![OWLv2 for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/compass-isbn-assets/textbook_empty_images/large_textbook_empty.svg)
When nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide, the following reaction occurs.
Â
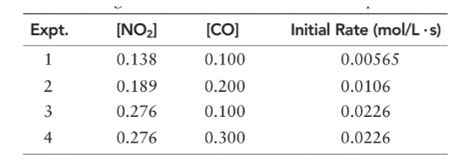
(a) What is the order of the reaction with respect to NO2, CO, and overall?
(b) Write the rate expression of the reaction.
(c) Calculate k for the reaction.
(d) When
(a)
Interpretation:
To determine the order of reaction with respect to BF3, NH3 and overall for the following reaction:
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 26QAP
Order of given reaction
With respect to NO2 =2
With respect to CO =0
Overall = 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Here the chemical reaction is:
![OWLv2 for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months), Chapter 11, Problem 26QAP](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781305079373/Chapter-11/images/html_79373-11-26qap_1.png)
Let’s assume the reaction to be ‘t’ order with respect to NO2 and ‘y’ order with respect to CO.
Then, rate law for experiment 1 in above reaction will be;
And, rate law for experiment 3 in above reaction will be;
Divide (1) by (2) to get value of ‘t’.
Thus, order with respect to CO is ZERO.
Now writing rate law for experiment 3 in above reaction will be;
And, rate law for experiment 4 in above reaction will be;
Divide (3) by (4) to get value of ‘y’.
Thus, order with respect to CO is ZERO.
And the order of reaction will be:
Thus, overall order of reaction is 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
To write the rate expression for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 26QAP
Rate law expression for above reaction will be;
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Order of reaction with respect to NO2 = 2
Order of reaction with respect to CO = 0
Let the rate constant be ‘k’.
Then, rate law expression for above reaction will be;
(c)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate constant for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 26QAP
Rate constant for given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Writing rate law for experiment 1 in above reaction will be;
Hence, the rate constant is
(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the rate of reaction at given concentration of reactants.
Concept introduction:
Rate of a chemical reaction: It tells us about the speed at which the reactants are converted into products.
Mathematically, rate of reaction is directly proportional to the product of concentration of each reactant raised to the power equal to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Let’s say we have a reaction:
Answer to Problem 26QAP
Rate of reaction for given reaction at given conditions is
Explanation of Solution
Here the chemical reaction is:
Rate law expression for above reaction:
Here we have:
[NO2 ]= 0.421 M
[CO] = 0.816 M
Rate constant = 0.297 L/mol.s
Plugging values in rate law as:
Hence, the rate of reaction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
OWLv2 for Masterton/Hurley's Chemistry: Principles and Reactions, 8th Edition, [Instant Access], 1 term (6 months)
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
- 0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward5.arrow_forward9arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





