
(a)
To Discuss:
A 30-year maturity bond making annual coupon payments with a coupon rate of 12% has duration of 11.54 years and convexity of 192.4. The bond currently sells at a yield to maturity of 8%.
To use a financial calculator or spreadsheet to find the price of the bond if its yield to maturity falls to 7%.
Introduction:
When specified payments are made by the issuer to the holder for a given period of time due to an obligation created by a security,then that security is known as Bond.The amount the holder will receive on maturity along with the coupon rate which is also known as the interest rate of the bond is known as the face value of the bond.The discount rate due to which the present payments from the bond become equal to its price i.e. it is the average
The time taken by the bond to change based on the interest rate changes is displayed by Convexity. Duration measures approximately a
Answer to Problem 26PS
Price of Bond using a financial calculator if yield to maturity falls to 7% is 1620.45.
Explanation of Solution
Price of the bond when the yield to maturity is 8% using a financial calculator can be calculated as below:
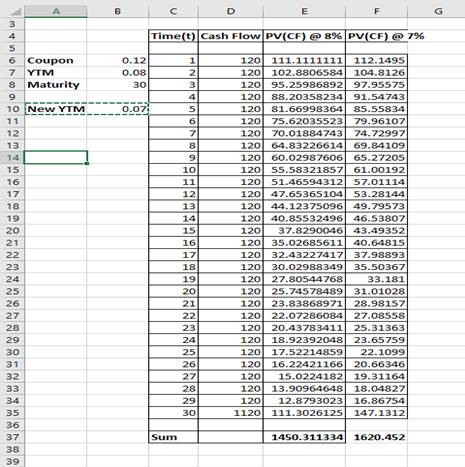
So, the price of the bond with 8% yield is 1450.31.
So, the price of the bond with 7% yield is 1620.45.
(b)
To Discuss:
A 30-year maturity bond making annual coupon payments with a coupon rate of 12% has duration of 11.54 years and convexity of 192.4The bond currently sells at a yield to maturity of 8%.
To predict the price using the duration rule.
Introduction:
When specified payments are made by the issuer to the holder for a given period of time due to an obligation created by a security, then that security is known as Bond. The amount the holder will receive on maturity along with the coupon rate which is also known as the interest rate of the bond is known as the face value of the bond. The discount rate due to which the present payments from the bond become equal to its price i.e. it is the average rate of return which a holder can expect from a bond, is known as Yield to Maturity.
The time taken by the bond to change based on the interest rate changes are displayed by Convexity.
Duration measures approximately a bond's price sensitivity to interest rates changes.
Answer to Problem 26PS
Price of Bond using the duration rule if yield to maturity falls to 7% is 1605.28.
Explanation of Solution
The price of the bond with 8% yield is 1450.31.
Price of the Bond using the duration rule, if yield to maturity falls to 7%:
Predicted Price change =
=
=154.97
Predicted new price=1450.31+154.97=1605.28
(c)
To Discuss:
A 30-year maturity bond making annual coupon payments with a coupon rate of 12% has duration of 11.54 years and convexity of 192.4.The bond currently sells at a yield to maturity of 8%.
To predict the price using the duration with convexity rule.
Introduction:
When specified payments are made by the issuer to the holder for a given period of time due to an obligation created by a security,then that security is known as Bond.The amount the holder will receive on maturity along with the coupon rate which is also known as the interest rate of the bond is known as the face value of the bond.The discount rate due to which the present payments from the bond become equal to its price i.e. it is the average rate of return which a holder can expect from a bond,is known as Yield to Maturity.
The time taken by the bond to change based on the interest rate changes is displayed by Convexity. Duration measures approximately a bond's price sensitivity to interest rates changes.
Answer to Problem 26PS
Price of Bond using the duration with convexity rule if yield to maturity falls to 7% is 1619.23.
Explanation of Solution
So, the price of the bond with 8% yield is 1450.31.
Price of the Bond using Duration-with-Convexity Rule, if yield to maturity falls to 7%:
Predicted price change =
=
=168.92
Predicted new price=1450.31+168.92=1619.23
(d)
To Discuss:
A 30-year maturity bond making annual coupon payments with a coupon rate of 12% has duration of 11.54 years and convexity of 192.4. The bond currently sells at a yield to maturity of 8%.
To determine the percent error for each rule and to conclude about the accuracy of the two rules.
Introduction:
When specified payments are made by the issuer to the holder for a given period of time due to an obligation created by a security,then that security is known as Bond.The amount the holder will receive on maturity along with the coupon rate which is also known as the interest rate of the bond is known as the face value of the bond.The discount rate due to which the present payments from the bond become equal to its price i.e. it is the average rate of return which a holder can expect from a bond,is known as Yield to Maturity.
The time taken by the bond to change based on the interest rate changes is displayed by Convexity. Duration measures approximately a bond's price sensitivity to interest rates changes.
Answer to Problem 26PS
The percentage error of duration rule is -.98% and percentage error of duration with convexity rule is -.075%.
Conclusion: The duration-with-convexity rule provides more accurate approximations tothe true change in price.
Explanation of Solution
Percent error for duration rule =
= -0.0094
= -0.94%
Percent error for duration with convexity rule=
= -0.00075
= -0.075%
The duration-with-convexity rule provides more accurate approximations to
the true change in price.
Conclusion: The percentage error using convexity with duration is less than one-tenth the error using only duration to estimate the price change.
(e)
To Discuss:
A 30-year maturity bond making annual coupon payments with a coupon rate of 12% has duration of 11.54 years and convexity of 192.4The bond currently sells at a yield to maturity of 8%.
To repeat the analysis if the bond's yield to maturity increases to 9% and to determine whether the conclusions about the accuracy of the two rules with parts (a)-(d) were consistent.
Introduction:
When specified payments are made by the issuer to the holder for a given period of time due to an obligation created by a security,then that security is known as Bond.The amount the holder will receive on maturity along with the coupon rate which is also known as the interest rate of the bond is known as the face value of the bond.The discount rate due to which the present payments from the bond become equal to its price i.e. it is the average rate of return which a holder can expect from a bond,is known as Yield to Maturity.
The time taken by the bond to change based on the interest rate changes is displayed by Convexity. Duration measures approximately a bond's price sensitivity to interest rates changes.
Answer to Problem 26PS
The conclusions about the accuracy of the two rules with parts (a)-(d) were consistent on repeating the analysis if the bond's yield to maturity increases to 9%.
Explanation of Solution
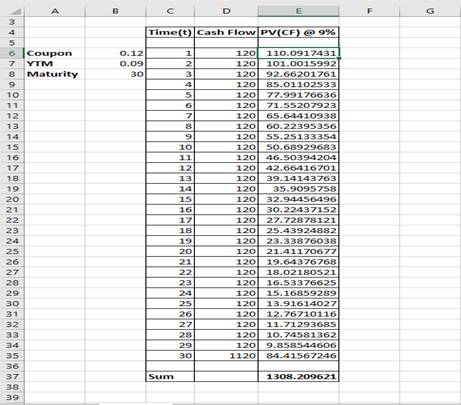
So, the price of the bond with 9% yield is 1308.21.
Price of the Bond using the duration rule, if yield to maturity rises to 9%:
Predicted Price change =
=
=-154.97
Predicted new price=1450.31-154.97
=1295.34
Percent error=
= -0.0098
= -0.98%
Price of the Bond using Duration-with-Convexity Rule, if yield to maturity rises to 9%:
Predicted price change =
=
= -141.02
Predicted new price=1450.31-141.02=1309.29
Percent error=
=0.00083
=0.083%
The percentage error using convexity with duration is less than one-tenth the error using only duration to estimate the price change.
