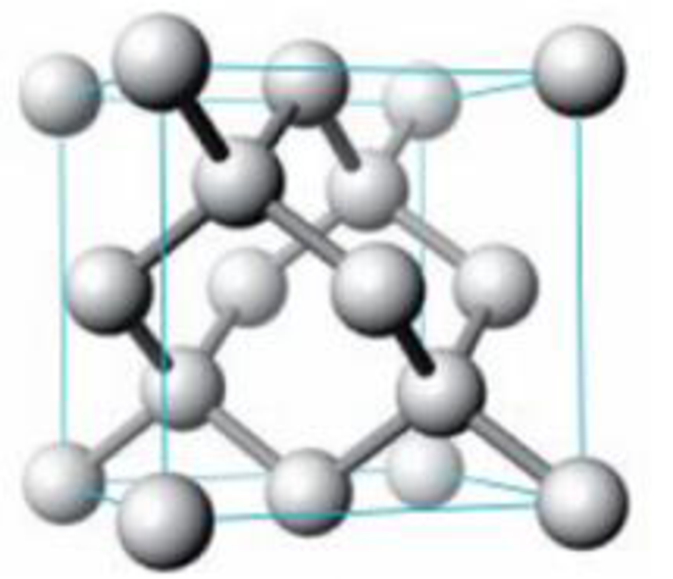
Unit cell for silicon
- (a) Describe this crystal as pc, bcc, or fcc.
- (b) What type of holes are occupied in the lattice?
- (c) How many Si atoms are there per unit cell?
- (d) Calculate the density of silicon in g/cm3 (given that the cube edge has a length of 543.1 pm).
- (e) Estimate the radius of the silicon atom. (Note: The Si atoms on the edges do not touch one another.)
(a)
Interpretation:
Given silicon crystal has to be described for PC, BCC or FCC.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contributions, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal
Explanation of Solution
The types of the lattice is face center cubic crystal, because It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
(b)
Interpretation:
The types of holes that are occupied in the lattice has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(c)
Interpretation:
Number of silicon atoms per unit cell has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Totally eight atoms in the unit cell
Explanation of Solution
Silicon atoms are located in one half of the tetrahedral holes.
(d)
Interpretation:
The density of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Density is
Explanation of Solution
The density of the silicon atom is given below,
(e)
Interpretation:
The radius of the silicon atom has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
- An ionic radii are the radius of an atom's ion in ionic crystals structure.
- An ionic solid is made up cations and anions held together by electrostatic forces in a rigid array or lattice.
- Positive charge ions are cations and negative charge ions are anions.
- Lattice Energy is mainly depends on the charge on the ion and radius or size of the ion.
- Ionic radius increases from top to bottom on the periodic table.
Ionic radius decreases from left to right the periodic table.
- The density of the unit cell:
- The face-centered cubic system:
It has lattice points on the faces of the cube, that each gives exactly one half contribution, in addition to the corner lattice points, giving a total of 4 lattice points per unit cell
Answer to Problem 47GQ
Radius is
Explanation of Solution
The radius of silicon atom can be calculated as,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
CHEMISTRY+CHEM...HYBRID ED.(LL)>CUSTOM<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning



