
Economic rents Taxes are a cost, and, therefore, changes in tax rates can affect consumer prices, project lives, and the value of existing firms. The following problem illustrates this. It also illustrates that tax changes that appear to be “good for business” do not always increase the value of existing firms. Indeed, unless new investment incentives increase consumer demand, they can work only by rendering existing equipment obsolete.
The manufacture of bucolic acid is a competitive business. Demand is steadily expanding, and new plants are constantly being opened. Expected cash flows from an investment in a new plant are as follows:
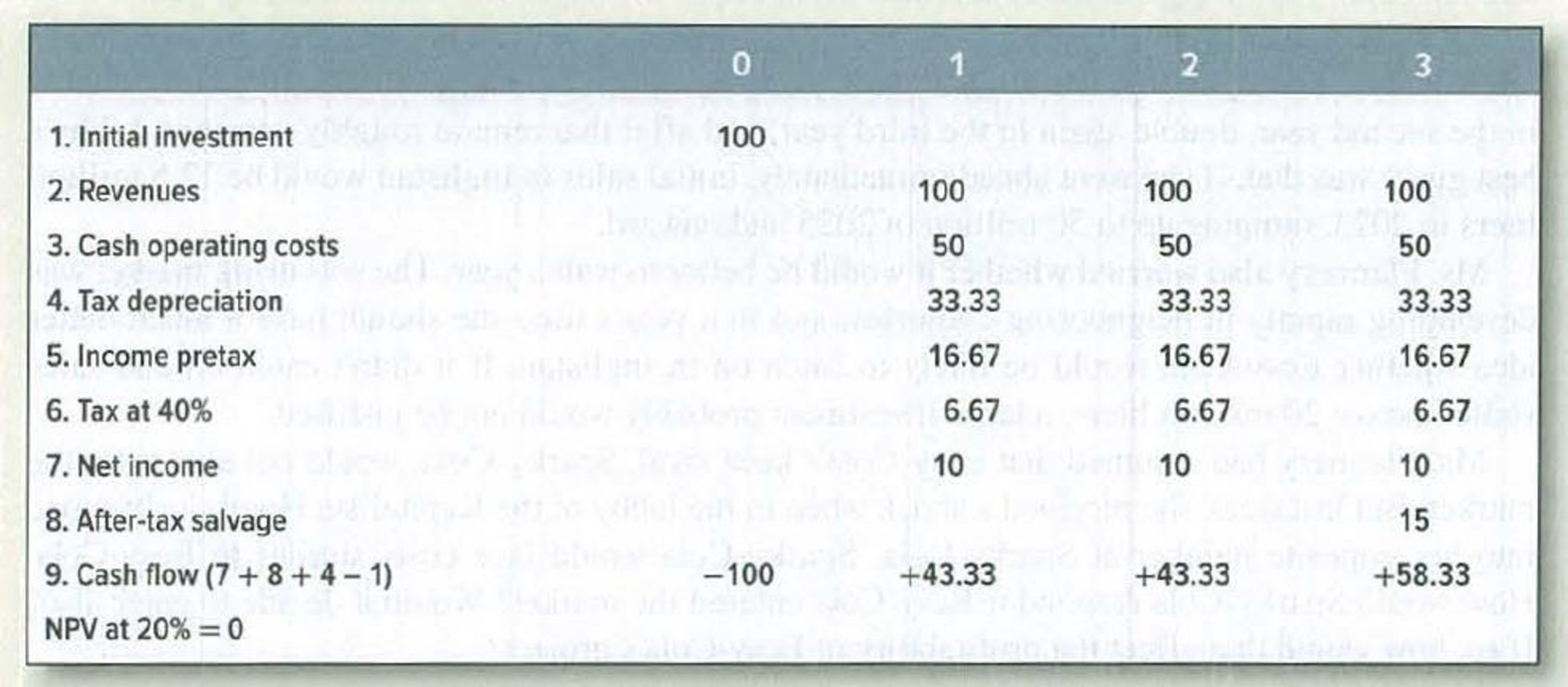
Assumptions:
- 1. Tax depreciation is straight-line over three years.
- 2. Pretax salvage value is 25 in year 3 and 50 if the asset is scrapped in year 2.
- 3. Tax on salvage value is 40% of the difference between salvage value and
depreciated investment. - 4. The cost of capital is 20%.
- a. What is the value of a one-year-old plant? Of a two-year-old plant?
- b. Suppose that the government now changes tax depreciation to allow a 100% writeoff in year 1. How does this affect the value of existing one- and two-year-old plants? Existing plants must continue using the original tax depreciation schedule.
- c. Would it now make sense to scrap existing plants when they are two rather than three years old?
- d. How would your answers change if the corporate income tax were abolished entirely?
a)
To determine: values of one year old plant and two year old plant.
Explanation of Solution
Here, value in the sense, present value.
Calculation of present value of one-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $76.62.
Calculation of present value of two-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $48.61.
b)
To determine: Effect of government on taxes on one and two year old plant and existing plants should continue using the schedule of original tax depreciation.
Explanation of Solution
Given the industry is competitive, the investments in new plant producing the product must yields zero NPV.
Calculation of Revenues (R) at which the NPV of new plant is zero:
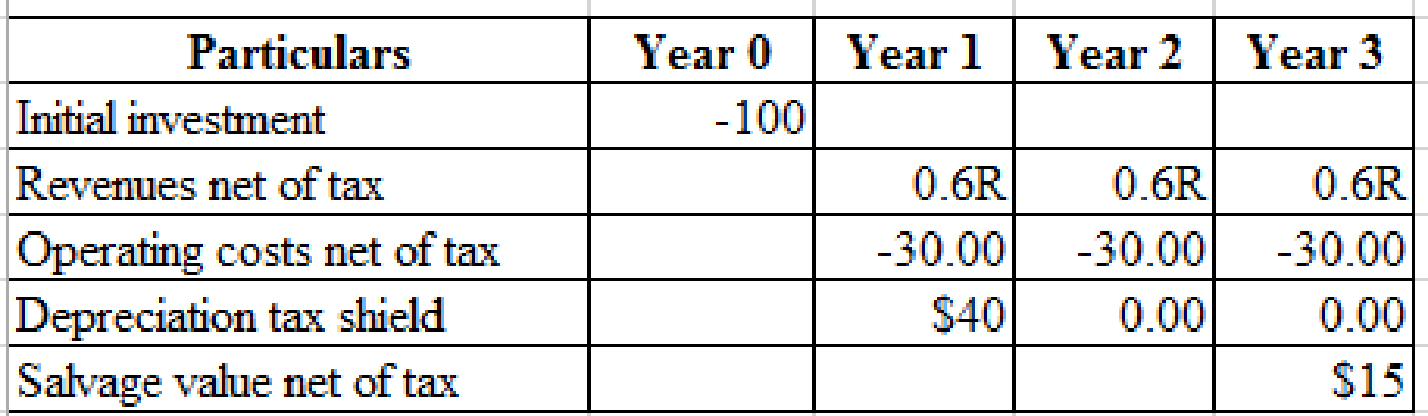
Hence,
By solving this, the value of R= $95.88.
By using the value of R we can calculate the present values of existing one and two years old plants.
Calculation of present value of one and two-year old plants:
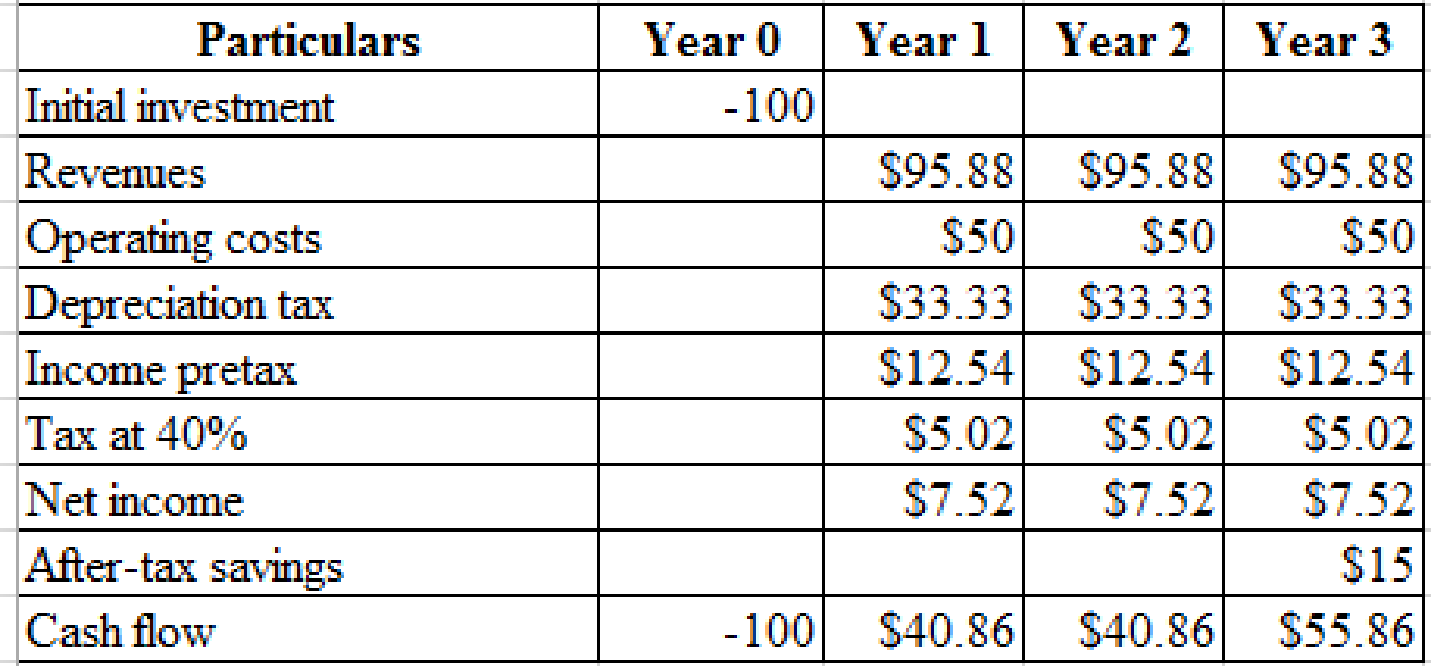
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $72.84.
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $46.55
c)
To determine: Net salvage value of two year old plant.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of salvage value:
The salvage value is $43.33.
d)
To determine: Values the corporate tax rates are abolished entirely.
Explanation of Solution
Solving for zero NPV:
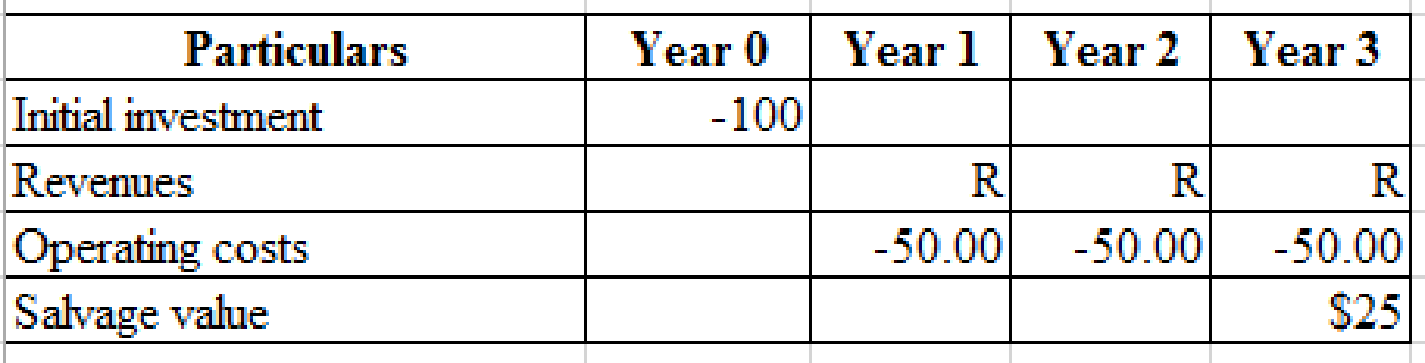
By using the revenues of $90.60
Calculation of present value of one-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of one-year old plant is $79.40.
Calculation of present value of two-year old plant:
Hence, the present value of two-year old plant is $54.67
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF CORPORATE FINANCE
- How are HRISs changing how companies manage their compensation and benefit plans?arrow_forward3. A bond's yield to maturity (YTM) is:A. The coupon rateB. The rate of return required by investorsC. The market price of the bondD. The par value of the bondarrow_forwardNeed help The time value of money concept suggests:A. A dollar today is worth less than a dollar tomorrowB. Money loses value over time due to inflationC. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the futureD. Interest has no effect on present valuearrow_forward
- The time value of money concept suggests:A. A dollar today is worth less than a dollar tomorrowB. Money loses value over time due to inflationC. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the futureD. Interest has no effect on present valuearrow_forward(Related to Checkpoint 17.1) (Forecasting discretionary financing needs) Huang Electronics, Inc., operates a chain of electrical lighting and fixture distribution centers throughout northern Arizona. The firm is anticipating expansion of its sales in the coming year as a result of recent population growth trends. The firm's financial analyst has prepared pro forma balance sheets that reflect three different rates of growth in firm sales for the coming year and the corresponding non-discretionary sources of financing the firm expects to have available, as follows: a. What are the firm's discretionary financing needs under each of the three growth scenarios? b. What potential sources of financing are there for Huang Electronics to fulfill its needs for discretionary financing? a. The discretionary financing needs for a 10% growth scenario are $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forward(Related to Checkpoint 17.1) (Forecasting discretionary financing needs) In the spring of 2023, the Caswell Publishing Company established a custom publishing business for its business clients. These clients consisted principally of small- to medium-size companies in Round Rock, Texas. However, the company's plans were disrupted when it landed a large printing contract which it expects will run for several years. Specifically, the new contract will increase firm revenues by 100 percent. Consequently, Caswell's managers know they will need to make some significant changes in firm capacity, and quickly. The following balance sheet for 2023 and pro forma balance sheet for 2024 reflect the firm's estimates of the financial impact of the 100 percent revenue growth: a. How much new discretionary financing will Caswell require based on the above estimates? b. Given the nature of the new contract and the specific needs for financing that the firm expects, what recommendations might you offer…arrow_forward
- (Related to Checkpoint 17.1) (Forecasting discretionary financing needs) Bates Fabricators, Inc. estimates that it invests 25 cents in assets for each dollar of new sales. However, 4 cents in profits are produced by each dollar of additional sales, of which 1 cent(s) can be reinvested in the firm. If sales rise by $773,000 next year from their current level of $5.36 million, and the ratio of spontaneous liabilities to sales is 0.17, what will be the firm's need for discretionary financing? (Hint: In this situation, you do not know what the firm's existing level of assets is, nor do you know how those assets have been financed. Thus, you must estimate the change in financing needs and match this change with the expected changes in spontaneous liabilities, retained earnings, and other sources of discretionary financing.) The discretionary financing needs will be $ (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.need helparrow_forwardHello expert see carefully I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forward
- I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful. helloarrow_forwardI mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful. hiarrow_forwardHello tutor i need help I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values. please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.arrow_forward
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning

