
Downward sloping of aggregate demand curve.
Explanation of Solution
The aggregate demand (AD) curve shows an inverse relation between
The aggregate demand curve slopes downward due to three reasons:
Real balance effect: A change in the price level produces the real balance effect. A rise in the price level, results in a decrease in the
Interest Rate Effect: Assuming the money supply in the economy to be fixed, rise in price level implies more money required for purchases and pay for inputs. So, an increase in money demanded would increase the price paid for it, that is. the interest rate. The rise in interest rate will increase the borrowing costs which decrease the investment expenditure. This will decrease the quantity of real output demanded, thus decreasing the aggregate demand.
Foreign Purchases Effect: It is one of the key reasons behind the sloping of the aggregate demand curve. When the domestic price level rises relative to foreign price levels, foreigners buy fewer domestic goods as it becomes more expensive and people (domestic) opt for more foreign goods. Therefore, the export of domestic goods decline and import of foreign goods rise. As a result, there will be a decline in the overall demand for our domestic output. Thus the aggregate quantity demanded of GDP will decline. This slopes the AD curve downwards.
The reasons for downward sloping of AD curve are different from the reason for downward sloping of demand curve of a single-product. Assuming, a constant money income, substitution effect can work on a single product, whereby dropping prices of a single product make it relatively cheaper product compared to the other products whose price have not been changed. Also, the consumer has become richer in real terms, as he could afford more of the product whose price has been declined. But with the AD curve, as all the prices are falling implies dropping of the price level, thus single product substitution effect is not applicable in AD curve. Also, while dealing with demand of a single product, money income is assumed to be fixed. But this assumption is not applicable in case of AD curve because with regard to the circular flow of the economy, lower prices indicate lower incomes. Thus a decline in the price level does not necessarily imply an increase in the nominal income of the economy as a whole since as prices are dropping, so are the receipts or revenue of the sellers.
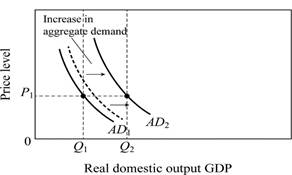
Figure-1
The multiplier effect acts on the initial change in spending to generate an even greater shift in the aggregate demand curve.
For instance, Figure 1 shows how multiplier effect works on an increase in income expenditure. The initial increase in spending is reflected by the broken line of AD curve, and then multiplier effect shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate Demand: It refers to the total value of the goods and services available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Multiplier effect: Multiplier refers to the ratio of change in the real GDP to the change in initial consumption at constant price rate. Multiplier is positively related to the marginal propensity to consumer and negatively related with the marginal propensity to save.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
MACROECONOMICS W/CONNECT
- 17. Given that C=$700+0.8Y, I=$300, G=$600, what is Y if Y=C+I+G?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write explanation in paragraphs and if you use currency use USD currency: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forward
- Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 4. Draw a Keynesian AD curve in P – Y space and list the shift factors that will shift theKeynesian AD curve upward and to the right. Draw a separate Classical AD curve in P – Yspace and list the shift factors that will shift the Classical AD curve upward and to the right.arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 15. How is the Keynesian expenditure multiplier implicit in the Keynesian version of the AD/ASmodel? Explain and show mathematically. (note: this is a tough one)arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 13. What would happen to the net exports function in Europe and the US respectively if thedemand for dollars rises worldwide? Explain why.arrow_forward
- 20. Given the mathematical model below, solve for the expenditure multiplier for a) government spending, G; and b) for consumer taxes, T. (medium difficulty) Y=C+I+G C=Co+b(Y-T) 1 = 10 T=To+tY G = Go+gYarrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 11. What exactly is a rectangular hyperbola and what relevance is it to classical economics?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 9. Explain the difference between absolute and comparative advantage in a family setting, i.e.using parents and children. What can we glean from knowing about comparative andabsolute advantages?arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
 Macroeconomics: Principles and Policy (MindTap Co...EconomicsISBN:9781305280601Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. BlinderPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Principles and Policy (MindTap Co...EconomicsISBN:9781305280601Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. BlinderPublisher:Cengage Learning





