
Concept explainers
(a)
To express: The monthly cost in terms of the distance driven d assuming the function follows a linear function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 18E
The equation of the monthly cost in terms of the distance driven d is
Explanation of Solution
Let d represents the number of miles driven in a month and C represents the monthly cost in dollars.
Recall the general equation of the linear function
Since the cost function follows a linear function, the equation of the cost C in terms of the number of miles driven d is in the form of
According to the given data, there are two points such as (480, 380) and (800, 460).
Obtain the slope m by using the two point formula as follows.
Thus, the slope is
Use the slope
Thus, the required equation is
(b)
To predict: The monthly cost of driving 1500 miles.
(b)
Answer to Problem 18E
The monthly cost of driving 1500 miles is $635.
Explanation of Solution
From part (a), the equation of the monthly cost in terms of the distance driven d is
Substitute
Thus, the cost of driving 500 miles is $635.
(c)
To sketch: The graph of the cost as a function of distance driven and interpret the slope.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Let x-axis represents the number of miles driven and y-axis represents the monthly cost in dollars.
From part (a), the equation of the monthly cost as a function of distance driven is
Obtain the values of C for several values of d as tabulated in Table 1 and draw the graph as shown below in Figure 1.
| d | C |
| 0 | 260 |
| 500 | 385 |
| 1000 | 510 |
Table 1
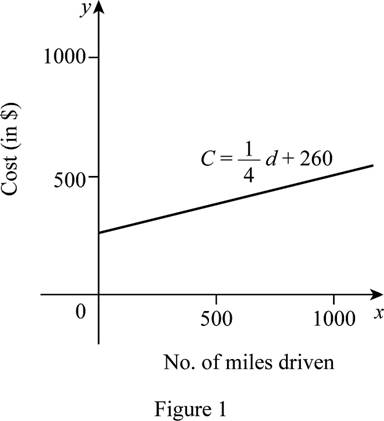
From Figure 1, it is observed that the graph is a straight line as the function is linear.
Also, notice that the cost increases as the number of miles increases. That is, if the distance driven increases by 320, then the cost increases by $80 ($0.25 per mile.)
Thus, the slope is,
(d)
To explain: The meaning of C-intercept.
(d)
Answer to Problem 18E
The C-intercept of the cost function is 260 and it represents the fixed manufacturing cost per day.
Explanation of Solution
From part (a), the equation of the monthly cost as a function of the distance driven is
Since it follows a linear function, the constant term c is considered as the y-intercept.
Thus, the y-intercept is 260.
The C-intercept represents the fixed monthly cost as it is the constant term.
(e)
To explain: Why a linear function is suitable for this model.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Since the monthly cost is fixed and the cost increases as the distance driven increases, the function follows the linear function.
Thus, the linear function is suitable for this situation.
Chapter 1 Solutions
Bundle: Single Variable Calculus: Concepts And Contexts, Enhanced Edition, 4th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Stewart's Calculus: Concepts And Contexts, Multi-term
- 8–23. Sketching vector fields Sketch the following vector fieldsarrow_forward25-30. Normal and tangential components For the vector field F and curve C, complete the following: a. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is tangent to C. b. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is normal to C. c. Sketch C and a few representative vectors of F on C. 25. F = (2½³, 0); c = {(x, y); y − x² = 1} 26. F = x (23 - 212) ; C = {(x, y); y = x² = 1}) , 2 27. F(x, y); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 4} 28. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 1} 29. F = (x, y); C = 30. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x = 1} {(x, y): x² + y² = 1}arrow_forward٣/١ B msl kd 180 Ka, Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 /0001 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ DC 7) rotor a ' (y+xlny + xe*)dx + (xsiny + xlnx + dy = 0. Q1// Find the solution of: ( 357arrow_forward
- ۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 B. 180 msl Kas Sin (I) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30): 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds 120×50 looo G 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Find the general solution of the following equations: QI//y(4)-16y= 0. Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2ll yll-4y/ +13y=esinx.arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-180 60 msl kd Kas Sin () 2 I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا مريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3 Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating ined sove in peaper 5) Synchronous speed s 120×50 6 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط Look 7) rotov DC I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Solve the following equations: 0 Q1// Find the solution of: ( y • with y(0) = 1. dx x²+y²arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/3 1 B-180-60 msl Ka Sin (1) Isin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 6) 1 0.05 G 50105 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 2- A hot ball (D=15 cm ) is cooled by forced air T.-30°C, the rate of heat transfer from the ball is 460.86 W. Take for the air -0.025 Wim °C and Nu=144.89, find the ball surface temperature a) 300 °C 16 b) 327 °C c) 376 °C d) None か = 750 01arrow_forward
- Don't do 14. Please solve 19arrow_forwardPlease solve 14 and 15arrow_forward1. Consider the following system of equations: x13x2 + 4x3 - 5x4 = 7 -2x13x2 + x3 - 6x4 = 7 x16x213x3 - 21x4 = 28 a) Solve the system. Write your solution in parametric and vector form. b) What is a geometric description of the solution. 7 c) Is v = 7 in the span of the set S= [28. 1 HE 3 -5 3 ·6 ? If it is, write v 6 as a linear combination of the vectors in S. Justify. d) How many solutions are there to the associated homogeneous system for the system above? Justify. e) Let A be the coefficient matrix from the system above. Find the set of all solutions to Ax = 0. f) Is there a solution to Ax=b for all b in R³? Justify.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





