
Concept explainers
Cash flow statement gives the information related to the
To Determine: Journal entries and cash flow statement
Explanation of Solution
Purchase of the equipment
|
Date |
Account title and explanation |
post ref. |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
|
Equipment |
36,000 |
|||
|
Cash |
36,000 |
|||
|
(to record the purchase of the equipment) |
Table (1)
- Equipment account is the assets account. Here, assets have been purchased which increase the assets of the company. So, debit the equipment assets account.
- Cash is the assets account. Here cash has been paid to acquire the equipment assets which decrease the assets of the company. So, credt the cash account.
Issue of share
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Cash | 60,000 | |||
| Common stock | 60,000 | |||
| (to record issue of the common stock) |
Table (2)
- Cash is assets account of the company. Here, cash of the company is increased which increase the assets of the company. So, debit the cash account.
- Common stock is the liability account. Here, common stock increases the debt of the company. So, credit the common stock account.
Declared and payment of the dividends
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Dividends | 89,000 | |||
| Cash | 89,000 | |||
| (to record the payment of the dividend) |
Table (3)
- A dividend is the expense account which increased the debt of the company. Hence, debit dividend account.
- Cash is the assets account. Here cash reduces the debts of the company. So credit the cash account.
Increase in the
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Account receivable | 14,000 | |||
| Sales | 14,000 | |||
| (to record the account receivable) |
Table (4)
- Account receivable account is the assets account. Here, account receivable is increase by sale on credit. So debit the account receivable account.
- Sales account is the revenue account. Here, sales generate revenue for the company. So, credit the sale account.
Purchase the inventory by cash
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Inventory account | 440 | |||
| Cash | 440 | |||
| (to record the purchase of the inventory) |
Table (5)
- Inventory is the assets account. Here, the inventory of the company is decreasing which decreases the asset of the company. So, debit the inventory account.
- Cash is the asset account. Here, cash of the company is decreasing which decrease the asset value of the company. So credit the assets account.
Increase in the account payable
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Purchase | 16,000 | |||
| Account payable | 16,000 | |||
| (to record the account payable) |
Table (6)
- Purchase is the expense account. Here, something is purchase due to which purchase expense is increased. So, debit the purchase account.
- Account payable is the liability account. Here, account payable is increased. So, credit the account payable account.
Increase in the income tax payable
| Date | Account title and explanation | post ref. | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Retained earning | 3,000 | |||
| Income tax payable | 3,000 | |||
| (to record the income tax payable) |
Table (7)
Retained earnings belong to the share holders which reduces the wealth of the share. Hence, debit the retained earnings account.- Income tax payable is the liability account. Here, the income tax payable is increasing which increases the liabilities of the company. So, credit the income tax payable account.
Cash flow statement (Indirect method)
|
Cash flow statement For the year December 31,2017 |
|
|
Particulars |
Amount ($) |
|
Cash flow from operating activities: |
|
|
Net income |
136,000 |
|
Adjustment for non cash expenses |
|
|
Add:
|
54,000 |
|
Adjustment for |
|
|
Less: Increase in net working capital |
(68,000) |
|
Net cash flow from operating activities(A) |
122,000 |
|
Cash paid from acquiring new equipment |
(36,000) |
|
Cash flow from investing activities(B) |
(36,000) |
|
|
|
|
Cash from issuance of shares |
60,000 |
|
cash paid for dividends |
(89,000) |
|
Cash flow from financing activities(C) |
(29,000) |
|
|
|
|
Net increase in cash (A)+(B)+(C) |
(57,000) |
|
Cash and cash equivalent December 31,2016 |
107,000 |
|
Cash and cash equivalent December 31,2017 |
164,000 |
Table (8)
Working note:
Calculate the increase/decrease in the net working capital
| Particulars | 2017(X) | 2016(Y) | Increase/decrease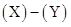 |
| Account receivable | 83,000 | 71,000 | 12,000 |
| Inventory | 601,000 | 526,000 | 75,000 |
| Increase/decrease in current assets(D) | 87,000 | ||
| Accounts payable | 87,000 | 71,000 | 16,000 |
| Income tax payable | 28,000 | 25,000 | 3,000 |
| Increase/decrease in current liabilities(E) | |||
| Increase/decrease in working capital(D)-(E) | 68,000 |
Table (9)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting
- Critically analyse the role of financial reporting in investment decision-making,emphasizing the qualitative characteristics that enhance the usefulness of financialstatements. Discuss how financial reporting influences both investor confidence andregulatory decisions, using relevant examples.arrow_forwardHelp need!!arrow_forwardAnswer please correarrow_forward
- Answer should be coarrow_forwardSolve quiarrow_forwardAssess the role of modern accounting theories in guiding research in accounting.Discuss how contemporary theories, such as stakeholder theory, legitimacy theory, andbehavioral accounting theory, shape research questions, hypotheses formulation, andempirical analysis.arrow_forward
- Need answerarrow_forwardDefine research methodology in the context of accounting theory and discuss theimportance of selecting appropriate research methodology. Evaluate the strengths andlimitations of quantitative and qualitative approaches in accounting research.arrow_forwardCritically evaluate the progress and challenges in achieving a single set of globalaccounting standards. Discuss the benefits and drawbacks of globalization inaccounting, providing relevant examples.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





