
Fletcher Fabrication, Inc., produces three products by a joint production process. Raw materials are put into production in Department X, and at the end of processing in this department, three products appear. Product A is sold at the split-off point with no further processing. Products B and C require further processing before they are sold. Product B is processed in Department Y, and product C is processed in Department Z. The company uses the estimated net realizable value method of allocating joint production costs. Following is a summary of costs and other data for the quarter ended June 30.
No inventories were on hand at the beginning of the quarter. No raw material was on hand at June 30. All units on hand at the end of the quarter were fully complete as to processing.
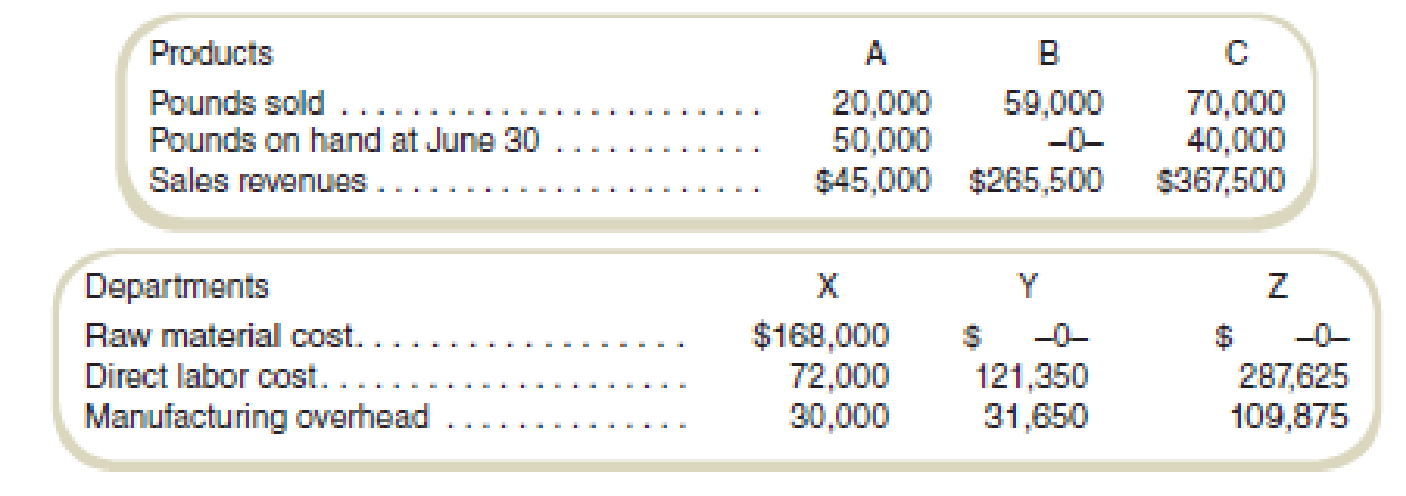
Required
- a. Determine the following amounts for each product: (1) estimated net realizable value used for allocating joint costs, (2) joint costs allocated to each of the three products, (3) cost of goods sold, and (4) finished goods inventory costs, June 30.
- b. Assume that the entire output of product A could be processed further at an additional cost of $6.00 per pound and then sold for $12.90 per pound. What would have been the effect on operating profits if all of product A output for the quarter had been further processed and then sold rather than being sold at the split-off point?
- c. Write a memo to management indicating whether the company should process product A further and why.
a.
Determine the following amounts for each product:
(1) The estimated net realizable value used for allocating joint costs
(2) The joint costs allocated to each of the three products
(3) The cost of goods sold, and
(4) The finished goods inventory costs, June 30.
Explanation of Solution
Joint cost allocation:
Joint cost allocation allocates the common cost of the various departments of the business. IT, accounting and administration services are utilized by various departments so it should be allocated to the various departments based on the usage of the cost.
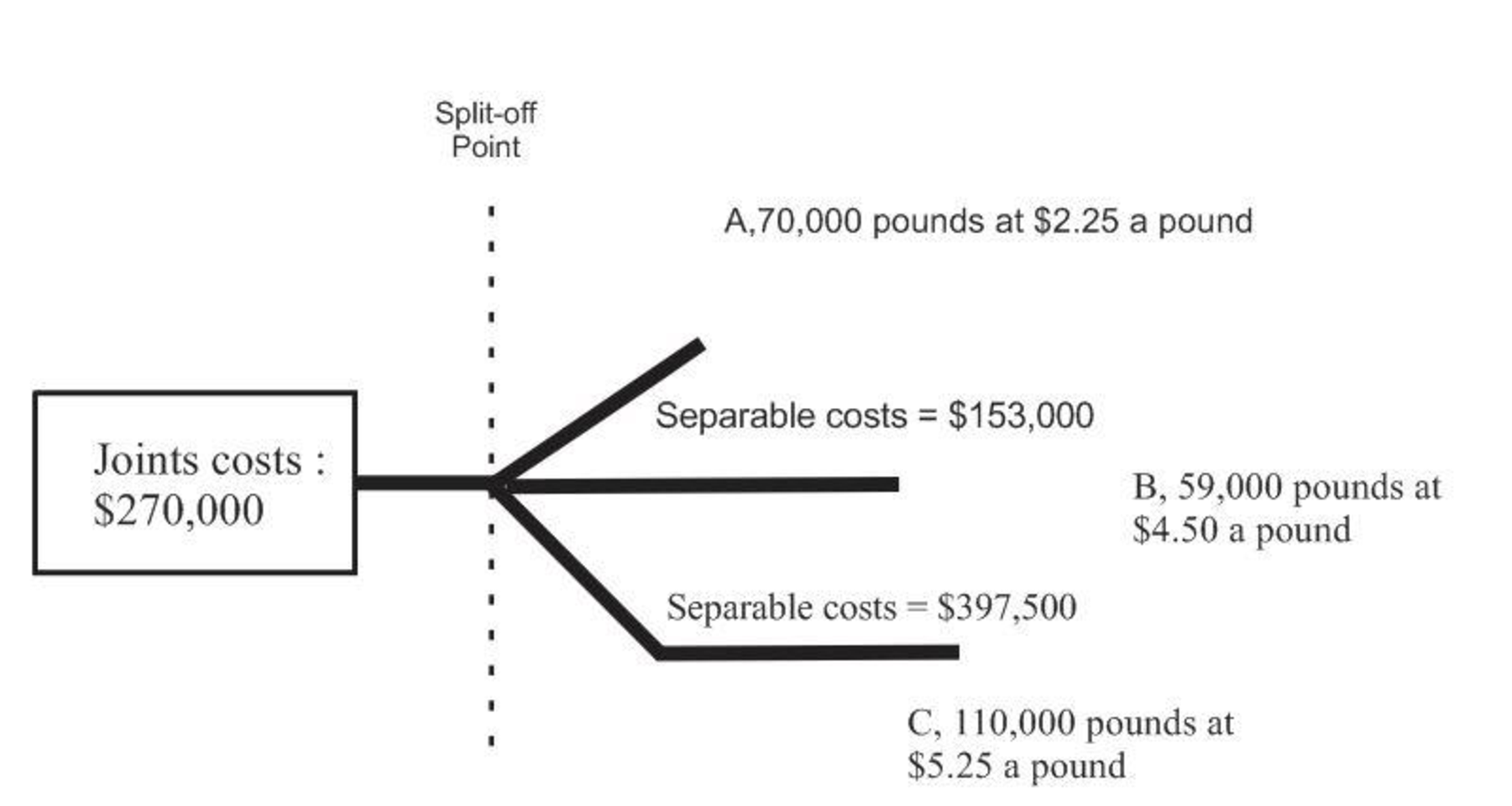
Determine the estimated net realizable value used for allocating joint costs:
1.
| Particulars | Product A | Product B | Product C | Total |
| Selling price per pound: | ||||
| A: | $ 2 | |||
| C: | $ 5 | |||
| Pounds produced: | ||||
| A: | 70,000 | |||
| C: | 110,000 | |||
| Gross sales values | $ 157,500 | $ 265,500 | $ 577,500 | |
| Less: Costs of separate processing: | ||||
| A: | $ - | |||
| B: | $ 153,000 | |||
| C: | $ 397,500 | |||
| Estimated net realizable values at split-off point | $ 157,500 | $ 112,500 | $ 180,000 | $450,000 |
| Percentage of total | 35% | 25% | 40% | 100% |
Table: (1)
2.
Determine the joint costs allocated to each of the three products:
Product A:
Product B:
Product C:
Total joint costs:
Thus, the total amount of the joint cost is $270,000.
3.
| Particulars | Total costs | Cost of goods sold | Ending inventory |
| Product A: | |||
| Joint costs allocated | $ 94,500 | ||
| Sold: | $ 27,000 | ||
| Inventory | $ 67,500 | ||
| Product B: | |||
| Joint costs allocated | $ 67,500 | ||
| Separate processing costs | $ 153,000 | ||
| Total of sales | $ 220,500 | $ 220,500 | $ - |
| Product C: | |||
| Joint costs allocated | $ 108,000 | ||
| Separate processing costs | $ 397,500 | ||
| Total costs of Z | $ 505,500 | ||
| Sold: | $ 321,682 | ||
| Inventory | $ 183,818 | ||
| Total | $ 820,500 | $ 569,182 | $ 251,318 |
Table: (2)
4.
Thus, the cost of the finished goods inventory as on June 30 is $569,182.
b.
Identify the effect on operating profits if all of the product A output had been further processed for the quarter and then sold rather than being sold at the split-off point.
Explanation of Solution
Operating profit:
The operating profit is the excess of total revenues over total expenses after adjusting for depreciation and taxes.
Compute the incremental revenue of further processing:
Compute the incremental costs of further processing:
Compute the effect on operating profits:
Thus, the operating profits have been increased by $325,500 when all of the product A output for the quarter had been further processed and then sold rather than being sold at the split-off point.
c.
Prepare a memo to management indicating whether product A should be processed by the company or not.
Explanation of Solution
Memo
From
ABC
To
XYZ
Re: Whether product A should be continued by the management or not.
Dear XYZ,
I am glad to share that Product A is going to bring an additional operating profit of $325,500. So, here I am explaining to you whether Product A should be continued by the management.
Product A:
The incremental revenue arising out of the product is $745,500, and the incremental costs are $420,000. Thus, it results in an extra profit of $325,500.
Thus, the company should continue with product A because it is going to be profitable if it is further processed.
I hope now you are clear about the information I have provided regarding whether the product should be processed or not. You can revert if you need some more information or clarification on the information provided.
Regards,
ABC
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING BUNDLE
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Management (14th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Macroeconomics
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Foundations of Financial Management
- What is the amount of total assets on these financial accounting question?arrow_forwardOn July 10, Queer Optics sells merchandise on account to Vision Plus (VP) for $5,200, terms 3/10, n/30. On July 14, VP returns merchandise worth $1,200 to Queer Optics. On July 18, VP completely fulfills its obligation to Queer Optics by making a cash payment. What is the amount of cash paid by VP to Queer Optics?arrow_forwardA company reports total liabilities of $2,100 and stockholders' equity of $1,600. What is the amount of total assets?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


