![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)](https://www.bartleby.com/isbn_cover_images/9781305863170/9781305863170_largeCoverImage.jpg)
Diethylhydrazine reacts with iodine according to the following equation:
Â
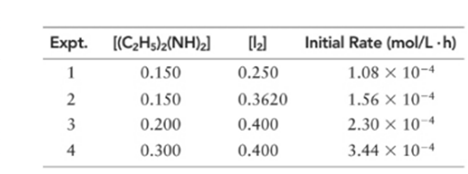
(a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to diethylhydrazine, iodine, and overall?
(b) Write the rate expression of the reaction.
(c) Calculate k for the reaction.
(d) What must [(C2H5)2] be so that the rate of the reaction is
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the order of reaction with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2, I2 and overall for the following reaction:
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Order of given reaction:
With respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 =1
With respect to I2 =1
Overall =2.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Here the chemical reaction is:
![OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months), Chapter 11, Problem 28QAP](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305079373/Chapter-11/images/html_79373-11-28qap_1.png)
Let’s assume the reaction to be ‘t’ order with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 and ‘y’ order with respect to I2.
Then, rate law for experiment 1, 2, 3 and 4 in above reaction will be;
Dividing (1) by (2) to get value of ‘y’.
Thus, order with respect to I2 is 1
Dividing (3) by (4) to get value of ‘t’.
Thus, order with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 1.
And the order of reaction will be:
Thus, overall order of reaction is 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
To write the rate expression for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Rate law expression for above reaction will be;
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Order of reaction with respect to (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 = 1
Order of reaction with respect to I2 = 1
Let the rate constant be ‘k’.
Then, rate law expression for above reaction will be;
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate constant and its unit for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Rate constant is
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Writing rate law for experiment 1 in above reaction will be;
Hence, the rate constant is
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 28QAP
Concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 0.347 mol/L
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Rate law expression for above reaction:
Here we have:
[(C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 ]= let it ‘y’ M
[I2 ] = 0.500 M
Rate constant =
Rate of reaction = 5.00×10-4 mol/L.h
Plugging values in rate law as:
Hence, the concentration of (C2 H5 )2 (NH)2 is 0.347 mol/L
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 4 terms (24 months)
- Using reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: 2NO2 (g) = N2O4(g) AGº = -5.4 kJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 4.53 atm of dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) at 279. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2O4 tend to rise or fall? Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding NO2? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding NO2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2O4 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to '2' rise by adding NO2? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of NO 2 needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 00 rise ☐ x10 fall yes no ☐ atm G Ar 1arrow_forwardWhy do we analyse salt?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H H CH3OH, H+ H Select to Add Arrows H° 0:0 'H + Q HH ■ Select to Add Arrows CH3OH, H* H. H CH3OH, H+ HH ■ Select to Add Arrows i Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStaxChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





