
Concept explainers
Mott Company recently implemented a JIT manufacturing system. After one year of operation, Heidi Burrows, president of the company, wanted to compare product cost under the JIT system with product cost under the old system. Mott’s two products are weed eaters and lawn edgers. The unit prime costs under the old system are as follows:

Under the old manufacturing system, the company operated three service centers and two production departments.

Under the old system, the overhead costs of the service departments were allocated directly to the producing departments and then to the products passing through them. (Both products passed through each producing department.) The overhead rate for the Machining Department was based on machine hours, and the overhead rate for assembly was based on direct labor hours. During the last year of operations for the old system, the Machining Department used 80,000 machine hours, and the Assembly Department used 20,000 direct labor hours. Each weed eater required 1.0 machine hour in Machining and 0.25 direct labor hour in Assembly. Each lawn edger required 2.0 machine hours in Machining and 0.5 hour in Assembly. Bases for allocation of the service costs are as follows:
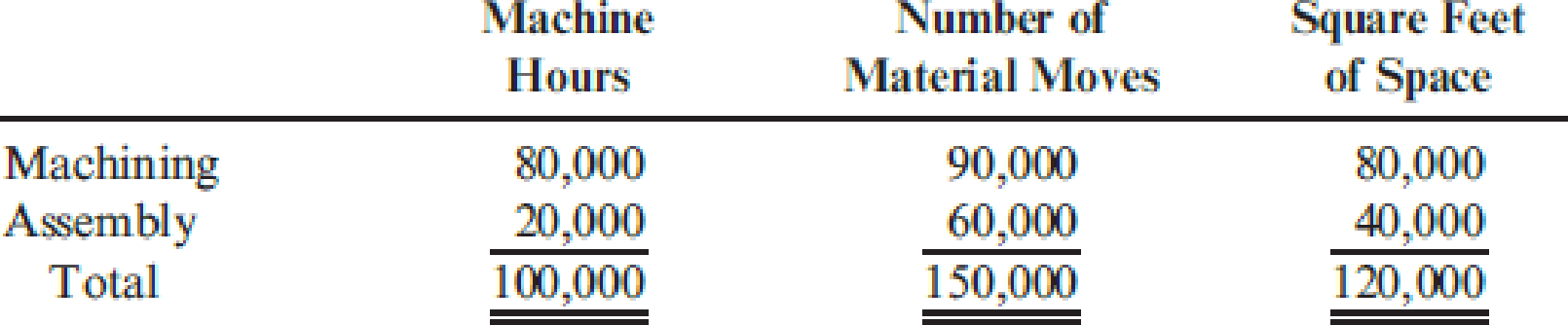
Upon implementing JIT, a manufacturing cell for each product was created to replace the departmental structure. Each cell occupied 40,000 square feet. Maintenance and materials handling were both decentralized to the cell level. Essentially, cell workers were trained to operate the machines in each cell, assemble the components, maintain the machines, and move the partially completed units from one point to the next within the cell. During the first year of the JIT system, the company produced and sold 20,000 weed eaters and 30,000 lawn edgers. This output was identical to that for the last year of operations under the old system. The following costs have been assigned to the manufacturing cells:
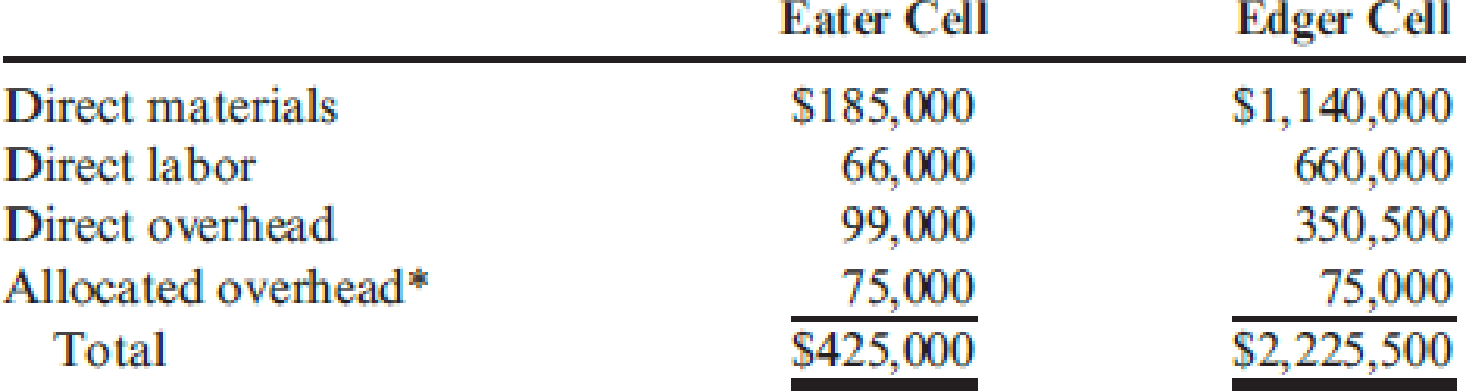
Required:
- 1. Compute the unit cost for each product under the old manufacturing system.
- 2. Compute the unit cost for each product under the JIT system.
- 3. Which of the unit costs is more accurate? Explain. Include in your explanation a discussion of how the computational approaches differ.
- 4. Calculate the decrease in overhead costs under JIT, and provide some possible reasons that explain the decrease.
1.
Calculate the unit cost of each product under old manufacturing system.
Explanation of Solution
Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing system: Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing system is an approach to manufacturing, that eliminates and reduces the non-value-added activities and it concentrates on both product quality and efficiency.
Calculate the unit cost of each product under old manufacturing system as follows:
| Particulars | Eaters | Edgers |
| Direct materials | $12.00 | $45.00 |
| Direct labor | $4.00 | $30.00 |
| Overhead (7) | $10.07 | $20.14 |
| Total | $26.07 | $95.14 |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the allocation ratios for machining and assembly.
| Particulars | Machine hour | Allocation ratio | Material moves | Allocation ratio | Square feet | Allocation ratio |
| Machining | 80,000 | 4/5 | 90,000 | 3/5 | 80,000 | 2/3 |
| Assembly | 20,000 | 1/5 | 60,000 | 2/5 | 40,000 | 1/3 |
| Total | 100,000 | 150,000 | 120,000 |
Table (2)
Note: Formula for allocation ratio is
Working note (2):
Calculate the direct overhead cost of maintenance.
For machining department:
For assembly department:
Working note (3):
Calculate the direct overhead cost of material handling.
For machining department:
For assembly department:
Working note (4):
Calculate the direct overhead cost of building and grounds.
For machining department:
For assembly department:
Working note (5):
Calculate the total direct overhead cost for each department.
| Particulars | Machining | Assembly |
| Direct overhead costs | $280,000 | $175,0000 |
| Add: Direct overhead cost for maintenance (2) | $88,000 | $22,000 |
| Add: Direct overhead cost for material handling (3) | $54,000 | $36,000 |
| Add: Direct overhead cost for building and grounds (4) | $100,000 | $50,000 |
| Total | $522,000 | $283,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (6):
Calculate the direct overhead cost per hour for each department.
For machining department:
For assembly department:
Working note (7):
Calculate the direct overhead cost per unit for each product.
For Eaters:
For Edgers:
2.
Calculate the unit cost of each product under JIT system.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the unit cost of each product under JIT system as follows:
Unit cost of Eaters under JIT:
Unit cost of Edgers under JIT:
3.
Identify the unit cost which is more accurate, and explain the manner in which the computational approaches differ.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the unit cost which is more accurate, and explain the manner in which the computational approaches differ as follows:
Just in time inventory costs are more accurate because,
- The building and ground costs are assigned for activity based approach.
- All costs of company (except the building and grounds) are directly attributable to each product.
The assignment of the company should be measured at the activity based costing method, because the company traces the cost and products based on each activity of the production. Since, both cells (Eaters and Edgers) are dedicated to produce a single product, whatever causal factors that are used to allocate each cell is same as the final product.
The functional based costing system first assigns the cost to each department, and then assigns the cost to the product based on the cost drivers, but the maintenance and materials handing cost is not a unit-based activities.
4.
Ascertain the decrease in overhead costs under just in time method and given some possible reasons.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the decrease in overhead costs under Just in time method and given some possible reasons as follows:
In this case, the overhead cost has been decreased by $205,500 and the decrease in overhead cost is explained by the following factors:
- Usage of interdisciplinary labor,
- Total quality control,
- Decentralization of services and
- Physical organization of the manufacturing cell.
Working note (8):
Calculate the overhead cost under JIT.
Working note (9):
Calculate the Pre-JIT overhead cost.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management
- Louisa Pharmaceutical Company is a maker of drugs for high blood pressure and uses a process costing system. The following information pertains to the final department of Goodheart's blockbuster drug called Mintia. Beginning work-in-process (40% completed) 1,025 units Transferred-in 4,900 units Normal spoilage 445 units Abnormal spoilage 245 units Good units transferred out 4,500 units Ending work-in-process (1/3 completed) 735 units Conversion costs in beginning inventory $ 3,250 Current conversion costs $ 7,800 Louisa calculates separate costs of spoilage by computing both normal and abnormal spoiled units. Normal spoilage costs are reallocated to good units and abnormal spoilage costs are charged as a loss. The units of Mintia that are spoiled are the result of defects not discovered before inspection of finished units. Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Using the weighted-average method, answer the following question: What are the…arrow_forwardQuick answerarrow_forwardChoice???arrow_forward
- On November 30, Sullivan Enterprises had Accounts Receivable of $145,600. During the month of December, the company received total payments of $175,000 from credit customers. The Accounts Receivable on December 31 was $98,200. What was the number of credit sales during December?arrow_forwardPaterson Manufacturing uses both standards and budgets. For the year, estimated production of Product Z is 620,000 units. The total estimated cost for materials and labor are $1,512,000 and $1,984,000, respectively. Compute the estimates for: (a) a standard cost per unit (b) a budgeted cost for total production (Round standard costs to 2 decimal places, e.g., $1.25.)arrow_forwardQuestion: Gujri Place Clock Shop sold a grandfather clock for $2,250 subject to a 9% sales tax. The entry in the general journal will include a credit to Sales for a) $2,250.00 b) $2,092.50 c) $2,452.50. choose the correct optionarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




