
Concept explainers
Draw the products formed when A is treated with each reagent: (a)
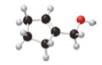
A
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed when A is treated with
Concept introduction: The addition of
Answer to Problem 28P
The product formed when A is treated with
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is,
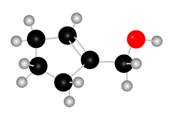
Figure 1
The red coloured balls have two bonds. So, these are the oxygen atoms. Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of A is,
Figure 2
When A is treated with
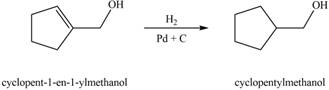
Figure 3
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed when A is treated with
Concept introduction: In presence of peroxide alkene is oxidized to epoxide this is known as epoxidation. The weak pi bond of alkene and weak
Answer to Problem 28P
The product formed when A is treated with
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is,
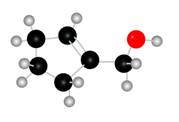
Figure 1
The red coloured balls have two bonds. So, these are the oxygen atoms. Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the A is,

Figure 2
In presence of
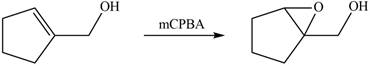
Figure 4
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed when A is treated with
Concept introduction: Alcohols are oxidized to different carbonyl compounds depending upon the reagents and alcohol used. In presence of strong oxidizing reagents such as
Answer to Problem 28P
The product formed when A is treated with
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is,
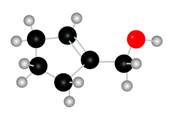
Figure 1
The red coloured balls have two bonds. So, these are the oxygen atoms. Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the A is,
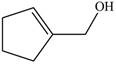
Figure 2
The chemical reaction of A with
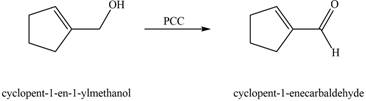
Figure 5
The primary alcohol is oxidized to aldehyde in presence of mild oxidizing reagent
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed when A is treated with
Concept introduction: Alcohols are oxidized to different carbonyl compounds depending upon the reagents and alcohol used. In presence of strong oxidizing reagents such as
Answer to Problem 28P
The product formed when A is treated with
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is

Figure 1
The red coloured balls have two bonds. So, these are the oxygen atoms. Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the A is,

Figure 2
When A is treated with
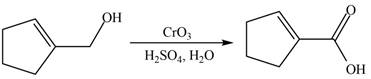
Figure 6
The primary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid in presence of strong oxidizing reagent
(e)
Interpretation: The product of formed when A is treated with Sharpless reagent
Concept introduction: Sharpless epoxidation involves the oxidation of double bond between carbon atoms to epoxide. This oxidation occurs only in allylic alcohol. This is an enantioselective oxidation, which means predominantly one enantiomer is formed. Sharpless reagents are
Answer to Problem 28P
The product of formed when A is treated with Sharpless reagent
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
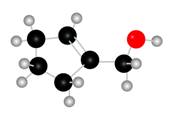
Figure 1
The red coloured balls have two bonds. So, these are the oxygen atoms. Black coloured atoms have four bonds. So, these are the carbon atoms. The grey coloured balls have one bond. So, these are the hydrogen atoms. The molecular structure of the A is,
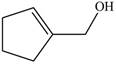
Figure 2
When epoxidation is done using
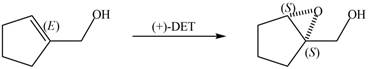
Figure 7
(a) The product formed when A is treated with
(b) The product formed when A is treated with
(c) The product formed when A is treated with
(d) The product formed when A is treated with
(e) The product of formed when A is treated with Sharpless reagent
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Physical Science
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
- 14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forward
