
a.
Calculate pre-determined
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pre-determined Overhead Rate: Predetermined overhead rate is a measure used to allocate the estimated manufacturing overhead cost to the products or job orders during a particular period. This is generally evaluated at the beginning of each reporting period. The evaluation takes into account the estimated manufacturing overhead cost and the estimated allocation base that includes direct labor hours, direct labor in dollars, machine hours and direct materials. The pre-determined overhead rate is calculated as follows:
Calculate Pre-determined overhead rate:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Rent on factory space | $30,000 |
| Indirect materials | $15,000 |
| Maintenance costs for factory equipment | $5,000 |
| Utilities costs for factory space | $4,000 |
| $12,000 | |
| Total estimated overhead cost (A) | $66,000 |
| Estimated direct labor hours (B) | 6,500 hours |
| Pre-determined overhead rate (C) | $10.15 per labor hour |
Table (1)
Hence, the pre-determined overhead rate is $10.15 per labor hour.
Requirements b., c., and d.
Determine the ending balance in (b) raw materials inventory, (c) finished goods inventory, (d) work-in process inventory.
Requirements b., c., and d.
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Raw materials inventory: Raw material inventory are the primary materials which are used in the production process to get the finished product.
The ending balance of raw materials inventory is $7,100 (Refer Table (2).
(c)
Finished goods inventory: Finished goods inventory are the goods that are ready for sale after completing the production process.
The ending balance of raw materials inventory is $83,085(Refer Table (2).
(d)
Work-in-process inventory: Work-in-process inventory is the middle part of raw materials and finished goods. This inventory is the portion of the manufactured inventory for which the process has been started but not yet completed.
The ending balance of raw materials inventory is $54,630(Refer Table (2).
Working Note:
Compute the balance of raw material inventory:
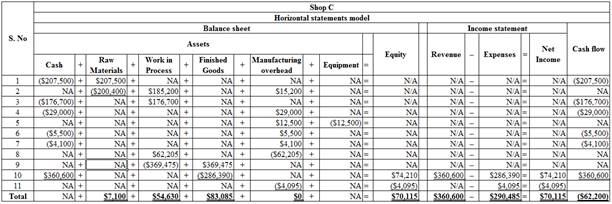
Table (2)
Note for 8:
Prepare summary
| Summary job cost sheet | ||||||
| Job Number | Direct Materials | Direct Labor | Manufacturing Overhead | Total costs | ||
| Rate | Hours | Cost | ||||
|
701 | $42,400 | $39,200 | $16.50 | 710 | $11,715 | $93,315 |
| 702 | $34,700 | $41,100 | $16.50 | 840 | $13,860 | $89,660 |
| 703 | $41,100 | $47,300 | $16.50 | 910 | $15,015 | $103,415 |
| 704 | $38,800 | $29,600 | $16.50 | 890 | $14,685 | $83,085 |
| 705 | $28,200 | $19,500 | $16.50 | 420 | $6,930 | $54,630 |
| Totals | $185,200 | $176,700 | 3,770 | $62,205 | $424,105 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the cost of manufacturing overhead is $62,205.
Note for 9:
Determine the
Note: Refer table (3) for the total costs of the respective jobs.
Note for 10.
Cash of $360,000 is the sum of sales price of Jobs 701, 702 and 703 and the cost of finished goods sold is $286,390 which is the sum total of costs of Jobs 701, 702 and 703.
Note for 11.
The total of manufacturing overhead is $66,300 (Refer table (2)). The balance of Manufacturing Overhead before under-applied overhead is
e.
Determine the cost of goods manufactured.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods manufactured: The cost of goods manufactured is the total costs incurred for the manufacturing of a product which is transferred from work-in process inventory account to the finished goods inventory account.
The Cost of goods manufactured is $369,475 (Refer Note 9).
f.
Determine the cost of goods sold.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods sold is the total of all the expenses incurred by a company to sell the goods during the given period.
The cost of goods sold is $286,390 (Refer Note 10).
g.
Determine the amount of gross margin that would be earned from Jobs 701, 702 and 703.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Gross margin (gross profit): Gross margin is the amount of revenue earned from goods sold over the costs incurred for the goods sold.
Compute the amount of gross margin that would be earned from Jobs 701, 702 and 703:
| Computation of gross margin for Shop C | |||
| Job Number |
Sales Price (1) | Cost of goods sold (2) |
Gross Margin |
| 701 | $128,000 | $93,315 | $34,685 |
| 702 | $120,100 | $89,660 | $30,440 |
| 703 | $112,500 | $103,415 | $9,085 |
Table (4)
Note: Refer table (3) for the cost of goods sold (total cost column) for each job.
Thus, the gross margin earned from Jobs 701, 702 and 703 are $34,685, $30,440 and $9,085.
h.
Determine the amount of over applied or under applied of overhead that would exist at the end of the year.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Manufacturing overhead costs: The costs, which do not relate directly with the manufacturing of products, are referred to as manufacturing overhead costs or indirect costs. Manufacturing overhead cost per unit is the cost of manufacturing overhead incurred to produce one unit of product.
Determine the amount of over applied or under applied of overhead:
Given, the total of manufacturing overhead is $66,300 (Refer table (2)) and the manufacturing overhead cost applied to work in process is $62,205 (Refer Table (3)).
Thus, the under applied of overhead that would exist at the end of the year is $4,095.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts
- Hunger Games Corporation has had a defined benefit pension plan for three decades. Two years ago, the company improved the benefits at a cost of $2,800,000. Pension plan assets were $84,000,000 while pension obligations were $76,000,000 at the beginning of the year. For the current year, Hunger Games 's pension plan incurred current service cost of $6,400,000 and interest of $8,600,000. The pension's assets earned $9,000,000, which is $400,000 below expectations. There were no actuarial gains or losses for the year. Required Compute the pension expense for the year. Record the journal entries for Hunger Games's pension plan.arrow_forwardI need guidance with this financial accounting problem using the right financial principles.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward
- Can you explain this financial accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardIn the first two years of operations, Expos company reports taxable income of $125,000 and $65,000, respectively. In the first two years, the company paid $50,000 and $13,000. It is now the end of the third year, and the company has a loss of $160,000 for tax purposes. The company carries losses to the earliest year possible. The tax rate is currently 25%. Required Compute the amount of income tax payable or receivable in the current (third) year.arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





