
Concept explainers
Find the total resistance and the current flow in each branch for the circuit.
Answer to Problem 19P
The total resistance is
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The supply voltage is
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
Formula used:
Formula to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit,
Here,
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the voltage across the resistor
Here,
Rearrange the equation for the current flow through the resistance
Formula to calculate the total current drawn by the circuit,
Calculation:
Refer to Figure problem 12.19 in the textbook, and redraw it as Figure 1, with the two light bulbs represents the resistors
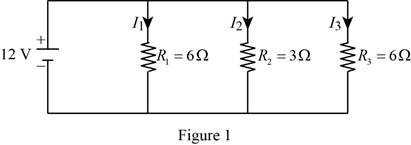
Substitute
Reduce the equation as,
The voltage drop across the each light bulb and the resistor is equal to the
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Hence,
The total resistance is
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
The current flows through the branch
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK ENGINEERING FUNDAMENTALS: AN INTROD
- 1. A W10x60 with sections properties shown is to be used as a column. If the unsupported length is 5.0m, find the Safe Axial Load that can be carried by the section. Use Fy=248 MPa and K=1.50 (35pts) Section Properties: A = 11355 mm2 Ix = 142x106 mm4 rx = 111.51 mm Iy = 48 x 106 mm4 ry = 65.28 mm 2. A Steel Column will be required to carry a total load of 500KN. If a tubular section will be utilized and the required dimension must not exceed 400x400, what will be the required thickness of the section (tf=tw). Use Fy=248 MPa L=4.5m, K=1.0 and 80% of initial fa will be used. (50pts) Note: Plate thickness available are: 2mm, 3mm, 4mm, 6mm, 8mm and 10mm 3. A steel tension rod will be subjected to a tension load of 320 KN. What will be the required diameter of the rod if Fy=248 MPa (15pts)arrow_forwardfor purposes of orientation every contour may must display what?arrow_forwardDuring calibration of an LVDT, the data shown in the accompanying table were obtained. Using a spreadsheetprogram, plot the relation between the micrometer reading and voltage. What is the linear range of the LVDT? Determinethe calibration factor of the LVDT by obtaining the best fit line of the data within the linear range.arrow_forward
- Develop a signal design and timing for the intersection shown in the figure below. In each case accommodate both vehicular and pedestrian movements. In general, use the following values for the problem: pedestrian walking speed = 1 [m/s], vehicle deceleration = 3 [m/s²], driver reaction time = 1.5 [s], length of vehicle = 6 [m], and level grade = 0. If you need to assume other variables and parameters to solve this problem clearly state that in your report and explain the reason. A250 1100 One-way Speed limit = 50 [km/h] Pedestrian = 15 per each crosswalk Crosswalk widths = 3 [m] Lane width = 4 [m] Saturation flow = 1800 [veh/h/lane] 1100 ↑ 200 70 80 900arrow_forwardhow land use and urban structure contribute to financial stability or instability.arrow_forwardQ1 parts B and C but plz draw it out or something plz put it on a bread board with resistors and a voltage source please do not show it in the schematic way like in the picture there if you can show it on like thinkercadarrow_forward
- Sketch the effective stress profile for the silt layer to a depth of 5 meters for a uniform layer of silt having a depth to the water table of 4 m (choose several discrete points with depth and plot by hand). Use Bishop's definition of effective stress for the silt layer, assuming x =S.. Assume a value of G. = 2.65 and that the gravimetric water content of the silt below the water table is 20%. Use the SWRC for the silt from the figure below. Assume that the air pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure (i.e., zero). Consider variations in total unit weight with the degree of saturation in your calculations. 100000 a. 10000 Sand: a = 0.3 kPa, n = 3.0 Silt: a=0.05 kPa, n=2.5 0.01 kPa, n = 1.8 1000 Clay: Matric suction (kPa) 00 100 10 10 1 0.1 ° 20 60 80 40 Saturation (%) 100 10arrow_forwardYou are asked to design a two-story commercial building that has reinforced masonry shear walls as shown below. The height of the parapet above the roof is 2 feet. The walls are to be constructed of 8-inch CMU and are to be fully grouted. The building is assigned to SDC D, and therefore, the walls have to be special RM shear walls according to TMS 402. There are 6 shear walls to resist the lateral seismic force along one principal axis of the building and 4 shear walls along the other axis. The corner walls are flanged walls meeting the requirements in Sec. 5.2.3 of TMS 402-22. The columns carry only gravity loads and no lateral seismic forces. The floor and roof diaphragms are relatively flexible in out-of-plane bending compared to the in-plane flexural stiffness of the walls, so that you can ignore the coupling moments and shear forces exerted by the diaphragms on the walls. However, the in-plane stiffness of the diagrams is high so that their planar deformation can be ignored.…arrow_forwardDevelop a signal design and timing for the intersection shown in the figure below. In each case accommodate both vehicular and pedestrian movements. In general, use the following values for the problem: pedestrian walking speed = 1 [m/s], vehicle deceleration = 3 [m/s²], driver reaction time = 1.5 [s], length of vehicle 6 [m], and level grade = 0. If you need to assume = other variables and parameters to solve this problem clearly state that in your report and explain the reason. 250 1100 One-way Speed limit = 50 [km/h] Pedestrian = 15 per each crosswalk Crosswalk widths = 3 [m] Lane width = 4 [m] Saturation flow = 1800 [veh/h/lane] 1100 70 80 T 200 900arrow_forward
- A pre-timed four-phase signal has critical lane group flow rates for the first three phases of 260, 280, and 310 [veh/h] (saturation flow rates are 2000 [veh/h/In] for all phases). The lost time is known to be 5 seconds for each phase. If the cycle length is 90 seconds, what is the estimated effective green time of the fourth phase?arrow_forwarda. Assume a bus line with N stops, where the distance between stops is S. Free flow speed of the bus is v, with acceleration and deceleration, a. P passengers per stop are boarding and alighting, and the time needed for a passenger to board or alight is T seconds. What is the average speed of a bus? b. Following on part (a), assume the origins of passengers are spread uniformly along the bus route. The destination of all passengers is the last stop. The walking speed of passengers is u. Determine the average travel time (walking + in-vehicle) of passengers. c. Simplify the above equation when N is large enough (approximating N-1/2 by N-1). Consider now that you can decide on S, where you replace N=L/S (L is the length of the route). Find the value of S that minimises the travelling time of the passengers. d. In the same setting as (c), assume that some passengers do not go to the terminal but alight before. Explain if your answer from (c) would increase or decrease and why. If you need…arrow_forwardThe minimum cycle length for an intersection is determined to be 95 seconds. The critical lane group flow ratios were calculated as 0.235, 0.25, 0.17, and 0.125, respectively. Assuming 5 seconds lost per phase, determine which X was used.arrow_forward
 Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285852225Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337402415Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
Residential Construction Academy: House Wiring (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337402415Author:Gregory W FletcherPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





