
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100591310
Author: McMurry
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 1.10, Problem 14P
Interpretation Introduction
a) The oxygen atom in dimethyl ether, CH3-O-CH3
Interpretation:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom in dimethyl ether is to be identified. Further its expected geometry is to be stated.Concept introduction:
The electrons present in the valence shell of an atom that are not involved in bonding with other atoms are called nonbonding or lone pair of electrons. In a molecule, if an atom has only single electrons in all hybridized orbitals then the bonds formed by these orbitals will be equivalent in all respects. The molecule will thus have a regular structure. But if the atom contains single electron as well as unshared pairs of electrons in the hybridized orbitals, the orbitals with unshared pair of electrons will tend to occupy as much space as those orbitals involved in bonding. The bond angles will be slightly different from the expected bond angle and hence the molecule will not have a regular geometry.To determine:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on oxygen atom in dimethyl ether and its expected geometry.Interpretation Introduction
b) The nitrogen atom in trimethylamine, CH3-N- [CH3]2
Interpretation:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on nitrogen atom in trimethylamine, is to be identified. Further its expected geometry is to be stated.Concept introduction:
The electrons present in the valence shell of an atom that are not involved in bonding with other atoms are called nonbonding or lone pair of electrons. In a molecule, if an atom has only single electrons in all hybridized orbitals then the bonds formed by these orbitals will be equivalent in all respects. The molecule will thus have a regular structure. But if the atom contains single electron as well as unshared pairs of electrons in the hybridized orbitals, the orbitals with unshared pair of electrons will tend to occupy as much space as those orbitals involved in bonding. The bond angles will be slightly different from the expected bond angle and hence the molecule will not have a regular geometry.To determine:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on nitrogen atom in trimethylamine and its expected geometry.Interpretation Introduction
c) The phosphorus atom in phosphine, PH3
Interpretation:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on phosphorus atom in phosphine is to be identified. Further the expected geometry of phosphorus atom in phosphine is to be stated.Concept introduction:
The electrons present in the valence shell of an atom that are not involved in bonding with other atoms are called nonbonding or lone pair of electrons. In a molecule, if an atom has only single electrons in all hybridized orbitals then the bonds formed by these orbitals will be equivalent in all respects. The molecule will thus have a regular structure. But if the atom contains single electron as well as unshared pairs of electrons in the hybridized orbitals, the orbitals with unshared pair of electrons will tend to occupy as much space as those orbitals involved in bonding. The bond angles will be slightly different from the expected bond angle and hence the geometry of the molecule will be pyramidal.To determine:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on phosphorus atom in phosphine and its expected geometry.Answer:
The phosphorus atom in phosphine has one lone pair of electrons. The phosphorus atom is in sp3 hybridized state with one orbital occupied by lone pairs of electrons. Hence the geometry will be pyramid.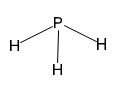
Explanation:
Phosphorus atom has five electrons in its valence shell. It has formed three single bonds with three hydrogen atoms in phosphine. Therefore one lone pair of electrons remains on phosphorus atom. In phosphine the phosphorus atom is in sp3 hybridized state. Three of the sp3 hybrid orbitals containing single electron are utilized for forming three P-H sigma bonds. The fourth sp3 hybrid orbital accommodates the lone pair of electrons and it occupy as much space as a P-H bond does. The H-P-H bond angles deviate slightly from the normal tetrahedral angle. Hence the shape is pyramidal.Conclusion:
The phosphorus atom in phosphine has one lone pair of electrons. The phosphorus atom is in sp3 hybridized state with one orbital occupied by lone pairs of electrons. Hence the structure will be pyramidal.
Interpretation Introduction
d) The sulfur atom in the amino acid methionine
Interpretation:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on sulfur atom in the amino acid methionine is to be identified and to state its expected geometry.Concept introduction:
The electrons present in the valence shell of an atom that are not involved in bonding with other atoms are called nonbonding or lone pair of electrons. In a molecule, if an atom has only single electrons in all hybridized orbitals then the bonds formed by these orbitals will be equivalent in all respects. The molecule will thus have a regular structure. But if the atom contains single electron as well as unshared pairs of electrons in the hybridized orbitals, the orbitals with unshared pair of electrons will tend to occupy as much space as those orbitals involved in bonding. The bond angles will be slightly different from the expected bond angle.To determine:
The number of nonbonding lone pair of electrons present on sulfur atom in the amino acid methionine and its expected geometry.Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
О
δα
HO-
H
-Br
δα
HO--
+
+
-Br
[B]
8+
HO-
-Br
δα
न
1/2
-
51%
+ »
GAY
Organic Reactions Assignment
/26
Write the type of reaction that is occurring on the line provided then complete the reaction. Only include the
major products and any byproducts (e.g. H₂O) but no minor products. Please use either full structural
diagrams or the combination method shown in the lesson. Skeletal/line diagrams will not be accepted.
H3C
1.
2.
CH3
A
Acid
OH
Type of Reaction:
NH
Type of Reaction:
+ H₂O
Catalyst
+ HBr
3.
Type of Reaction:
H3C
4.
Type Reaction:
5. H3C
CH2 + H2O
OH
+
[0]
CH3
Type of Reaction:
6. OH
CH3
HO
CH3 +
Type of Reaction:
7.
Type of Reaction:
+ [H]
humbnai
Concentration Terms[1].pdf ox + New
Home
Edit
Sign in
Comment
Convert
Page
Fill & Sign
Protect
Tools
Batch
+WPS A
Free Trial
Share
Inter Concreting Concentration forms.
Hydrogen peroxide is
a powerful oxidizing agent
wed in concentrated solution in rocket fuels and
in dilute solution as a
hair bleach. An aqueous
sulation of H2O2 is 30% by mass and has
density of #liligime calculat the
Ⓒmolality
⑥mole fraction of
molarity.
20
9.
B. A sample of Commercial Concentrated hydrochloric
ET
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 1.3 - Give the ground-state electron configuration for...Ch. 1.3 - How many electrons does each of the following...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 3PCh. 1.4 - Convert the following representation of ethane,...Ch. 1.4 - What are likely formulas for the following...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 1.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 1.7 - Draw a line-bond structure for propane, CH3CH2CH3....Ch. 1.7 - Convert the following molecular model of hexane, a...Ch. 1.8 - Draw a line-bond structure for propene, CH3CH=CH2....
Ch. 1.8 - Draw a line-bond structure for 1, 3-butadiene,...Ch. 1.8 - Following is a molecular model of aspirin...Ch. 1.9 - Draw a line-bond structure for propyne, CH3C≡CH....Ch. 1.10 - Prob. 14PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 15PCh. 1.12 - Prob. 16PCh. 1.12 - The following molecular model is a representation...Ch. 1.SE - Convert each of the following molecular models...Ch. 1.SE - The following model is a representation of citric...Ch. 1.SE - The following model is a representation of...Ch. 1.SE - The following model is a representation of...Ch. 1.SE - How many valence electrons does each of the...Ch. 1.SE - Give the ground-state electron configuration for...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 24APCh. 1.SE - Prob. 25APCh. 1.SE - Draw an electron-dot structure for acetonitrile,...Ch. 1.SE - Draw a line-bond structure for vinyl chloride,...Ch. 1.SE - Fill in any nonbonding valence electrons that are...Ch. 1.SE - Convert the following line-bond structures into...Ch. 1.SE - Convert the following molecular formulas into...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 31APCh. 1.SE - Oxaloacetic acid, an important intermediate in...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 33APCh. 1.SE - Potassium methoxide, KOCH3, contains both covalent...Ch. 1.SE - What is the hybridization of each carbon atom in...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 36APCh. 1.SE - Prob. 37APCh. 1.SE - What bond angles do you expect for each of the...Ch. 1.SE - Propose structures for molecules that meet the...Ch. 1.SE - What kind of hybridization do you expect for each...Ch. 1.SE - Pyridoxal phosphate, a close relative of vitamin...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 42APCh. 1.SE - Prob. 43APCh. 1.SE - Quetiapine, marketed as Seroquel, is a heavily...Ch. 1.SE - Tell the number of hydrogens bonded to each carbon...Ch. 1.SE - Why do you suppose no one has ever been able to...Ch. 1.SE - Allene, H2C=C=CH2, is somewhat unusual in that it...Ch. 1.SE - Allene (see Problem 1-47) is structurally related...Ch. 1.SE - Complete the electron-dot structure of caffeine,...Ch. 1.SE - Most stable organic species have tetravalent...Ch. 1.SE - A carbanion is a species that contains a...Ch. 1.SE - Divalent carbon species called carbenes are...Ch. 1.SE - There are two different substances with the...Ch. 1.SE - There are two different substances with the...Ch. 1.SE - There are two different substances with the...Ch. 1.SE - Prob. 56APCh. 1.SE - Among the most common over-the-counter drugs you...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forward
- Draw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forward
- Choose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward
- 6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forwardWhat is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY