
Program plan:
- Item, start variablesare used for input. There is structure listnode having data, nextPtr member variables which represents the linked list node.
- void insert(node **head, int value) function inserts the node in the a linked list.
- node *concat(node *flist, node *slist) function concat the two linked list and return the resultant linked list.
- void printList(node *head) function display the contents of the linked list.
Program description:
The main purpose of the program is to perform the concatenation of two linked list by implanting the concept which is same as strcat() function of string.
Explanation of Solution
Program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <alloc.h>
#include <ctype.h>
//structure of node of the linked list
typedefstruct listnode
{
int data;
struct listnode *nextPtr;
} node;
//function to insert a node in a linked list
void insert(node &head,int value);
//recursive function to concate the linked list
node *concat(node *flist, node *slist);
//function to print the content of linked list
void printList(node *head);
//main starts here
void main()
{
int item;
node *flist,*slist;
clrscr();
//initialization of start node of linked list
flist =NULL;
slist =NULL;
//loop to getting input from the user for first linked list
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter value to insert in a First List: 0 to End ");
scanf("%d",&item);
//check condition to terminate while loop
if(item ==0)
break;
//insert value in a linked list
insert(&flist, item);
}
//loop to getting input from the user for second linked list
while(1)
{
printf("\nEnter value to insert in a Second List: 0 to End ");
scanf("%d",&item);
//check condition to terminate while loop
if(item ==0)
break;
//insert value in a linked list
insert(&slist, item);
}
// print the contents of linked list
printf("\n Content of First List are as follows : ");
printList(flist);
// print the contents of linked list
printf("\n Content of Second List are as follows : ");
printList(slist);
//call the function to reverse the linked list
// and store the address of first node
flist = concat(flist, slist);
//print the contents of concated list
printf("\n Concatenated List contents are as follows : ");
printList(flist);
getch();
}
//function definition to insert node in a linked list
void insert(node &head,int value)
{
node *ptr,*tempnode;
//memory allocation for the new node
ptr = malloc(sizeof(node));
//copy the value to the new node
ptr->data = value;
//set node's pointer to NULL
ptr->nextPtr =NULL;
//if the list is empty
if(*head ==NULL)
//make the first node
*head = ptr;
else
{
//copy the address of first node
tempnode =*head;
//traverse the list using loop until it reaches
//to the last node
while(tempnode->nextPtr !=NULL)
tempnode = tempnode->nextPtr;
//make the new node as last node
tempnode->nextPtr = ptr;
}
}
//function defintion to concat the list
node *concat(node *flist, node *slist)
{
node *ptr;
//check if list is empty
if(flist ==NULL|| slist ==NULL)
{
printf("\none of the lists is empty");
//return the node
returnNULL;
}
else
{
//store first node address
ptr = flist;
//traverse list until last node is not encountered
while(ptr->nextPtr !=NULL)
ptr = ptr->nextPtr;
//store the address of first node of second list
ptr->nextPtr = slist;
}
//return new list
return flist;
}
//function definition to display linked list contents
void printList(node *head)
{
node *ptr;
//stores the address of first node
ptr = head;
//traverse the list until it reaches to the NULL
while(ptr !=NULL)
{
//print the content of current node
printf("%d ", ptr->data);
//goto the next node
ptr = ptr->nextPtr;
}
}
Explanation:In the above code, a structure is created which represents the node of the linked list. Two starting nodes are initialized which contains the address of first node of each list. User is asked to enter the values for first linked list and linked list is created using insert() function by passing the starting pointer and value. This process is repeated to create the second linked list. printList() function is used to display the contents of both lists. Both lists are concatenated using the concat() function by passing the both list. In this function first list is traversed up to last node and then last node pointer points to the first node of second list. Starting node address is returned and stored in the pointer. Finally, concatenated list is displayed using printList() function.
Sample output:
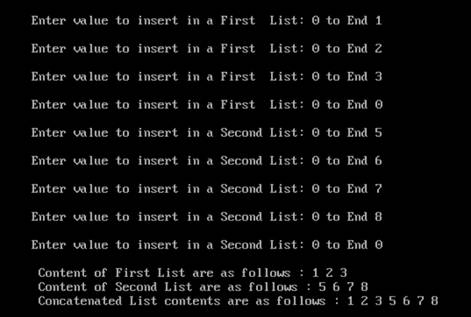
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
C How To Program Plus Mylab Programming With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
- Draw an ERD that represents a book in a library system. Be sure to add relationship types, key attributes, attributes and multiplicity on the ERD.arrow_forward2:21 m Ο 21% AlmaNet WE ARE HIRING Experienced Freshers Salesforce Platform Developer APPLY NOW SEND YOUR CV: Email: hr.almanet@gmail.com Contact: +91 6264643660 Visit: www.almanet.in Locations: India, USA, UK, Vietnam (Remote & Hybrid Options Available)arrow_forwardProvide a detailed explanation of the architecture on the diagramarrow_forward
- hello please explain the architecture in the diagram below. thanks youarrow_forwardComplete the JavaScript function addPixels () to calculate the sum of pixelAmount and the given element's cssProperty value, and return the new "px" value. Ex: If helloElem's width is 150px, then calling addPixels (hello Elem, "width", 50) should return 150px + 50px = "200px". SHOW EXPECTED HTML JavaScript 1 function addPixels (element, cssProperty, pixelAmount) { 2 3 /* Your solution goes here *1 4 } 5 6 const helloElem = document.querySelector("# helloMessage"); 7 const newVal = addPixels (helloElem, "width", 50); 8 helloElem.style.setProperty("width", newVal); [arrow_forwardSolve in MATLABarrow_forward
- Hello please look at the attached picture. I need an detailed explanation of the architecturearrow_forwardInformation Security Risk and Vulnerability Assessment 1- Which TCP/IP protocol is used to convert the IP address to the Mac address? Explain 2-What popular switch feature allows you to create communication boundaries between systems connected to the switch3- what types of vulnerability directly related to the programmer of the software?4- Who ensures the entity implements appropriate security controls to protect an asset? Please do not use AI and add refrencearrow_forwardFind the voltage V0 across the 4K resistor using the mesh method or nodal analysis. Note: I have already simulated it and the value it should give is -1.714Varrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning




