
Concept explainers
Match the vapor pressure diagrams with the solute-solvent combinations and explain your answers.
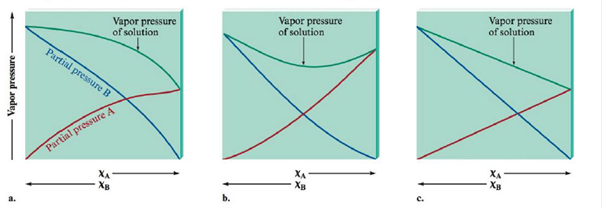
a.  and
and 
b.  and
and 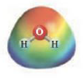
c. 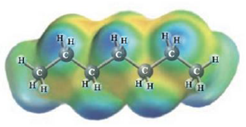 and
and 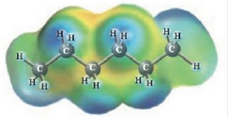
d. 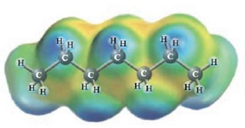 and
and 
(a)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
A Negative deviations from Raoult’s law is the right option for Acetone-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the second diagram match with Acetone and Water
The second diagram illustrates negative variation from Raoult's law. This occurs whilst the solute-solvent connections are stronger than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
These two molecules are named Acetone (
(b)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
A Positive deviation from Raoult’s law is the right option for Ethanol-Water solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the first diagram match with
The first diagram shows positive deviation from Raoult's law. This occurs when the solute-solvent connections are weaker than the connections in pure solvent and pure solute.
These two molecules are named Ethanol (
(c)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
No deviation from Raoult’s law is the correct choice for Heptane-Hexane. solution.
Explanation of Solution
To find the polarity of Heptane and Hexane
Heptane and Hexane
The third diagram illustrates an perfect solution with no difference from Raoult's law. This occurs what time the solute-solvent interactions are concerning equal to the pure solvent and pure solute interactions.
These two molecules are named Heptane (
(d)
Interpretation:
The dissolution of the given following solute and solvent has to be explained using Raoult’s law.
Concept Introduction: Concept introduction:
Raoult's law:
The mole fraction of a solute is related to the vapor pressure of the solution thus,
Answer to Problem 69E
Heptane and Water results in positive deviations from Raoult’s law (the first diagram).
Explanation of Solution
To find: The Heptane Vs Water.
These two molecules are named Heptane (
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemistry (Instructor's)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Physical Universe
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
- For the structure below, draw the resonance structure that is indicated by the curved arrow(s). Be sure to include formal charges. :ÖH Modify the second structure given to draw the new resonance structure. Include lone pairs and charges in your structure. Use the + and - tools to add/remove charges to an atom, and use the single bond tool to add/remove double bonds.arrow_forwardUsing the table of Reactants and Products provided in the Hints section, provide the major product (with the correct stereochemistry when applicable) for questions below by selecting the letter that corresponds to the exact chemical structures for the possible product. OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp A/arrow_forwardUsing arrows to designate the flow of electrons, complete the reaction below and provide a detailed mechanism for the formation of the product OH conc Hydrochloric acid 40°C Temp All chemical structures should be hand drawn on a piece of paper Paragraph BI UAE +varrow_forward
- draw out the following structures plesearrow_forwardDraw everything on a piece of paper outlining the synthesis from acetaldehyde to 2 cyclopentene carboxaldehyde using carbon based reagants with 3 carbons or fewers. Here is the attached image.arrow_forwardManoharan Mariappan, FR.D., 34) Complete the following reaction starting from hex-1-yne proceeding via different substitution reactions forming 2-heptanone. (25 pts). A Sia₂BH H₂O₂ NaOH Br D Mechanism for reaction D - ether-cleavage: 10 B Ph-MgCI, THF H₁₂O+ D HBr (XS) C TsCl, Py CH3-CH2-CH2-ONaarrow_forward
- In the table below, the correct structure for (2R)-3-methylpentan-2-ol (IUPAC name) can be represented by the letter OH OH HE > ' ÕH C B OH D A/ E OHarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: + A Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardWhy is analysing salt content (using Mohr titration) in both regular & salt reduced tomato sauce important?arrow_forward
- In the image below, correctly name the glassware # _P ( Blank 1) and T ( Blank 2). 景 A W Blank # 1 Blank #2 1000 +19 E E D 0 0-0 G H A A K Π 12 R M N S 0-0-arrow_forwardFeedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: CN Δ + A ? NC Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. esc Check 80 MH F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 50 @ # C % 95 € Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C A DII F6 F7 F8 7 * 8 Λ & 6 F9 F10 9 0 4arrow_forwardIncorrect Feedback: Your answer is incorrect. Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: ཤིགས་བྱ རྩ་ཅད་ཀྱིས་༢༩ + Some important notes: A ^ ? • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. E Check 0 لا Save For La ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of All F9 Aarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





