
Systematic versus Unsystematic Risk. Consider the following information on Stocks I and II:
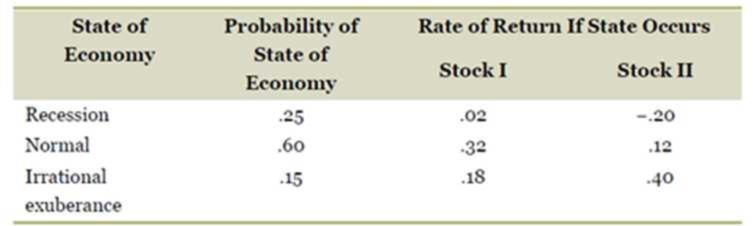
The market risk premium is 7 percent, and the risk-free rate is 4 percent. Which stock has the most systematic risk? Which one has the most unsystematic risk? Which stock is “riskier”? Explain
To determine: The stock that has the most systematic risk and the most unsystematic risk.
Introduction:
Systematic risk refers to the market-specific risk that affects all the stocks in the market.
Unsystematic risk refers to the company-specific risk that affects only the individual company.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The probability of having a recession, normal economy, and irrational exuberance is 0.25, 0.60, and 0.15 respectively. Stock I will yield 2%, 32%, and 18% when there is a recession, normal economy, and irrational exuberance respectively.
Stock II will yield −20%, 12%, and 40% when there is a recession, normal economy, and irrational exuberance respectively. The market risk premium is 7% and the risk-free rate is 4%.
The formula to calculate the expected return on the stock:
Expected returns=[(Possible returns(R1)×Probability(P1))+...+(Possible returns(Rn)×Probability(Pn))]
The formula to calculate the beta of the stock:
E(Ri)=Rf+[E(RM)−Rf]×βi
Where,
E(Ri) refers to the expected return on a risky asset
Rf refers to the risk-free rate
E(RM) refers to the expected return on the market portfolio
βi refers to the beta coefficient of the risky asset relative to the market portfolio
The formula to calculate the standard deviation:
Standarddeviation}=√([(Possible returns(R1)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P1)]+...+[(Possible returns(Rn)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(Pn)])
Compute the expected return on Stock I:
R1 is the returns during the recession. The probability of having a recession is P1. Similarly, R2 is the returns in a normal economy. The probability of having a normal is P2. R3 is the returns in irrational exuberance. The probability of having an irrational exuberance is P3.
Expected returns=[(Possible returns(R1)×Probability(P1))+(Possible returns(R2)×Probability(P2))+(Possible returns(R2)×Probability(P2))]=((0.25)×0.02)+(0.60×0.32)+(0.15×0.18)=(0.005+0.192+0.027)=0.2240
Hence, the expected return on Stock I is 0.2240 or 22.40 percent.
Compute the beta of Stock I:
E(RI)=Rf+[E(RM)−Rf]×βI0.2240=0.04+[0.07]×βI(0.2240−0.04)=0.07βI0.1840.07=βI2.63=βI
Hence, the beta of Stock I is 2.63.
Compute the standard deviation of Stock I:
R1 is the returns during the recession. The probability of having a recession is P1. Similarly, R2 is the returns in a normal economy. The probability of having a normal is P2. R3 is the returns in irrational exuberance. The probability of having an irrational exuberance is P3.
Standarddeviation}=√([(Possible returns(R1)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P1)]+[(Possible returns(R2)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P2)]+[(Possible returns(R3)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P3)])=√[[(0.02−0.2240)2×0.25]+[(0.32−0.2240)2×0.60]+[(0.18−0.2240)2×0.15]]=√((−0.204)2×0.25)+((0.096)2×0.60)+((−0.044)2×0.15)=√(0.041616×0.25)+(0.009216×0.60)+(0.001936×0.15)
=√0.010404+0.0055296+0.0002904=√0.016224=0.1274
Hence, the standard deviation of Stock I is 0.1274 or 12.74%.
Compute the expected return on Stock II:
R1 is the returns during the recession. The probability of having a recession is P1. Similarly, R2 is the returns in a normal economy. The probability of having a normal is P2. R3 is the returns in irrational exuberance. The probability of having an irrational exuberance is P3.
Expected returns=[(Possible returns(R1)×Probability(P1))+(Possible returns(R2)×Probability(P2))+(Possible returns(R2)×Probability(P2))]=((−0.20)×(0.25))+(0.12×0.60)+(0.40×0.15)=(−0.05+0.072+0.06)=0.0820
Hence, the expected return on Stock II is 0.0820 or 8.20 percent.
Compute the beta of Stock II:
E(RII)=Rf+[E(RM)−Rf]×βII0.0820=0.04+[0.07]×βII(0.0820−0.04)=0.07βII0.0420.07=βII0.6=βII
Hence, the beta of Stock II is 0.6.
Compute the standard deviation of Stock II:
R1 is the returns during the recession. The probability of having a recession is P1. Similarly, R2 is the returns in a normal economy. The probability of having a normal is P2. R3 is the returns in irrational exuberance. The probability of having an irrational exuberance is P3.
Standarddeviation}=√([(Possible returns(R1)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P1)]+[(Possible returns(R2)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P2)]+[(Possible returns(R3)−Expected returnsE(R))2× Probability(P3)])=√[[((−0.20)−0.0820)2×0.25]+[(0.12−0.0820)2×0.60]+[(0.40−0.0820)2×0.15]]=√((−0.282)2×0.25)+((0.038)2×0.60)+((0.318)2×0.15)=√(0.079524×0.25)+(0.001444×0.60)+(0.101124×0.15)
=√(0.019881+0.0008664+0.0151686)=√0.035916=0.1895
Hence, the standard deviation of Stock II is 0.1895 or 18.95%.
Interpretation:
The beta refers to the systematic risk of the stock. Stock I has higher beta than Stock II. Hence, the systematic risk of Stock I is higher.
The standard deviation indicates the total risk of the stock. The standard deviation is high for Stock II despite having a low beta. Hence, a major portion of the standard deviation of Stock II is the unsystematic risk. Therefore, Stock II has higher unsystematic risk than Stock I.
To discuss: The riskier Stock among Stock I and Stock II.
Introduction:
Risk refers to the movement or fluctuation in the value of an investment. The movement can be positive or negative. A positive fluctuation in the price benefits the investor. The investor will lose money if the price movement is negative.
Explanation of Solution
The formation of a portfolio helps in diversifying the unsystematic risk. Although, the Stock II has a higher unsystematic risk, it can be diversified completely. However, the beta cannot be eliminated. Hence, the Stock I is riskier than Stock II.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- Could you help explain, what is the complete salary survey analysis, and ensuring the data is relevant and up-to-date? What is the job evaluation and compensation plan? How to ensure the final report is comprehensive, clearly structured, and aligned with the company vision?arrow_forwardThe maturity value of an $35,000 non-interest-bearing, simple discount 4%, 120-day note is:arrow_forwardCarl Sonntag wanted to compare what proceeds he would receive with a simple interest note versus a simple discount note. Both had the same terms: $18,905 at 10% for 4 years. Use ordinary interest as needed. Calculate the simple interest note proceeds. Calculate the simple discount note proceeds.arrow_forward
- What you're solving for Solving for maturity value, discount period, bank discount, and proceeds of a note. What's given in the problem Face value: $55300 Rate of interest: 10% Length of note: 95 days Date of note: August 23rd Date note discounted: September 18th Bank discount rate:9 percentarrow_forwardAll tutor giving incorrect solnarrow_forwardSolve this question and don't use aiarrow_forward
 Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning



