
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.7, Problem 32P
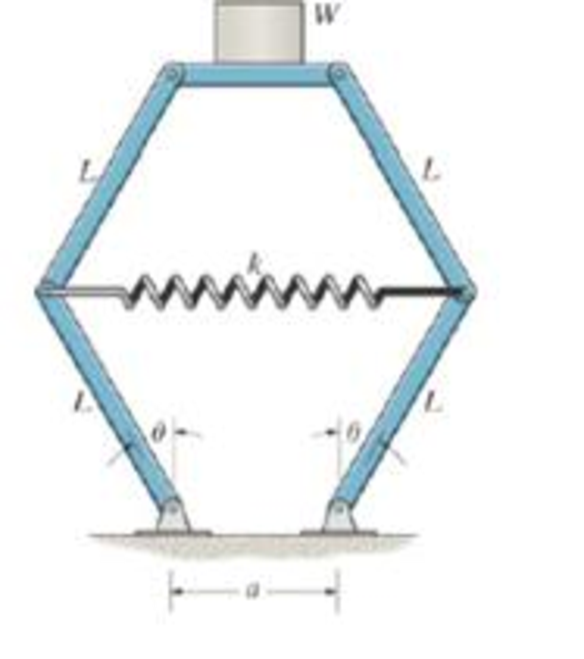
Determine the angle θ for equilibrium when a weight W is supported on the platform. Neglect the weight of the members. What value W would be required to keep the scale in neutral equilibrium when θ = 0°?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
PROBLEM 3.23
3.23 Under normal operating condi-
tions a motor exerts a torque of
magnitude TF at F. The shafts
are made of a steel for which
the allowable shearing stress is
82 MPa and have diameters of
dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20
mm. Knowing that rp = 165
mm and rg114 mm, deter-
mine the largest torque TF
which may be exerted at F.
TF
F
rG-
rp
B
CH
TE
E
1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure
mode and describe the observed plane of failure.
(b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown
in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross
section.
M
M
Fig. 1
(c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis.
(d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.
using the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottom
Chapter 11 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 11.3 - Each link has a mass of 20 kg.Ch. 11.3 - Determine the magnitude of force P required to...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 5FPCh. 11.3 - Determine the angle for equilibrium. The spring...Ch. 11.3 - Each of the four links has a length L and is pin...Ch. 11.3 - The lamp weighs 10 lb.Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 4P
Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 11.3 - It vertical forces P1 = P2 = 30 lb act at C and E...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.3 - if the uniform inks AB and CD each weigh 10 lb....Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 10PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 16PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.3 - The lever is in balance when the load and block...Ch. 11.3 - If the load F weighs 20 lb and the block G weighs...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder...Ch. 11.3 - Determine the horizontal compressive force F...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 26PCh. 11.7 - If the potential function for a conservative...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.7 - Determine the equilibrium positions and...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 30PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 31PCh. 11.7 - Determine the angle for equilibrium when a weight...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 33PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 34PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 35PCh. 11.7 - The bars each have a mass of 3 Kg one the...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 37PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 38PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 39PCh. 11.7 - It is unstretched when the rod assembly is in the...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 41PCh. 11.7 - Determine the weight W2, that is on the pan in...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 43PCh. 11.7 - Determine the steepest grade along which it can...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 45PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 46PCh. 11.7 - Point C is coincident with B when OA is...Ch. 11.7 - If the block has three equal sides of length d,...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 49PCh. 11.7 - Prob. 50RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 51RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 52RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 53RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 54RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 55RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 56RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 57RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 58RPCh. 11.7 - If both spring DE and BC are unstretched when =...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 60RPCh. 11.7 - Prob. 61RPCh. 11.7 - Determine the horizontal force P required to hold...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward
- 1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License