
Concept explainers
Exercises 9 through 12 refer to a variation of the Koch snowflake called the Koch antisnowflake. The Koch antisnowflake is much like the Koch snowflake, but it is based on a recursive rule that removes equilateral triangles. The recursive replacement rule for the Koch antisnowflake is as follows:
Koch Antisnowflake
• Start: Start with a solid seed equilateral triangle [Fig. 12-36(a) ].
• Replacement rule: In each step replace any boundary line segment ____ with a ![]() (where the point is always facing toward the interior of the snowflake). [Figures 12-36(b) and (c) show the figures obtained at Steps 1 and 2, respectively.
(where the point is always facing toward the interior of the snowflake). [Figures 12-36(b) and (c) show the figures obtained at Steps 1 and 2, respectively.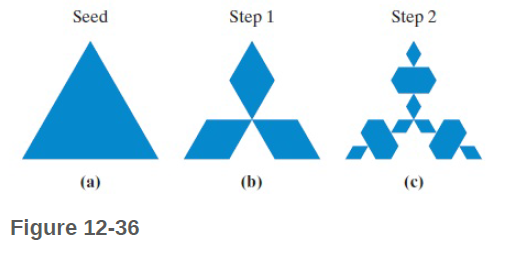
Assume that the seed triangle of the Koch antisnowflake has area
Table
| R | S | T | Q | |
| Start |
|
|
|
|
| Step
|
|
|
|
|
| Step
|
|
|
|
|
| Step
|
||||
| Step
|
||||
| Step
|
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EXCURSIONS IN MOD.MATH W/ACCESS >BI<
- Find all solutions of cos(x + 1) = cos(x − 1) = Π - - = 1 in the interval [0, 2π). 6arrow_forwardSolve the equation 2 cos 2x + √√3 = 0 for 0 ≤ 0 < 2π.arrow_forwardConsider y (t) — y" (t) − y' (t) + y(t) = 0 (a) Denote new variables x1(t) := y(t), x2(t) := y' (t), x3(t) = y"(t) and solve the following system 0 1 0 x1(t) X' (t) = 0 1 X(t), X(t) = x2(t) -1 1 1 x3(t) = y(t) y' (t) y" (t) (b) Use your solution to the system to find the solution to the original equation (verify!).arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning  Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL




