
Concept explainers
A
Adequate information:
EPS in 2016 is $1.25 and in 2011 is $0.75
The payout ratio is 50%
The current value of the stock is $37.75
The flotation cost for new equity is 15%
The expected net income in 2017 is $18 million
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
To compute: EPS growth rate and dividend in 2017.
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio.Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
A
Explanation of Solution
Firstly, the EPS growth rate will be calculated which is as follows:
Now, the total dividend for the year 2017 will be calculated:
Thus, the EPS growth for 2017 is 10.76% and the dividend in 2017 is $9,000,000.
B
Adequate information:
EPS in 2016 is $1.25 and in 2011 is $0.75
The payout ratio is 50%
The current value of the stock is $37.75
The flotation cost for new equity is 15%
The expected net income in 2017 is $18 million
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
To compute: Cost of
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio. Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
B
Explanation of Solution
Computation of cost of retained earnings or existing equity and cost of new equity:
Cost of retained earnings = (Dividend for 2017/ Current value of stock) + growth rate
= (0.6922/37.75) +0.1076
= 12.59%
Cost of new equity = (Dividend for 2017/ (Current value of stock- flotation cost)) + growth rate
= (0.6922/37.75-(37.75*15%))+0.1076
= (0.6922/32.0875) +0.1076
=12.92%
Note:
Dividend per share for 2017 is calculated as follows:
Thus, the cost of retained earnings is 12.59% and the cost of new equity will be 12.92%.
C
Adequate information:
EPS in 2016 is $1.25 and in 2011 is $0.75
The payout ratio is 50%
The current value of the stock is $37.75
The flotation cost for new equity is 15%
The expected net income in 2017 is $18 million
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
Debt is 25%
Equity is 75%
To compute:Break-even retained earnings.
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio. Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
C
Explanation of Solution
In the given case, equity proportion is 75%, the retention of net income of $18 million will be 50% as 50% is payout as a dividend. Therefore, the maximum that can be raised above the level of retained earnings can be calculated as follows:
Break-even point associated with retained earnings = Retention/ Equity proportion
= $18*(1-50%)/ 0.75
= $12 million
Thus, beyond the $12 million amount firm may issue new equity.
D
Adequate information:
EPS in 2016 is $1.25 and in 2011 is $0.75
The payout ratio is 50%
The current value of the stock is $37.75
The flotation cost for new equity is 15%
The expected net income in 2017 is $18 million
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
To compute: After-tax cost of new debt.
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio. Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
D
Explanation of Solution
Computation of after-tax cost of debt:
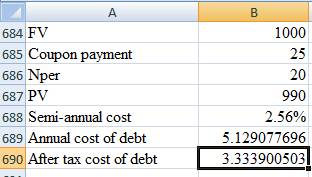
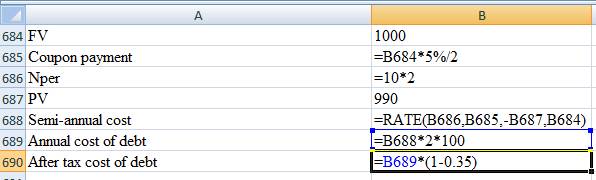
Thus, the after-tax cost of debt is 3.33%
E
Adequate information:
The proportion of debt and equity is 25% and 75% respectively.
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
The cost of retained earnings is 12.59% and the cost of new equity will be 12.92%.
To compute: WACC with the cost of retained earnings and with the cost of new equity.
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio. Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
E
Explanation of Solution
Formula for WACC:
WACC = Weights of debt*after tax cost of debt + weights of equity*
Computation of WACC with the cost of retained earnings:
Weighted Average cost of capital = (12.59%*.75) + (3.33%*.25)
= 10.28%
Computation of WACC with the cost of new equity:
Weighted Average cost of capital = (12.92%*.75)+(3.33%*.25)
= 10.52%
Thus, WACC with retained earnings is 10.28% and the cost of new equity is 10.52%
F
Adequate information:
EPS in 2016 is $1.25 and in 2011 is $0.75
The payout ratio is 50%
The current value of the stock is $37.75
The flotation cost for new equity is 15%
The expected net income in 2017 is $18 million
A semi-annual bond for 10 years at a 5% coupon can be issued with a 1% flotation cost
Par value of $1000
The tax rate is 35%
To draw: A scattered diagram that depicts the firm’s Marginal WACC.
Introduction: Dividend for the year 2017 can be calculated by multiplying the Earnings per share 2017 and dividend payout ratio. Earnings per share can be defined as the company’s net income divided by the number of shares outstanding.
F
Explanation of Solution
Data for Marginal Weighted Average Cost of Capital:
| Total capital ($) | WACC% |
| 0 | 10.28% |
| 12,000,000 | 10.28% |
| 15,000,000 | 10.52% |
| 20,000,000 | 10.52% |
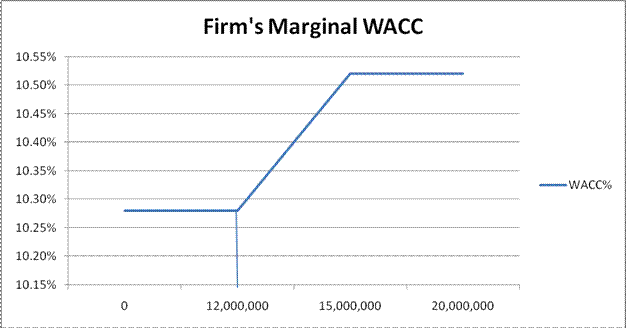
Thus, the blue line in the graph shows the breakeven point is at $12,000,000 where WACC is 10.28%. If the new cost of equity is issued then WACC increases to 10.52% which is the firm’s marginal WACC.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK 3N3-EBK: FINANCIAL ANALYSIS WITH MI
- Beta Company Ltd issued 10% perpetual debt of Rs. 1,00,000. The company's tax rate is 50%. Determine the cost of capital (before tax as well as after tax) assuming the debt is issued at 10 percent premium. helparrow_forwardFinance subject qn solve.arrow_forwardPlease help with questionsarrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
