
Label the parts of this kidney and nephron.
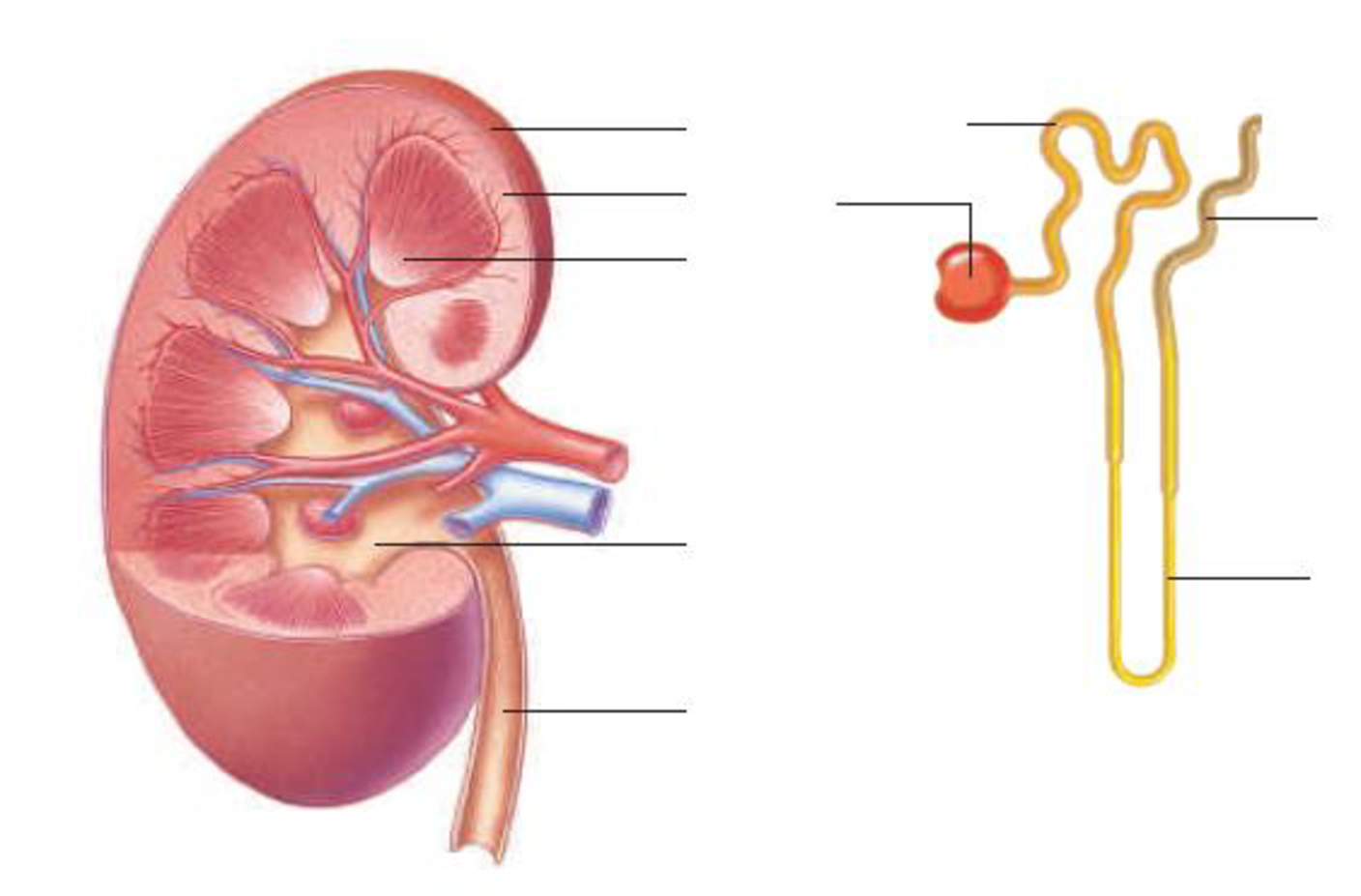
To label: The parts of the kidney and nephron.
