
1.
Compute the time interest earned for Company E.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio:
Times interest earned quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense.
Compute the time interest earned for Company E.
Therefore, time interest earned by Company E is 1.33.
2.
Compute the time interest earned for Company S.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Times interest earned ratio:
Times interest earned quantifies the number of times the earnings before interest and taxes can pay the interest expense.
Compute the time interest earned for Company S.
Therefore, time interest earned by Company S is 2.0.
3.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 10%, on each company’s net income.
3.
Explanation of Solution
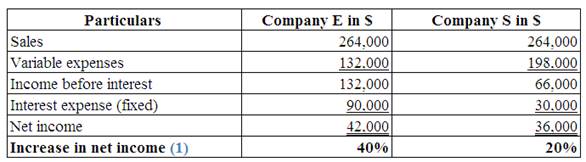
(Table 1)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.10
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
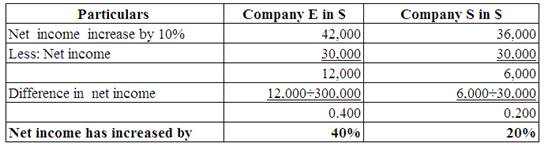
(Table 2)
4.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 40%, on each company’s net income.
4.
Explanation of Solution
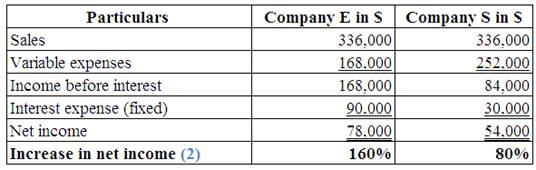
(Table 3)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.40
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
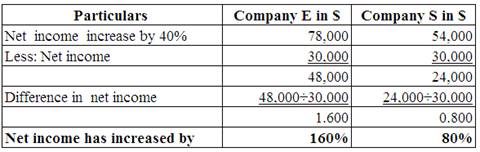
(Table 4)
5.
Identify the effect of increase in sales by 90%, on each company’s net income.
5.
Explanation of Solution
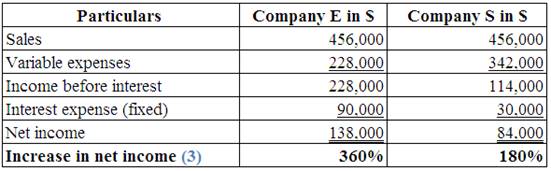
(Table 5)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 1.90
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
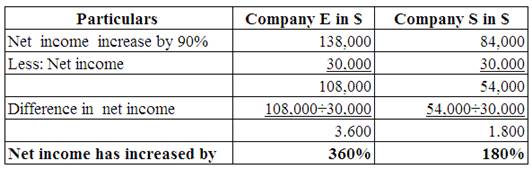
(Table 6)
6.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 20%, on each company’s net income.
6.
Explanation of Solution
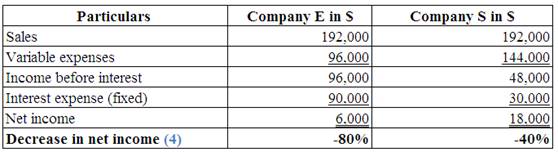
(Table 7)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.80
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
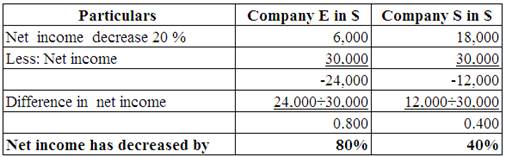
(Table 8)
7.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 50%, on each company’s net income.
7.
Explanation of Solution
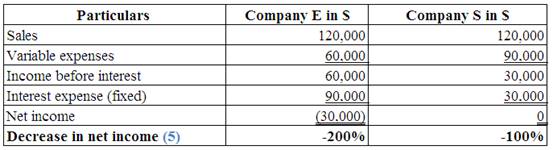
(Table 9)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.50
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
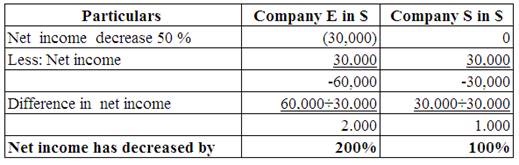
(Table 10)
8.
Identify the effect of decreases in sales by 80%, on each company’s net income.
8.
Explanation of Solution
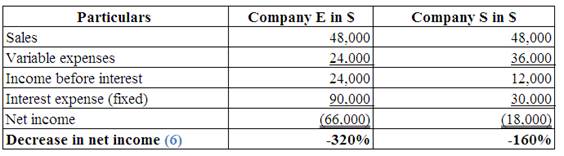
(Table 11)
Note:
Multiply the prior sales by 0.20
Working Note:
Calculate the increase in the value of net income.
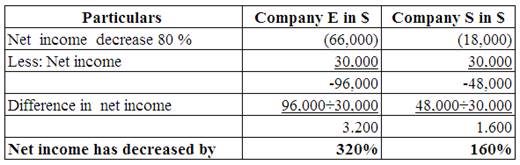
(Table 12)
9.
Comment on the results from requirement 3 through 8 in relation to the fixed-cost strategies of the two companies and the ratio values computed under requirement 1 and 2.
9.
Explanation of Solution
The higher fixed cost strategy of Company E shows the effect of increases and decreases in the value of sales. When sales increase, the value of net income increases. When sales decrease, the value of net income decreases. The higher fixed cost strategy of Company E is indicated by a lower value of the times interest earned ratio.
The higher fixed cost strategy works goods when there is increase in sales. Therefore, Company E enjoys has greater percent increases in the value of its net income. The Company is protected with the lower fixed cost strategy, when there is a decrease in sales level. Company S experiences smaller percent decreases in the value of net income because it has made this choice.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting, Chapters 1-17 - With Access (Looseleaf)
- Depreciation Direct Labor Direct Materials Fixed Costs Overhead Supervision Total Costs Total Fixed Costs Total Variable Costs Variable Costs Units Produced $ Budget Actual 1A to Favorable Unfavorable Neither Favorable nor Unfavorablearrow_forwardWhat is the company's plantwide overhead rate?arrow_forwardCould you help me solve this financial accounting question using appropriate calculation techniques?arrow_forward
- general accounting questionarrow_forwardIsabella Traders reported owner’s equity of $84,000 at the beginning of the year and $143,000 at the end of the year. The owner made no additional investments and withdrew $41,000 during the year. The net income for the year amounted to: A) $100,000 B) $96,000 C) $88,000 D) $86,000arrow_forwardSolve with explanation and accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





