
(a):
Calculate the economic service life.
(a):
Explanation of Solution
First cost (FC) is $180,000. Annual cost (AC) in year 1 and 2 is $84,000 after it increases by $5,000 per year. Salvage value (SV) is 25% to the first cost. MARR (i) is 15%. Time period (n) is 5 years.
Table -1 shows the total annual salvage value for different years as follows:
Table -1
| Year | AC | SV |
| 1 | 84,000 | 45,000 |
| 2 | 84,000 | 45,000 |
| 3 | 89,000 | 45,000 |
| 4 | 94,000 | 45,000 |
| 5 | 99,000 | 45,000 |
Total annual value (TA) of the cost can be calculated using the formula as follows:
The value of n1 in the first year is 1. Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the total annual value in the year 1.
The total annual value in the year 1 is -$246,000.
Table -2 shows the total annual value for the different years that are obtained using Equation (1) as follows:
Table -2
| Year | Total annual value |
| 1 | -246,000 |
| 2 | -173,791 |
| 3 | -1581,317 |
| 4 | -141,190 |
| 5 | -135,934 |
Economic service life occurs at the time period where the annual value of the cost is lower. The lower total annual value -$135,934 occurs at the year 5. Thus, economic service life is 5.
(b):
Calculate the economic service life using spreadsheet.
(b):
Explanation of Solution
Total annual value (TA) of the cost can be calculated using the spreadsheet as follows:
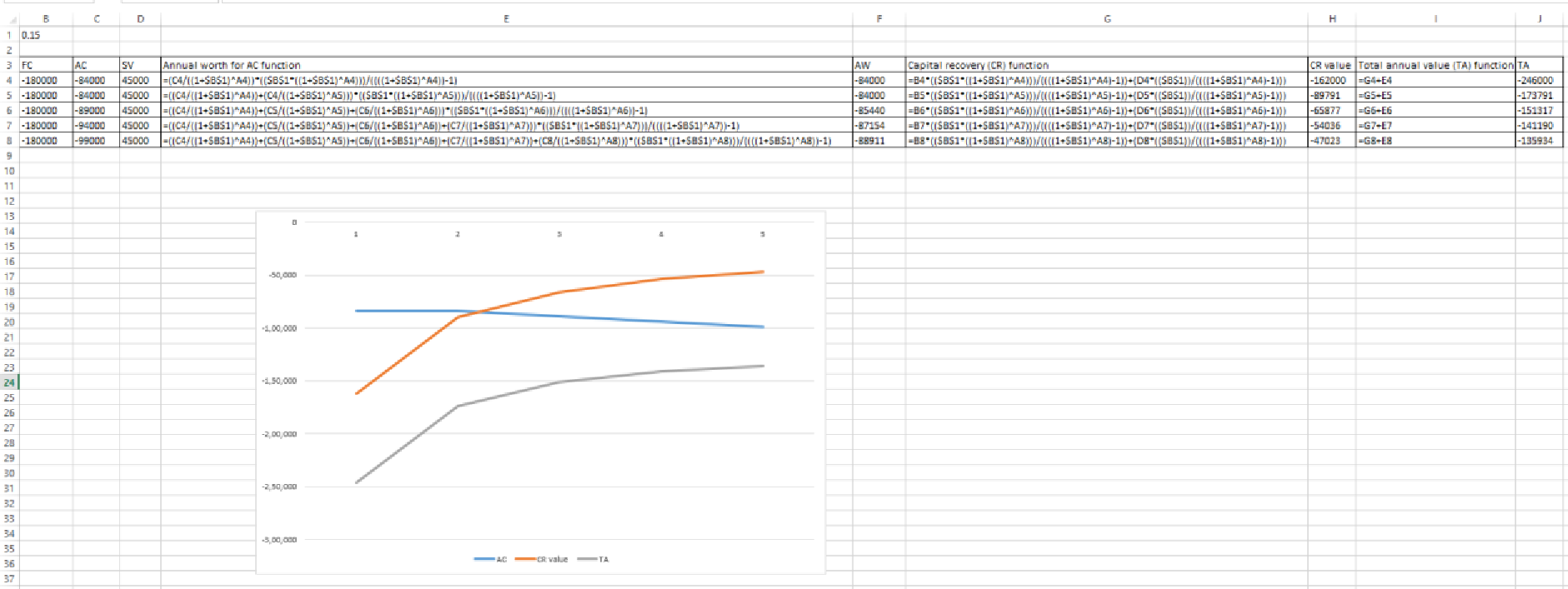
Thus, the lower value of the total annual value is -$135,934 and the economic service life is 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Engineering Economy
- 17. Given that C=$700+0.8Y, I=$300, G=$600, what is Y if Y=C+I+G?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write explanation in paragraphs and if you use currency use USD currency: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forward
- Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 4. Draw a Keynesian AD curve in P – Y space and list the shift factors that will shift theKeynesian AD curve upward and to the right. Draw a separate Classical AD curve in P – Yspace and list the shift factors that will shift the Classical AD curve upward and to the right.arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 15. How is the Keynesian expenditure multiplier implicit in the Keynesian version of the AD/ASmodel? Explain and show mathematically. (note: this is a tough one)arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 13. What would happen to the net exports function in Europe and the US respectively if thedemand for dollars rises worldwide? Explain why.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





