
1.
Calculate the gross profit for each product in total and per square yard.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the gross profit for each product in total and per square yard:
| Product | ||
| Particulars | Commercial | Residential |
| Sales: | ||
| $448,000 | ||
| $150,000 | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Variable cost: | ||
| $280,000 | ||
| $90,000 | ||
| Fixed costs: | ||
| $130,676 | ||
| $9,000 | ||
| Gross profit | $37,324 | $51,000 |
| Gross profit per square yard: | ||
| $1.33 | ||
| $8.50 | ||
Table (1)
2.
Calculate the contribution margin for each product in total and per square yard.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the contribution margin for each product in total and per square yard:
| Product | ||
| Particulars | Commercial | Residential |
| Sales: | ||
| $448,000 | ||
| $150,000 | ||
| Less: Variable cost: | ||
| $280,000 | ||
| $90,000 | ||
| Gross profit | $168,000 | $60,000 |
| Contribution margin per square yard: | ||
| $6.00 | ||
| $10.00 | ||
Table (2)
3 a.
Calculate the following:
- a. Compute the contribution margin per labor hour for each product.
- b. Compute the optimum product mix, on a weekly basis and state the number of square yards of each product that should be produced each week.
- c. Draw a graph for this problem, similar to the solution presented in Exhibit.
3 a.
Explanation of Solution
- a. Compute the contribution margin per labor hour for each product:
| Product | ||
| Particulars | Commercial | Residential |
| Contribution margin per square yard (A) | $6 | $10 |
| Labor hours per square yard (B) | 0.12 | 0.18 |
| Contribution margin per labor hour | $50 | $55.56 |
Table (3)
- b. Compute the optimum product mix, on a weekly basis and state the number of square yards of each product that should be produced each week.
| Product | Hours (a) | Square yards |
| Residential: | ||
| 1,440 | 8,000 | |
| Commercial: at 0.12 hour per square yard | ||
| $3,160 | $26,333 |
Table (4)
- c. Draw a graph for this problem, similar to the solution presented in Exhibit.
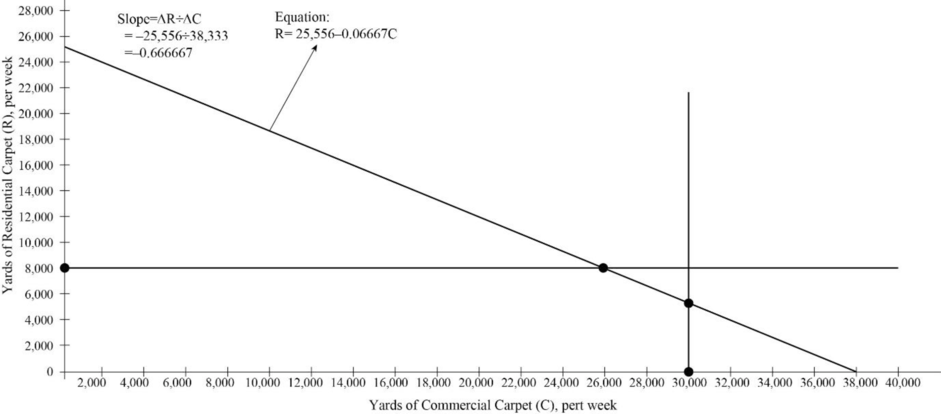
Figure (1)
4.
State the conceptual lesson that is associated with requirements 1 to 3.
4.
Explanation of Solution
- The major conceptual lesson is that neither of the profit measures described in requirement 1 or 2 is useful for ascertaining the short-term optimum product mix in the presence of resource constraints.
- Thus, for this purpose, it is essential to distribute available labor hours on the basis of the contribution margins expressed on a per-labor-hour basis.
5.
Indicate the primary role of the
5.
Explanation of Solution
The following are the major role of the management accountant in the given context:
- To work with engineers for calculating the labor-hour consumption of each product, and
- To develop accurate estimates of the contribution margins for each product and.
Together, these inputs permits to provide an optimum short-term product mix.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBOOK COST MANAGEMENT
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardThe company produced 6,200 units in May using 15,900 liters of direct material and 3,400 direct labor hours.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