The previous conclusion about the duration with convexity rule being more accurate is consistent with parts (a) - (d) if the bond's yield to maturity rises to 9%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIALS OF INVESTMENTS
- Dont answer i will unhelpful with incorrect values . please comment i will write values.arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? explain the part of finance.arrow_forwardPfizer Pharmecuticals has a $21,000 par value bond outstanding that pays 10 percent annual interest. The current yield to maturity on such bonds in the market is 13 percent. Compute the price of the bonds for the following maturity dates: a. 30 years b. 15 yearsarrow_forward
- Purina Pet Food earned $74 million last year and paid out 20 percent of earnings in dividends. a. By how much did the company's retained earnings increase? b. With 36 million shares outstanding and a stock price of $18, what was the dividend yield?arrow_forwardProfessor Brown has just retired after 25 years with Jessup University. Her total pension funds have an accumulated value of $504,000, and her life expectancy is 25 more years. Her pension fund manager assumes he can earn a 9 percent return on her assets. What will be her yearly annuity for the next 25 years?arrow_forwardCaroline Moore has a contract in which she will receive the following payments for the next four years: $10,000, $11,000, $9,000, and $8,000. She will then receive an annuity of $13,000 a year from the end of the 4th through the end of the 10th year. The appropriate discount rate is 11 percent. What is the percent value of all future payments?arrow_forward
- Nick Weber wants to have $120,000 at the end of 10 years, and his only investment outlet is an 8 percent long-term certicate of deposit (compounded annually). With the certificate of deposit, he made an initial investment at the beginning of the year year. How much does Nick need to deposit to get the $120,000 at the end of 10 years. a. What amount could Nick pay at the end of each year annually for 10 years to achieve this same objective?arrow_forwardHigh Hand Nursery has total assests of $900,000, current liabilities of $202,000, and long-term liabilities of $104,000. There is $90,000 in preferred stock outstanding. Twenty thousand shares of common stock have been issued. a. Compute book value (net worth) per share. b. If there is $40,000 in earnings available to common stockholders for dividends, and the firm's stock has a P/E of 22 times earnings per share, what is the current price of the stock? c. What is the ratio of market value per share to book value per share?arrow_forwardNeed the WACC % WACC and Optimal Capital Structure F. Pierce Products Inc. is considering changing its capital structure. F. Pierce currently has no debt and no preferred stock, but it would like to add some debt to take advantage of the tax shield. Its investment banker has indicated that the pre-tax cost of debt under various possible capital structures would be as follows: Market Debt-to-Value Ratio (wd) Market Equity-to-Value Ratio (ws) Market Debt-toEquity Ratio (D/S) Before-Tax Cost ofDebt (rd) 0.0 1.0 0.00 6.0 % 0.10 0.90 0.1111 6.4 0.20 0.80 0.2500 7.0 0.30 0.70 0.4286 8.2 0.40 0.60 0.6667 10.0 F. Pierce uses the CAPM to estimate its cost of common equity, rs, and at the time of the analaysis the risk-free rate is 5%, the market risk premium is 7%, and the company's tax rate is 25%. F. Pierce estimates that its beta now (which is "unlevered" because it currently has no debt) is 1.4. Based on this information, what…arrow_forward
- Ned's Co. has an average collection period of 45 days and an operating cycle of 130 days. It has a policy of keeping at least $10 on hand as a minimum cash balance, and has a beginning cash balance for the first quarter of $20. Beginning receivables for the quarter amount to $35. Sales for the first and second quarters are expected to be $110 and $125, respectively, while purchases amount to 80% of the next quarter's forecast sales. The accounts payable period is 90 days. What are the cash disbursements for the first quarter? Question 4 options: $92 $88 $76 $100 $110arrow_forwardLiberal credit terms for customers is associated with a restrictive short-term financial policy. Question 3 options: True Falsearrow_forwardAn accounts payable period decrease would increase the length of a firm's cash cycle. Consider each in isolation. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





