
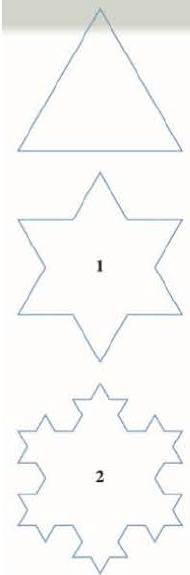
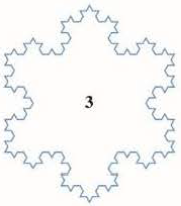
To construct the snowflake curve, start with an equilateral triangle with sides of length 1. Step 1 in the construction is to divide each side into three equal parts, construct an equilateral triangle on the middle part, and then delete the middle part (see the figure). Step 2 is to repeat step 1 for each side of the resulting
- (a) Let sn, ln, and pn represent the number of sides, the length of a side, and the total length of the nth approximating curve (the curve obtained alter step n of the construction), respectively. Find formulas for sn, ln, and pn.
- (b) Show that pn → ∞ as n → ∞.
- (c) Sum an infinite series to find the area enclosed by the snowflake curve.
Note: Parts (b) and (c) show that the snowflake curve is infinitely long but encloses only a finite area.
FIGURE FOR PROBLEM 5
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Multivariable Calculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Beginning and Intermediate Algebra
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Q3// x²y// +xy/ + (x² - ½) y = x³/². اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC Q4// x²y// - (2x+x²)y/ + (2 + x)y = x³. dy 2x+2y+4 = dx 2x-y-3arrow_forward۳/۱ R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B, 18060 msl Kas Sin() 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) kd اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses 5kw 120*50 loca G Rotor input 5 loo kw 6) 1 0.05 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط lookw 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 Q1// Find the solution of QI/Find the solution of Inxy= 7357 x+2y³ y' = xy3arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 msl 180 60 Kd Ka Sin (1) Isin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120*50 1000 6 S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط 100 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2lyl-4y+13y=esinx. Find the general solution of the following equations: " Qly (49) - 16y= 0. 151arrow_forward
- ۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw اذا میرید شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper dy please 04 12=-cosx.y + 2cosx with y(x) = 1 か 'Oy + xlny + xe")dx + (xsiny + xlnx +*dy=0. 01arrow_forward٣/١ R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B, 18060 msl kd Kas Sin (1) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses 5kw 120*50 loca G Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط lookw 7) rotor ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please DC 口 04 on its wheels as shown in figure. The the door is 8 m below the free surface o is located at the center of the d no water leaks an accident and lands at the bottom of the lake 12m high and I m wide, and the top edge of water Determine the hydrostatic force on the discuss if the driver can open the door, if ong person can lift 100 kg, the passenger The door can be approximated as a vertical rec | 279|-|(23+2+12+20=2) AA Find the general solution of the following equations: 11 - 1/4+xy/-(1-x²³)= 0. 2arrow_forward۳/۱ : +0 العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 Le msl 180 60 Kd Ka Sin (1) Isin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120*50 1000 6 S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses: 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 Q1// Find the solution of: ( texty Q1// Find the solution of: '' y' -2y= 22% √y³arrow_forward
- R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-180-60 msl kd Ka, Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw 120 50 G Rotor input 5 loo kw 6) 1 ۳/۱ 0.05 إذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please Find the general solution of the following equations: " yll + 4y = tan2x. Find the general solution of the following equations: 01-24+7=0 T el [A] G ха =T Marrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-18060 msl kd Kasi Sin (1) I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 120 x 50 G loo kw اذا میرید شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Solve the following equations: = dx x²+y2 with y(0) = 1. 7357 Solve the following equations: dy x³+3xy² Q1// = dx 3x²y+y³° 01arrow_forward٣/١ R2X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/3 1 B18060 msl Kd 3 Kol Sin (1) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا میرید شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds 120*50 G looo 1000-950 1000 50:05 Copper losses: 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 (Find the solution of the initial-valued problems: xy' + 2y = x³e* ;y(1) = 0 Q1// Find the solution of: (1) y' + ytqpx = see²x y³arrow_forward
- A fluid has density 800 kg/m³ and flows with velocity v = xi + yj + zk, where x, y, and z are measured in meters, and the components of u are measured in meters per second. Find the rate of flow outward through the part of the paraboloid z = 64 - x² - y² that lies above the xy plane.arrow_forward۳/۱ : +0 العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 Le msl 180 60 Kd Ka Sin (1) Isin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 S = 1000-950 1000 Copper bosses: 5kw Rotor input 5 6 : loo kw 6) 1 0.05 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط 100 7) rotor DC 1000 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please // Find the solution of: |(2xy³ + 4x)y' = x²y² + y² 351 // Find the solution of: (1) 2xyy' = 1+ y² 01 175 T Τ Marrow_forwardFind the flux of the vector field F = (y,−x, 2²) through the helicoid with parameterization r(u, v) = (u cos v, u sin v, v) 0 ≤ u≤ 3, 0 ≤v≤ oriented away from the origin.arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGALAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGALAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





