
Concept explainers
To Find:The tension in the backstay and the normal force that the deck exerts on the mast.
Answer to Problem 17P
The tension in thee backstay is
The normal force exerted by the deck on the mast is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Free body diagram for the given situation is as follows:
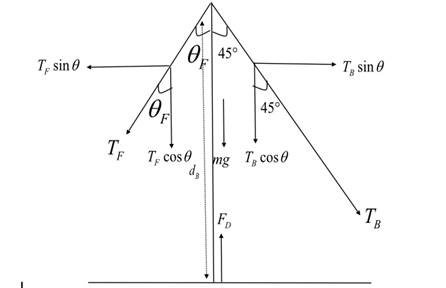
Formula used:
Apply the condition of translational and
Calculation:
Apply the condition of rotational equilibrium to the mast. The net torque due to tension by the wires is equal to zero and is represented as:
Torque due to the left side of the pole is given as
Torque due to right side of the pole is given as
Since the torque due to right side of the wire is in clock wise direction, it is negative.
Thus, the torque of horizontal components according to the condition of rotational equilibrium is given as
Here,
Substitute
From the figure, angle of forestay is obtained as follows:
Here,
Substitute
Determine the tension in the backstay as below.
Substitute the
Therefore, the tension in the backstay is
Torque due to the left side of the pole is given as,
Torque due to right side of the pole is given as,
Since the torque due to right side of the wire is in clock wise direction, it is negative.
Thus, the net torque of vertical components according to the condition of rotational equilibrium is given as,
Here,
Re-arrange the above equation for
Substitute
Conclusion:
The normal force exerted by the deck on the mast is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- no AI, pleasearrow_forwardSketch the resulting complex wave form, and then say whether it is a periodic or aperiodic wave.arrow_forwardDuring a concentric loading of the quadriceps muscle in the upper leg, an athlete extends his lower leg from a vertical position (see figure (a)) to a fully extended horizontal position (see figure (b)) at a constant angular speed of 45.0° per second. Two of the four quadriceps muscles, the vastis intermedius and the rectus femoris, terminate at the patellar tendon which is attached to the top of the tibia in the lower leg. The distance from the point of attachment of the patellar tendon to the rotation axis of the tibia relative to the femur is 4.10 cm in this athlete. a b (a) The two quadriceps muscles can exert a maximum force of 225 N through the patellar tendon. This force is applied at an angle of 25.0° to the section of the tibia between the attachment point and the rotation axis. What is the torque (in N⚫ m) exerted by the muscle on the lower leg during this motion? (Enter the magnitude.) N⚫ m (b) What is the power (in W) generated by the athlete during the motion? W (c)…arrow_forward
- = A hanging weight, with a mass of m₁ = 0.365 kg, is attached by a rope to a block with mass m₂ 0.835 kg as shown in the figure below. The rope goes over a pulley with a mass of M = 0.350 kg. The pulley can be modeled as a hollow cylinder with an inner radius of R₁ = 0.0200 m, and an outer radius of R2 = 0.0300 m; the mass of the spokes is negligible. As the weight falls, the block slides on the table, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the table is μk = 0.250. At the instant shown, the block is moving with a velocity of v; = 0.820 m/s toward the pulley. Assume that the pulley is free to spin without friction, that the rope does not stretch and does not slip on the pulley, and that the mass of the rope is negligible. mq R₂ R₁ mi (a) Using energy methods, find the speed of the block (in m/s) after it has moved a distance of 0.700 m away from the initial position shown. m/s (b) What is the angular speed of the pulley (in rad/s) after the block has moved this…arrow_forwardno AI, pleasearrow_forwardno AI, pleasearrow_forward
- no AI, pleasearrow_forwardTwo astronauts, each having a mass of 95.5 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. They are isolated in space, moving in circles around the point halfway between them at a speed of 4.60 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles, calculate each of the following. CG × d (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system kg m2/s (b) the rotational energy of the system KJ By pulling on the rope, the astronauts shorten the distance between them to 5.00 m. (c) What is the new angular momentum of the system? kg m2/s (d) What are their new speeds? m/s (e) What is the new rotational energy of the system? KJ (f) How much work is done by the astronauts in shortening the rope? KJarrow_forwardA uniform horizontal disk of radius 5.50 m turns without friction at w = 2.55 rev/s on a vertical axis through its center, as in the figure below. A feedback mechanism senses the angular speed of the disk, and a drive motor at A ensures that the angular speed remain constant while a m = 1.20 kg block on top of the disk slides outward in a radial slot. The block starts at the center of the disk at time t = 0 and moves outward with constant speed v = 1.25 cm/s relative to the disk until it reaches the edge at t = 360 s. The sliding block experiences no friction. Its motion is constrained to have constant radial speed by a brake at B, producing tension in a light string tied to the block. (a) Find the torque as a function of time that the drive motor must provide while the block is sliding. Hint: The torque is given by t = 2mrvw. t N.m (b) Find the value of this torque at t = 360 s, just before the sliding block finishes its motion. N.m (c) Find the power which the drive motor must…arrow_forward
- (a) A planet is in an elliptical orbit around a distant star. At its closest approach, the planet is 0.670 AU from the star and has a speed of 54.0 km/s. When the planet is at its farthest distance from the star of 36.0 AU, what is its speed (in km/s)? (1 AU is the average distance from the Earth to the Sun and is equal to 1.496 × 1011 m. You may assume that other planets and smaller objects in the star system exert negligible forces on the planet.) km/s (b) What If? A comet is in a highly elliptical orbit around the same star. The comet's greatest distance from the star is 25,700 times larger than its closest distance to the star. The comet's speed at its greatest distance is 2.40 x 10-2 km/s. What is the speed (in km/s) of the comet at its closest approach? km/sarrow_forwardYou are attending a county fair with your friend from your physics class. While walking around the fairgrounds, you discover a new game of skill. A thin rod of mass M = 0.505 kg and length = 2.70 m hangs from a friction-free pivot at its upper end as shown in the figure. Pivot Velcro M Incoming Velcro-covered ball m The front surface of the rod is covered with Velcro. You are to throw a Velcro-covered ball of mass m = 1.25 kg at the rod in an attempt to make it swing backward and rotate all the way across the top. The ball must stick to the rod at all times after striking it. If you cause the rod to rotate over the top position (that is, rotate 180° opposite of its starting position), you win a stuffed animal. Your friend volunteers to try his luck. He feels that the most torque would be applied to the rod by striking it at its lowest end. While he prepares to aim at the lowest point on the rod, you calculate how fast he must throw the ball to win the stuffed animal with this…arrow_forward56 is not the correct answer!arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





