
Concept explainers
• LO11–2
For each of the following depreciable assets, determine the missing amount (?). Abbreviations for depreciation methods are SL for straight line, SYD for sum-of-the-years’-digits, and DDB for double-declining balance.
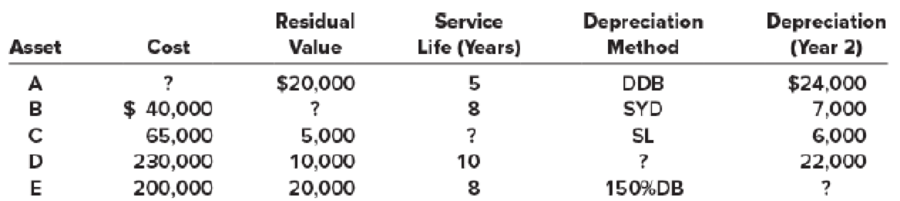
Depreciation:
Depreciation refers to the reduction in the monetary value of a fixed asset due to its wear and tear or obsolescence. It is a method of distributing the cost of the fixed assets over its estimated useful life. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
To determine: The missing amounts.
Explanation of Solution
Asset A:
In the given case cost of the asset is missing. Given information is residual value $20,000; service life 5 years, depreciation method: double declining balance method and depreciation in year 2 is $24,000.
Double declining balance (DDB) method:
In this method of depreciation, the depreciation is calculated by multiply beginning of year book value, not depreciable base, by an annual rate that is a multiple of the straight line rate.
Determine cost of the asset.
Beginning value of the asset A at year 1 is calculated as follows:
Hence, cost at year 1 is $100,000.
Asset B:
In given case residual value is missing. Given information is cost of the asset B is $40,000; service life is 8 years; depreciation method is sum of the year’s digit method; depreciation in year 2 is $7,000.
Sum-of- the-years’ digits (SYD) method:
Sum-of-the years’ digits method determines the depreciation expense by multiplying the depreciable base and declining fraction.
Determine the residual value of asset B
Working note:
Conclusion:
Hence, the residual value of the asset B is $4,000.
Asset C:
In the given case for asset C, estimated life is missing. Given information is as follows cost of the asset is $65,000; residual value of the asset is $5,000; depreciation method is straight line method and year 2 depreciation is $6,000.
Straight line method:
Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset.
Determine estimated life of the asset C
Hence, estimated life or service life of the asset C is 10 Years.
Asset D:
In the given case, method of depreciation is missing. Given information is as follows: cost of the asset D is $230,000; residual value of the asset D is $10,000; service life is 10 years; depreciation for year 2 is $22,000.
Determine the method of depreciation.
Hence, straight line method of depreciation is used to determine the depreciation of asset D.
Asset E:
In the given situation depreciation for year 2 is missing. Given information is as follows: cost of the asset E $200,000; residual value of the asset E is $20,000; service life is 8 years; depreciation method is 150% declining method.
One hundred fifty percent declining balance:
In this method of depreciation, the depreciation is calculated by multiply beginning of year book value, not depreciable base, by an annual rate that is a 150% or 1.5 of the straight line rate.
Determine the depreciation on asset E for year 2.
Depreciation on asset E for year 1 is $37,500
For year 2 depreciation expense is calculated as follows
Hence, depreciation expense for year 2 is $30,469.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING
- Answerarrow_forwardReliable Production company has a beginning finished goods inventory of $24,500, raw material purchases of $31,200, cost of goods manufactured of $42,800, and an ending finished goods inventory of $27,300. The cost of goods sold for this company is?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning



