
a)
Record the given events in a horizontal statements model. In the
a)
Explanation of Solution
Record the given events in a horizontal statements model.
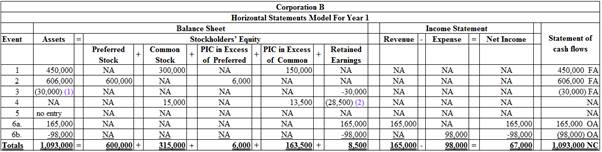
Table (1)
Note:
- 1) In the Event 5, Corporation B issued 2 for 1 split on the shares of outstanding common stock. There is no financial transaction is taken place. There is an increase in number of shares issued and outstanding but no effect on the amount. Thus, this event will not affect the
balance sheet , income statement, and statement of cash flows. - 2) Event 7 is refers about the closing entries, thus, it does not affect the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows.
- 3) PIC stands for paid-in-capital.
Working note:
Calculate the cash dividend amount for 5%
Corporation B issued 6,000 shares of $100 par, 5% preferred stock. Dividend on one preferred stock is $5
Calculate the stock dividend:
Corporation B issued 30,000 shares no par common stock. 5% of the stock dividend issued on no par common stock. On the date of dividend declaration market price per share is $19.
Therefore 1,500 shares are issued as a stock dividend.
On the date of dividend declaration market price per share is $19. The amount of stock dividend is recorded in the balance sheet is $28,500
b)
Record the year 1 transactions in general journal form and post them to T-accounts.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Record the year 1 transactions in general journal form.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation |
Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| 1. | Cash | 450,000 | ||
| Common Stock, No Par | 300,000 | |||
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, common stock | 150,000 | |||
| (To record issue of common stock ) | ||||
| 2. | Cash | 606,000 | ||
| Preferred Stock, $20 Par | 600,000 | |||
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, preferred stock | 6,000 | |||
| (To record issue of preferred stock) | ||||
| 3. | Dividends (1) | 30,000 | ||
| Cash | 30,00 | |||
| (To record cash dividend) | ||||
| 4. | 28,500 | |||
| Common Stock, No Par | 15,000 | |||
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, common stock | 13,500 | |||
| (To record stock dividend) | ||||
| 5. | No | |||
| 6a. | Cash | 165,000 | ||
| Service Revenue | 165,000 | |||
| (To record service revenue) | ||||
| 6b. | Operating Expenses | 98,000 | ||
| Cash | 98,000 | |||
| (To record operating expense) | ||||
| 7. | Service Revenue | 165,000 | ||
| Operating Expenses | 98,000 | |||
| Dividends | 30,000 | |||
| Retained Earnings | 37,000 | |||
| (To record closing entries for service revenue, operating expenses, and dividends) |
Table (2)
| Cash | |||
| Beginning Balance | 0 | ||
| 1 | 450,000 | 3. | 30,000 |
| 2 | 606,000 | 6b. | 98,000 |
| 6a. | 165,000 | ||
| Ending Balance | 1,093,000 | ||
| Retained earnings | ||||
| 4. | 28,500 | 7. | 37,000 | |
| Ending Balance | 8,500 | |||
| Preferred stock | |||
| 2. | 600,000 | ||
| Ending Balance | 600,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| 1. | 300,000 | ||
| 4. | 15,000 | ||
| Ending Balance | 315,000 | ||
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, preferred stock | |||
| 2. | 6,000 | ||
| Ending Balance | 6,000 | ||
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, common stock | |||
| 1. | 150,000 | ||
| 4. | 13,500 | ||
| Ending Balance | 163,500 | ||
| Dividends | |||
| 3. | 30,000 | 7. | 30,000 |
| Ending Balance | 0 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| 7. | 165,000 | 6a. | 165,000 |
| Ending Balance | 0 | ||
| Operating expenses | |||
| 6b. | 98,000 | 7. | 98,000 |
| Ending Balance | 0 | ||
c)
Prepare the
c)
Explanation of Solution
Stockholders’ equity:
The claims of owners on a company’s resources, after the liabilities are paid off, are referred to as stockholders’ equity. Two main components of stockholders’ equity are paid-in capital and retained earnings.
Preferred stock: The stock that provides a fixed amount of return (dividend) to its stockholder before paying dividends to common stockholders is referred as preferred stock.
Common stock: These are the ordinary shares that a corporation issues to the investors in order to raise funds. In return, the investors receive a share of profit from the profits earned by the corporation in the form of dividend.
Stockholders’ Equity Section: It is refers to the section of the balance sheet that shows the available balance of each stockholder’s equity account as on reported date at the end of the financial year.
Retained earnings: Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth. In other words, Accumulated amount of all net income less the accumulated amount of dividends declared till date is known as retained earnings.
Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet at the end of Year 1.
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Preferred Stock, $100 par value, 5%, 6,000 shares issued and outstanding |
$600,000 | |
| Common Stock, no par value, 63,000 shares issued and outstanding |
315,000 | |
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, preferred stock | 6,000 | |
| Paid-in-capital in excess of par, common stock | 163,500 | |
| Total Paid-In Capital | $1,084,500 | |
| Retained Earnings | 8,500 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $1,093,000 |
Table (3)
Therefore, at the end of the Year 1, Corporation B’s total stockholders’ equity is $1,093,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





