
In
a. The reflection with axis
b. The reflection with axis
c. The reflection with axis
d. The reflection with axis
1.
To find:
The image of
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The image of point P under the reflection with axis
Explanation of Solution
Given:
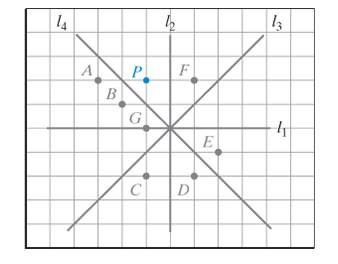
The given figure is,
A rigid motion that moves the object from its starting position to a new position, namely the mirror image of the starting position is called a reflection in the plane.
If a point
To find a image of point
Consider the given figure,
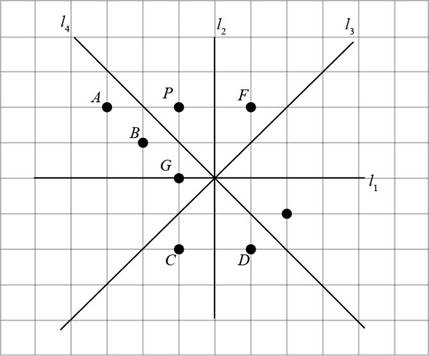
Figure (1)
In the given figure, the points E, C, and D lie on the opposite side of
Points E, D are opposite to point P but do not have same distance from
The point C is at same distance from
The image of P is point C.
Conclusion:
Thus, the image of point P under the reflection with axis
(b)
To find:
The image of
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The image of point P under the reflection with axis
Explanation of Solution
Given:
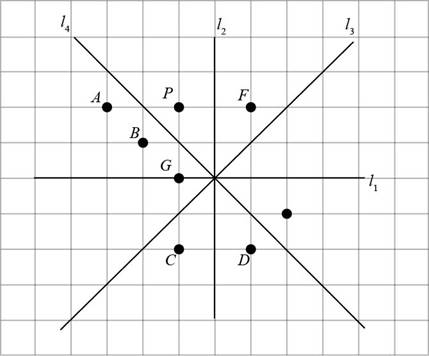
The given figure is,
A rigid motion that moves the object from its starting position to a new position, namely the mirror image of the starting position is called a reflection in the plane.
If a point
To find a image of point
Consider the given figure,
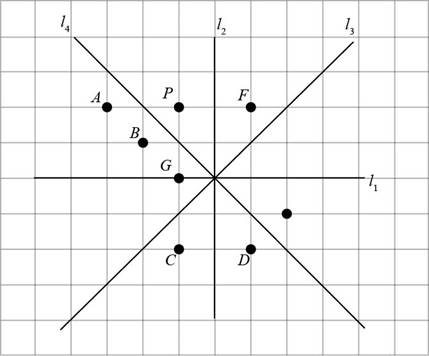
Figure (2)
In Figure (1), the points E, F, and D lie on the opposite side of
Points E, D are opposite to point P but do not have same distance from
The point F is at same distance from
The image of P is point F.
Conclusion:
Thus, the image of point P under the reflection with axis
(c)
To find:
The image of
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The image of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given figure is,

A rigid motion that moves the object from its starting position to a new position, namely the mirror image of the starting position is called a reflection in the plane.
If a point
To find a image of point
Consider the given figure,

Figure (3)
In the given figure, the points C, D, and E lie on the opposite side of
Points C and D are opposite to point P but do not have same distance from
Point E has same distance from
The image of P is point E.
Conclusion:
Thus, the image of point P under the reflection with axis
(d)
To find:
The image of
Answer to Problem 1E
Solution:
The image of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
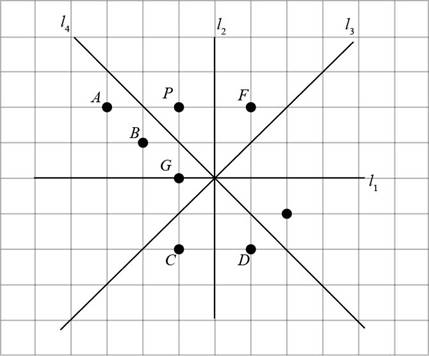
The given figure is,
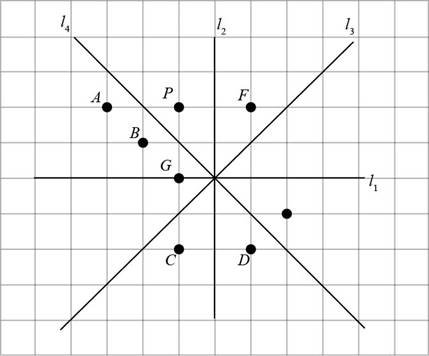
A rigid motion that moves the object from its starting position to a new position, namely the mirror image of the starting position is called a reflection in the plane.
If a point
To find a image of point
Consider the given figure,

Figure (4)
In the given figure, the points A, B, C, D, and G lie on the opposite side of
Points A, D, C and G are opposite to point P but do not have same distance from
Distance of point B from
The image of P is point B.
Conclusion:
Thus, the image of point P under the reflection with axis
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Excursions in Modern Mathematics, Books a la carte edition (9th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Elementary & Intermediate Algebra
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
- II Consider the following data matrix X: X1 X2 0.5 0.4 0.2 0.5 0.5 0.5 10.3 10 10.1 10.4 10.1 10.5 What will the resulting clusters be when using the k-Means method with k = 2. In your own words, explain why this result is indeed expected, i.e. why this clustering minimises the ESS map.arrow_forwardX Acellus | Student admin192c.acellus.com go 0:0 Hannah wants to have concrete stairs for her backdoor. How much concrete will be needed to build the stairs? 20 cm 70 cm 30 cm 15 cm 10 cm 45 cm cm 70 cm GIF 自 لاarrow_forwardwhy the answer is 3 and 10?arrow_forward
- 1 Hannah wants to have concrete stairs for her backdoor. How much concrete will be needed to build the stairs? 70 cm 30 cm 15 cm 10 cm 10 cm 20 cm 45 cm cm³ GIF GIF/ 2 3 4 qwe asdf 5 6 自 yu ty u 8 ghjk 9 P Z X C cv b vbnm ×arrow_forwardPS 9 Two films are shown on screen A and screen B at a cinema each evening. The numbers of people viewing the films on 12 consecutive evenings are shown in the back-to-back stem-and-leaf diagram. Screen A (12) Screen B (12) 8 037 34 7 6 4 0 534 74 1645678 92 71689 Key: 116|4 represents 61 viewers for A and 64 viewers for B A second stem-and-leaf diagram (with rows of the same width as the previous diagram) is drawn showing the total number of people viewing films at the cinema on each of these 12 evenings. Find the least and greatest possible number of rows that this second diagram could have. TIP On the evening when 30 people viewed films on screen A, there could have been as few as 37 or as many as 79 people viewing films on screen B.arrow_forwardskip A swimming pool plan has concrete stairs leading down into the shallow end How much concrete will be needed to build the stairs? Bift 9 ft 2 ft 1 ft 9 ft 2 ft 5 ft [ ? ] ft³arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL  Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell




