
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
10th Edition
ISBN: 2818440034374
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.2, Problem 1.6FP
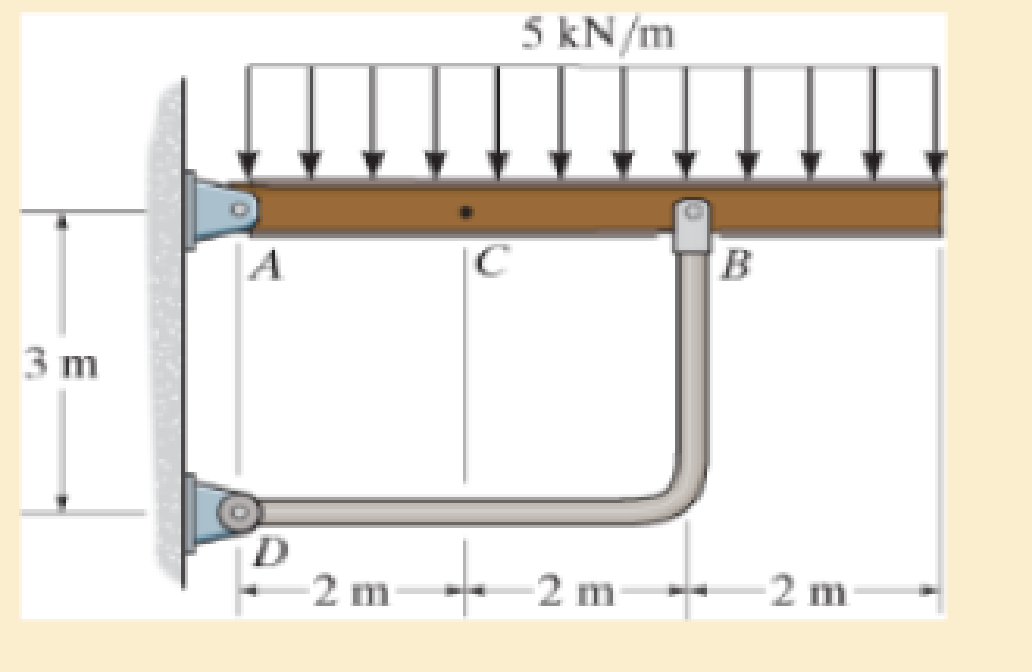
Determine the resultant internal normal force, shear force, and bending moment at point C in the beam.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending moment
Chapter 1 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 1.2 - In each case, explain how to find the resultant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The boom DF of the jib crane and the column DE...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The hand crank that is used in a press has the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - In each case, determine the largest internal shear...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest internal normal force in the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the internal normal force at section A...Ch. 1.5 - The lever is held to the fixed shaft using the pin...Ch. 1.5 - The single-V butt joint transmits the force of 5...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - The supporting wheel on a scaffold is held in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A and is...Ch. 1.5 - The small block has a thickness of 0.5 in. If the...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The board is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - If P=5 kN, determine the average shear stress in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads the...Ch. 1.5 - The column is made of concrete having a density of...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - If P = 15 kN, determine the average shear stress...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - The two steel members are joined together using a...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The two members used in the construction of an...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Rods AB and BC have diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm,...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the greatest constant angular velocity ...Ch. 1.5 - The radius of the pedestal is defined by r =...Ch. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - The tension member is fastened together using two...Ch. 1.7 - The steel swivel bushing in the elevator control...Ch. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the size of square bearing plates A and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - The steel pipe is supported on the circular base...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods support the vertical force...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and AC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required minimum thickness t of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 1.7 - The compound wooden beam is connected together by...Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The rods AB and CD are made of steel. Determine...Ch. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Every complete statement ends with a _____.
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Find the errors in the following code: 1. // Warning! This code contains ERRORS! if (x = = 1); y = 2; else if (...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
The first line of a function definition is known as the____ a. body b. introduction c. initialization d. header
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Rewrite the following if/else statements as conditional expressions: A) if (x y) z = 1; else z = 20; B) if (te...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Repeat Practice Program 5 of Chapter 3, but use a loop so the user can convert other temperatures. If the user ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What do the Ada and COBOL languages have in common?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- My ID#016948724 please solve this problems and show me every step clear to follow pleasearrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forward
- can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forwardhi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C-FEVzI8oe8;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bending Stress; Author: moodlemech;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QIqewkE6xM;License: Standard Youtube License