
Concept explainers
Gruman Company purchased a machine for $220,000 on January 2, 2016. It made the following estimates:
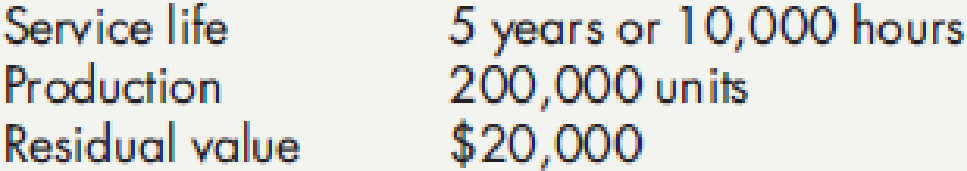
In 2016, Gruman uses the machine for 1,800 hours and produces 44,000 units. In 2017, Gruman uses the machine for 1,500 hours and produces 35,000 units.
Required:
- 1. Compute the
depreciation expense for 2016 and 2017 under each of the following methods:- a. straight-line
- b. sum-of-the-years’-digits (round to the nearest dollar)
- c. double-declining-balance
- d. activity method based on hours worked
- e. activity method based on units of output
- 2. For each method, what is the book value of the machine at the end of 2016? At the end of 2017?
- 3. Next Level If Gruman used a service life of 8 years or 15,000 hours and a residual value of $10,000, what would be the effect on (a) depreciation expense and (b) book value under the straight-line, sum-of-the-years’digits, and double-declining-balance depreciation methods?
1.
Compute the depreciation expense of Company G for 2016 and 2017 under the given depreciation method.
Explanation of Solution
Depreciation: Depreciation is a method of reducing the capitalized cost of long-lived operating assets or plant assets for the period the asset is used.
Straight-line depreciation method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset could be distributed equally throughout the useful life of the asset is referred to as straight-line method.
Activity method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production or hours worked each year. When the usefulness of an asset is related to the production cost of a unit, this method is more appropriate to use.
Sum-of- the-years’ digits method: Sum-of-the years’ digits method determines the depreciation by multiplying the depreciable base and declining fraction.
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
a. Straight line method:
2016:
2017:
b. Sum-of- the-years’ digits method:
| Year |
Depreciable Base ($) (1) |
Depreciation rate per year |
Depreciation expense ($) | ||
| 2016 | 200,000 | = | 66,667 | ||
| 2017 | 200,000 | = | 53,333 |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
Calculate the depreciable base of asset.
Working note (2):
Calculate the denominator of the fraction for sum-of-the-year’s digit.
c. Double-declining-balance method:
2016:
2017:
Working note (3):
Compute the depreciation rate:
Useful life = 5 years
d. Activity method (hours worked):
2016:
2017:
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost per hour.
e. Activity method (unit of output):
2016:
2017:
Working note (5):
Calculate the cost per unit.
2.
Calculate the book value of the machine at the end of 2016 and 2017 under each depreciation method.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the book value of the machine at the end of 2016 and 2017 under each depreciation method as follows:
| Year |
Book Value (A) |
Depreciation (B) |
Ending Book Value |
| a. Straight-line Method | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $40,000 | $180,000 |
| 2017 | $180,000 | $40,000 | $140,000 |
| b. Sum-of-the-years’-digits | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $66,667 | $153,333 |
| 2017 | $153,333 | $53,333 | $100,000 |
| c. Double-declining-balance | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $88,000 | $132,000 |
| 2017 | $132,000 | $52,800 | $79,200 |
| d. Activity based method on hours worked | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $36,000 | $184,000 |
| 2017 | $184,000 | $30,000 | $154,000 |
| e. Activity based method on units of output | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $44,000 | $176,000 |
| 2017 | $176,000 | $35,000 | $141,000 |
Table (2)
Note: Ending book value for 2016 is considered as the beginning book value for 2017.
3.
Identify the effect of (a) the depreciation expense and (b) book value under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method, assume that Company G used a service life of 8 years, or 15,000 hours and residual value of $10,000.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Identify the effect of the depreciation expense under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method as follows:
Straight line method:
2016:
2017:
Sum-of- the-years’ digits method:
| Year |
Depreciable Base ($) (6) |
Depreciation rate per year |
Depreciation expense ($) | ||
| 2016 | 210,000 | = | 46,667 | ||
| 2017 | 210,000 | = | 40,833 |
Table (3)
Working note (6):
Calculate the depreciable base of asset.
Working note (7):
Calculate the denominator of the fraction for sum-of-the-year’s digit.
Double-declining-balance method:
2016:
2017:
Working note (8):
Compute the depreciation rate:
Useful life = 5 years
b) Identify the effect of the book value under the straight line, sum of the year’s digit, and double-declining balance method as follows:
| Year |
Book Value (A) |
Depreciation (B) |
Ending Book Value |
| Straight-line Method | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $26,250 | $193,750 |
| 2017 | $193,750 | $26,250 | $167,500 |
| Sum-of-the-years’-digits | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $46,667 | $173,333 |
| 2017 | $173,333 | $40,833 | $132,500 |
| Double-declining-balance | |||
| 2016 | $220,000 | $55,000 | $165,000 |
| 2017 | $165,000 | $41,250 | $123,750 |
Table (4)
Note: Ending book value for 2016 is considered as the beginning book value for 2017.
When the service life of an asset increases, the depreciation expense gets decreased under straight line, sum of year’s digit, and double-declining balance method, and this decreased depreciation expense increases the ending book value of machinery.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis, 2017 Update
- In a fully integrated standard costing system standards costs eventually flow into the: a. cost of goods sold account b. standard cost account c. selling and administrative expenses account d. sales accountarrow_forwardNet sales total $438,000. Beginning and ending accounts receivable are $35,000 and $37,000, respectively. Calculate days' sales in receivables. A.27 days B.30 days C.36 days D.31 daysarrow_forwardProvide correct answerarrow_forward
- For the system shown in figure below, the per unit values of different quantities are E-1.2, V 1, X X2-0.4. Xa-0.2 Determine whether the system is stable for a sustained fault. The fault is cleared at 8-60°. Is the system stable? If so find the maximum rotor swing. Find the critical clearing angle. E25 G X'd 08 CB X2 F CB V28 Infinite busarrow_forwardGeisner Inc. has total assets of $1,000,000 and total liabilities of $600,000. The industry average debt-to-equity ratio is 1.20. Calculate Geisner's debt-to-equity ratio and indicate whether the company's default risk is higher or lower than the average of other companies in the industry.arrow_forwardHy expert give me solution this questionarrow_forward
- Baker's Market began the current month with inventory costing $35,250, then purchased additional inventory at a cost of $78,400. The perpetual inventory system indicates that inventory costing $82,500 was sold during the month for $88,250. An inventory count at month-end shows that inventory costing $29,000 is actually on hand. What amount of shrinkage occurred during the month? a) $350 b) $1,150 c) $1,750 d) $2,150arrow_forwardA pet store sells a pet waste disposal system for $60 each. The cost per unit, including the system and enzyme digester, is $42.50. What is the contribution margin per unit? A. $15.00 B. $17.50 C. $12.25 D. $19.00arrow_forwardNarchie sells a single product for $40. Variable costs are 80% of the selling price, and the company has fixed costs that amount to $152,000. Current sales total 16,000 units. What is the break-even point in units?arrow_forward
- A company sells 32,000 units at $25 per unit. The variable cost per unit is $20.50, and fixed costs are $52,000. (a) Determine the contribution margin ratio. (b) Determine the unit contribution margin. (c) Determine the income from operations.arrow_forwardhello tutor provide solutionarrow_forwardGerry Co. has a gross profit of $990,000 and $290,000 in depreciation expenses. Selling and administrative expense is $129,000. Given that the tax rate is 37%, compute the cash flow for Gerry Co. a. $700,000 b. $128,963 c. $649,730 d. $652,230arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



