
Use this information for Exercises 1–4: the preference ballots for an election for the best speaker in a contest are shown. There are three candidates: Peterson (P), Quintana (Q), and Ross (R).
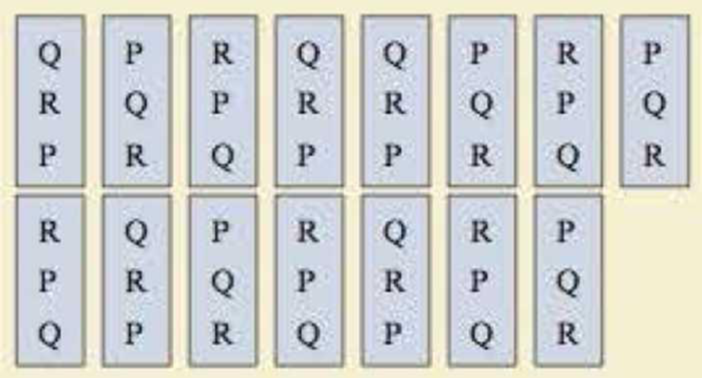
1. Construct a preference table for the results of the election.
To construct: The preference table for the results in the election.
Answer to Problem 1RE
The preference table for the results in the election are listed below.
| Number of votes | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| First choice | Q | P | R |
| Second choice | R | Q | P |
| Third choice | P | R | Q |
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The three candidates are Peterson (P), Quintana (Q) and Ross (R).
The preference table of the best speaker in a contest for the election are listed below.
| Q | P | R | Q | Q | P | R | P | R | Q | P | R | Q | R | P |
| R | Q | P | R | R | Q | P | Q | P | R | Q | P | R | P | Q |
| P | R | Q | P | P | R | Q | R | Q | P | R | Q | P | Q | R |
Calculation:
The choices are Peterson (P), Quintana (Q) and Ross (R).
From the ballot preference table, it is noticed that the candidate order QRP occurs 5 times, the candidate order PQR occurs 5 times and the candidate order RPQ occurs 5 times.
That is, the orders of QRP, PQR and RPQ is 5, 5 and 5.
Therefore, the preference table of the results in the election are listed below.
| Number of votes | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| First choice | Q | P | R |
| Second choice | R | Q | P |
| Third choice | P | R | Q |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
MATH IN OUR WORLD (LOOSELEAF)-W/ACCESS
- John and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forwardEvaluate F³ - dr where ♬ = (4z, -4y, x), and C' is given by (t) = (sin(t), t, cos(t)), 0≤t≤ñ .arrow_forward
- The details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. What is the simple moving average root mean square error? Round to two decimal places. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 207.13 B. 20.12 C. 14.39 D. 0.21arrow_forward5:00 PM Sat May 3 deltamath.com DeltaMath Given: ABBC and D is the midpoint of AC. Prove: ABD ≈ ACBD. ← Back to Home Deltamath Regents Review Week 3 Due: May 9 at 8:00 PM Grade: 97% Step Statement AB ≈ BC Reason 1 Given D is the midpoint of AC 2 BD BD 3 ADDC Calculating Volume (Mixed) Volume of Oblique Solids Volume, Density, and Unit 5 4 AABC is an isosceles triangle ZAZC Conversions (Level 1) Triangle Congruence Criteria try ZAD =/ DC Basic Triangle Proofs (Congruence Only - No CPCTC) Triangle Proofs (Reasons Only) Calculator Aseret Martinez Domi... Log Out Reflexive Property A midpoint divides a segment into two congruent segments The triangle has two congruent sides In a triangle, angles opposite of congruent sides are congruent An angle bisector divides an angle into two congruent angles B * A Ꭰ Note: the segment AC is a straight segment. 86%arrow_forwardEvaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- LANDMARKS Stonehenge is a British landmark made of huge stones arranged in a circular pattern that reflects the movements of Earth and the moon. The diagram shows that the angle formed by the north/south axis and the line aligned from the station stone to the northmost moonrise position measures 23.5°. a. Find measure of arc BC. b. Is arc ABC semicircle? Explain. c. If the circle measures about 100 feet across, approximately how far would you walk around the circle from point B to point sarsen circle B station stone trilithons horseshoe 71° 23.5° farthest north moonrise Sarrow_forwardMid-Term Review Find the formula for (f + g)(x). f(x) = x² - 10x + 25 and g(x) = x² - 10x + 24 (f + g) (x) = [ 2 ]x² X + DELL Skip Sarrow_forwardAmy and Samiha have a hat that contains two playing cards, one ace and one king. They are playing a game where they randomly pick a card out of the hat four times, with replacement. Amy thinks that the probability of getting exactly two aces in four picks is equal to the probability of not getting exactly two aces in four picks. Samiha disagrees. She thinks that the probability of not getting exactly two aces is greater. The sample space of possible outcomes is listed below. A represents an ace, and K represents a king. Who is correct?arrow_forward
- Consider the exponential function f(x) = 12x. Complete the sentences about the key features of the graph. The domain is all real numbers. The range is y> 0. The equation of the asymptote is y = 0 The y-intercept is 1arrow_forwardThe details of the clock sales at a supermarket for the past 6 weeks are shown in the table below. The time series appears to be relatively stable, without trend, seasonal, or cyclical effects. The simple moving average value of k is set at 2. If the smoothing constant is assumed to be 0.7, and setting F1 and F2=A1, what is the exponential smoothing sales forecast for week 7? Round to the nearest whole number. Week Units sold 1 88 2 44 3 54 4 65 5 72 6 85 Question content area bottom Part 1 A. 80 clocks B. 60 clocks C. 70 clocks D. 50 clocksarrow_forwardThe graph shows Alex's distance from home after biking for x hours. What is the average rate of change from -1 to 1 for the function? 4-2 о A. -2 О B. 2 О C. 1 O D. -1 ty 6 4 2 2 0 X 2 4arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