Introduction: The kidney is an important organ of the excretory system, and nephron is the basic structural unit of the kidney. As blood passes through the kidneys, it filters the nitrogenous waste to form urine. It maintains homeostasis of the body.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the parts of the kidney, and Fig.2 shows the parts of the nephron.
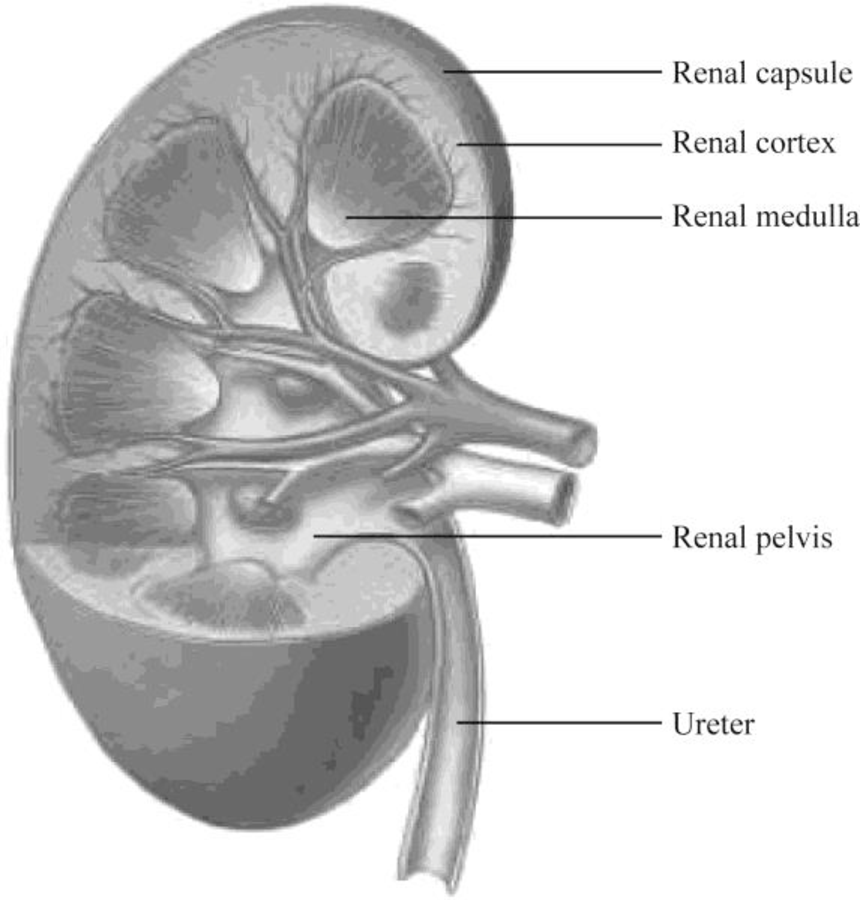
Fig.1: Kidney
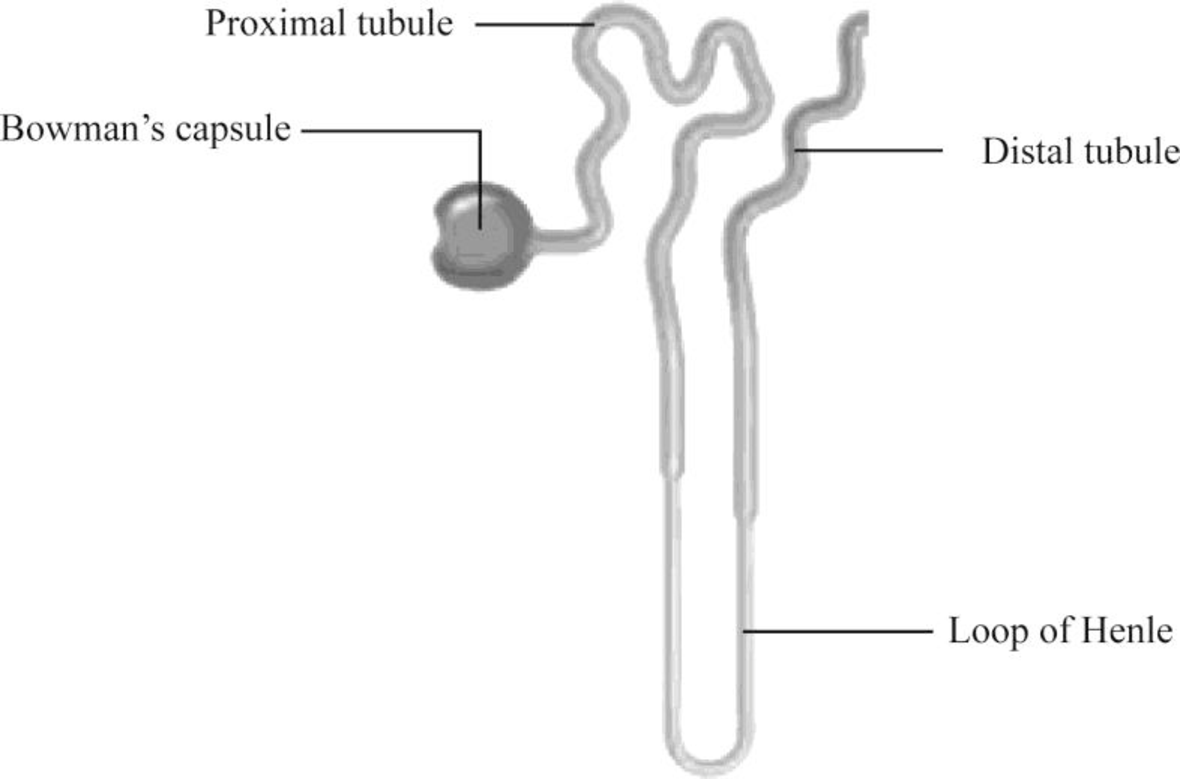
Fig.2: Nephron
Explanation of Solution
Structure of a kidney:
The kidney has two zones namely renal cortex and renal medulla. Renal cortex is the outer part of kidney. It consists of blood vessels that are connected to nephrons. Renal medulla is the inner part of the kidney containing 8–12 renal pyramids consisting of collecting tubules. Each kidney has a medially located space called renal sinus. This space is the urine drainage area. It is organized into minor calyces, major calyces, and a renal pelvis. There are 8 to 15 funnel-shaped minor calyces that are associated with the renal pyramid. Several minor calyces merge to form large major calyces. There are two to three major calyces in each kidney. The major calyces merge to form a large renal pelvis. Renal pelvis merges with the ureter at the medial edge of the kidneys.
Structure of a nephron:
Nephron is the functional filtration unit of kidney. It is microscopic in nature. Nephron has divided into renal corpuscle and renal tubule. Renal tubule is composed of simple epithelium that rests on the basement membrane. Renal tubule extends from the glomerular capsule (also called Bowman's capsule. It collects the material obtained from glomeruli) and ends at the collecting duct. It consists of three continuous sections. They are as follows:
- • The proximal convoluted tubule
- • The nephron loop
- • The distal convoluted tubule
The convoluted tubules reside in the cortex, but the nephron loop usually extends into the medulla from the cortex.
The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) is the first region of the renal tubule that is originated from the tubular pole of renal capsule. It consists of simple cuboidal epithelium and is marked by tall, apical microvilli that increase its surface area and reabsorption capacity. Under light microscope, the lumen of the proximal convoluted tubule looks fuzzy due to microvilli.
The nephron loop originates at the sharp bend in the proximal convoluted tubules. Each nephron has two limbs, namely descending limb and ascending limb. Both limbs are continuous at a hairpin within the medulla. From the proximal convoluted tubule, the descending limb extends medially to the tip of the nephron loop. Ascending limb of the nephron loop returns to the renal cortex and terminates at the distal convoluted tubule. Some parts of these limbs are classified as thick or thin according to the epithelia composing them. Thick segments of each limb have a simple cuboidal epithelium lining, whereas the thin segments of each limb have a simple squamous epithelium.
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) originates in the renal cortex at the end of the nephron loop’s thick ascending limb and extends to a collecting tubule. DCT is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium. DCT is smaller and has only sparse, short, apical microvilli. DCT does not look fuzzy when viewed under the light microscope.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
- students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forwardAmino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forward
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





