
Concept explainers
(a)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
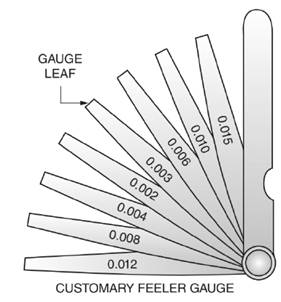
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(b)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
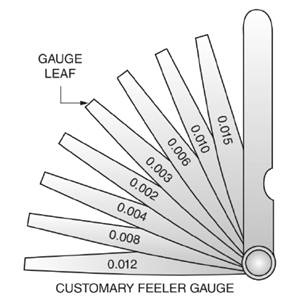
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(c)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
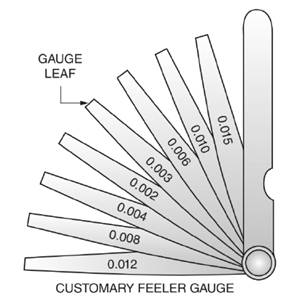
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(d)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
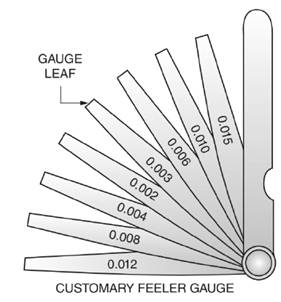
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(e)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
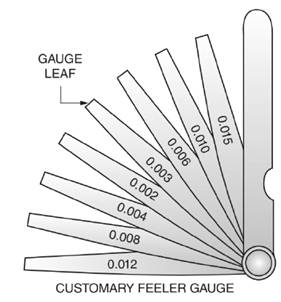
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(f)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
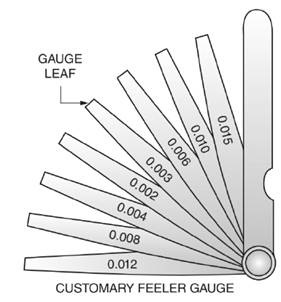
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(g)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
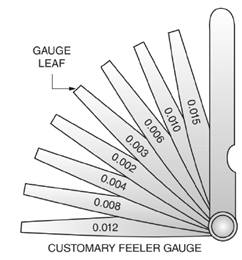
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
(h)
The smallest combination of gauge leaves thickness.
Answer to Problem 13A
Explanation of Solution
Given:
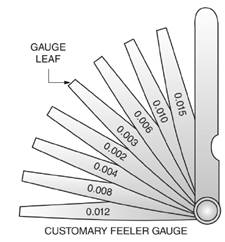
Thickness
Calculation:
In Figure a customary fleer gauge is given with different leaf thickness.
Thus, the smallest combination of leaves that will give a thickness of
Conclusion:
The combination of leaves is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Mathematics For Machine Technology
- Remix 4. Direction Fields/Phase Portraits. Use the given direction fields to plot solution curves to each of the given initial value problems. (a) x = x+2y 1111 y = -3x+y with x(0) = 1, y(0) = -1 (b) Consider the initial value problem corresponding to the given phase portrait. x = y y' = 3x + 2y Draw two "straight line solutions" passing through (0,0) (c) Make guesses for the equations of the straight line solutions: y = ax.arrow_forwardIt was homeworkarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 18) Find all the complex cube roots of -2i. Leave your answers in polar form with the argument in degrees.arrow_forward9) Write an equation for the hyperbola. 2+ -6-5-4-3-2 -2- -4- -5+ + 23 45 6xarrow_forward8) Find an equation for the hyperbola with vertices at vertices at (±7, 0) and foci at (±9, 0).arrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell


