
Experimental data are listed here for the reaction ![Chapter 11, Problem 11.20PAE, Experimental data are listed here for the reaction B: Time (s) IB] (mol/L) 0.00 0.000 10.0 0.326](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781337398909/Chapter-11/images/html_98909-11-11.20pae_image001.jpg) B:
B:
| Time (s) | IB] (mol/L) |
| 0.00 | 0.000 |
| 10.0 | 0.326 |
| 20.0 | 0.572 |
| 30.0 | 0.750 |
| 40.0 | 0.890 |
- Prepare a graph from these data, connect the points with a smooth line, and calculate the rate of change of [B] for each 10-s interval from 0.0 to 40.0 s. Does the rate of change decrease from one time interval to the next? Suggest a reason for this result.
- How is the rate of change of [AJ related to the rate of change of [B] in each time interval? Calculate the rate of change of [AJ for the time interval from 10.0 to 20.0 s.
- What is the instantaneous rate, A[B]/Ar, when [BI = 0.750 mol/L?
a)
Interpretation:
A graph based on the given data must be plotted and the rate of change of [B] for every 10 s interval must be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
- Chemical reactions proceed at a certain rate which is represented in terms of the change in concentration over a certain period of time
- The rate can be expressed either in terms of a decrease in concentration of the reactants or an increase in the concentration of products.
Answer to Problem 11.20PAE
Solution:
The plot is depicted below.
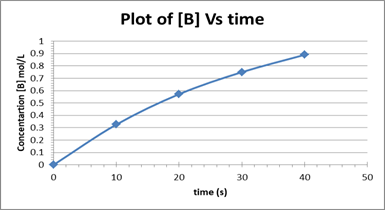
The rate of change of [B] decreases from one-time interval to the next.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
A plot of concentration of [B] vs time based on the given data is shown below:
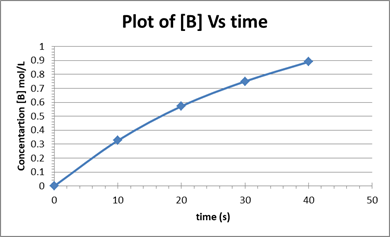
As per the above calculations, the rate of change decreases from one-time interval to the next. This is because as time increases the concentration of reactants decreases as a result the rate of formation of the products will also decrease.
(b)
Interpretation:
The relation between the rate of change of [A] and the rate of change of [B] must be explained. The rate of change of [A] for the time interval from 10.0 to 20.0 s should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
- Chemical reactions proceed at a certain rate which is represented in terms of the change in concentration over a certain period of time
- The rate can be expressed either in terms of a decrease in concentration of the reactants or an increase in the concentration of products.
Answer to Problem 11.20PAE
Solution:
The rate of change of A is half that of B and for time interval 10 to 20 s rate of change of [A] is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
Based on the stoichiometry of this reaction, the rate can be expressed as:
For the time interval between t = 10 to t = 20 s:
(c)
Interpretation:
The instantaneous rate must be calculated when [B] = 0.750 mol/L
Concept Introduction:
- Chemical reactions proceed at a certain rate which is represented in terms of the change in concentration over a certain period of time
- The rate can be expressed either in terms of a decrease in concentration of the reactants or an increase in the concentration of products.
- Average rate of a reaction can be defined as the difference in the concentrations measured at two different times whereas, instantaneous rate can be defined as the rate of a reaction at a particular instant in time.
Answer to Problem 11.20PAE
Solution: Rate = 0.200 mol/L-s
Explanation of Solution
Instantaneous rate can be deduced by drawing a tangent at the point of the curve that corresponds to a particular instant. The slope of the tangent gives the instantaneous rate. In this case the value of [B] = 0.075 mol/L corresponds to a time t = 30 sec. The tangent and the slope are depicted in the plot shown below:
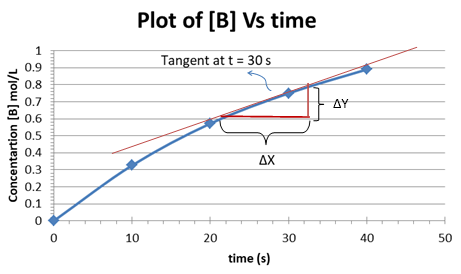
Therefore, the instantaneous rate is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
CHEM FOR ENGNRNG SDNTS (EBOOK) W/ACCES
- Synthesis of ZybanⓇ: 1. Write a mechanism for the bromination of m-chloropropiophenone. Br₂ CH2Cl2 Cl Br 2. Give the expected m/z (to a round number) for the molecular ion from the product above (including isotopic peaks). 3. What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forwardSynthesis of Ibuprofen-Part 2: 1. Some pain relievers including ibuprofen (MotrinⓇ) and naproxen (Aleve®) are "α-arylpropanoic acids." Look up the structure of naproxen (AleveⓇ), another a-arylpropionic acid. Using the same reactions that we used for making ibuprofen, show how to make naproxen from the compound below. Show all intermediates and reagents in your synthesis. Show how you would prepare ibuprofen starting from p-isobutylbenzene rather than p-isobutylacetophenenone. What reaction steps would need to change/add? 3. What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forwardAcid Catalyzed Aromatization of Carvone: 1. Starting with the ketone, below, draw a mechanism for the reaction to give the phenol as shown. H2SO4 HO- H₂O 2. Why do we use CDCl instead of CHCl, for acquiring our NMR spectra? 3. Why does it not matter which enantiomer of carvone is used for this reaction? What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forward
- Assign this H NMRarrow_forwardPlease complete these blanks need that asaparrow_forwardNitration of Methyl Benzoate: 1. Predict the major product for the reaction below AND provide a mechanism. Include ALL resonance structures for the intermediate. C(CH3)3 NO₂* ? 2. Assuming the stoichiometry is 1:1 for the reaction above, what volume of concentrated nitric acid would be required to mononitrate 0.50 grams of the compound above? What product(s) might you expect if you nitrated phenol instead of methyl benzoate? Explain your reasoning. What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forward
- Sodium Borohydride Reduction (continued on the next page): 1. Draw the product of each of the reactions below and give the formula mass to the nearest whole number. ? (1) NaBH (2) acid (1) NaBD4 (2) acid ? 2. In mass spectra, alcohols typically break as shown in equation 8 in chapter 11 (refer to your lab manual). The larger group is generally lost and this gives rise to the base peak in the mass spectrum. For the products of each of the reactions in question # 1, draw the ion corresponding to the base peak for that product and give its mass to charge ratio (m/z). 3. Given the reaction below, calculate how many mg of 1-phenyl-1-butanol that can be produced using 31 mg NaBH4 and an excess of butyrophenone. 4. + NaBH4 OH (after workup with dilute HCI) What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forwardAspirin from Wintergreen: 1. In isolating the salicylic acid, why is it important to press out as much of the water as possible? Write a step-by-step mechanism for the esterification of salicylic acid with acetic anhydride catalyzed by concentrated H₂SO4. 3. Calculate the exact monoisotopic mass of aspirin showing your work. What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forwardSynthesis of Ibuprofen-Part 1: 1. What characteristic absorption band changes would you expect in the IR spectrum on going from p-isobutylacetophenone to 1-(4-isobutylphenyl)-ethanol and then to 1-(4-isobutylphenyl)-1-choroethane as you did in the experiment today? Give approximate wavenumbers associated with each functional group change. Given that the mechanism of the chlorination reaction today involves formation of a benzylic carbocation, explain why the following rearranged product is not formed. محرم محمد 3. Why do we use dilute HCl for the first step of the reaction today and concentrated HCI for the second step? What signals appeared/disappeared/shifted that indicate that you have your intended product and not starting material? What other impurities are present in your product and how do you know?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





