
(a)
State whether the statement “addition of lime to clays increases the plasticity” is true or false.
(a)
Answer to Problem 11.1P
The given statement is
Explanation of Solution
Flocculation‑agglomeration is a chemical reaction that occurs when the lime is added to clayey soils and this reaction makes a texture change in the clay soil. In this process, the clay particle clumps together and forms larger particles due to the presence of lime resulting in plasticity reduction.
Therefore, the given statement is
(b)
State whether the statement “fly ash is pozzalanic” is true or false.
(b)
Answer to Problem 11.1P
The given statement is
Explanation of Solution
Fly ash is a by-product of pulverized coal and is extracted from flue gases through Electrostatic precipitator in dry form. Fly ash is a fine material and possesses good pozzalanic property.
Therefore, the given statement is
(c)
State whether the statement “vibrofoltation is more effective on clays than sands” is true or false.
(c)
Answer to Problem 11.1P
The given statement is
Explanation of Solution
Vibrofoltation is a construction technique used for the densification of thick layers of loose soils.
Refer Figure 11.3, “Effective range of grain-size distribution of soil for vibration” to identify the grain size in which vibrofloation is effective.
Vibrofoltation is effective for gravel, with 0% to 100% fines and with a grain size of 10 mm to 100 mm.
For coarse and fine sand, with a grain size of 0.1 mm to 10 mm and with 0% to 100% fines, vibrofoltation is effective.
For silts and clay, vibrofoltation is effective for clays with 0% to 40% fines and with a grain size of 0.1 mm to 0.001 mm.
Thus, vibrofoltation is more effective on sands than clays.
Therefore, the given statement is
(d)
State whether the statement “pre-compression is mostly applied on normally consolidated clays” is true or false.
(d)
Answer to Problem 11.1P
The given statement is
Explanation of Solution
Normally consolidation clays (NCC) are highly compressible. Thus, large constructions over the layer of NCC soils result in large consolidation settlement.
Pre-compression is applied on NCC to prevent the post consolidation settlement.
Ordinary soils generally are not highly compressive and thus less post consolidation settlement.
Thus, pre-compression are mostly applied on NCC.
Therefore, the given statement is
(e)
State whether the statement “duration of pre-compression is shorter, when the surcharge is larger in pre-compression” is true or false.
(e)
Answer to Problem 11.1P
The given statement is
Explanation of Solution
Show the pre-compression on normally consolidated clay due to structural load
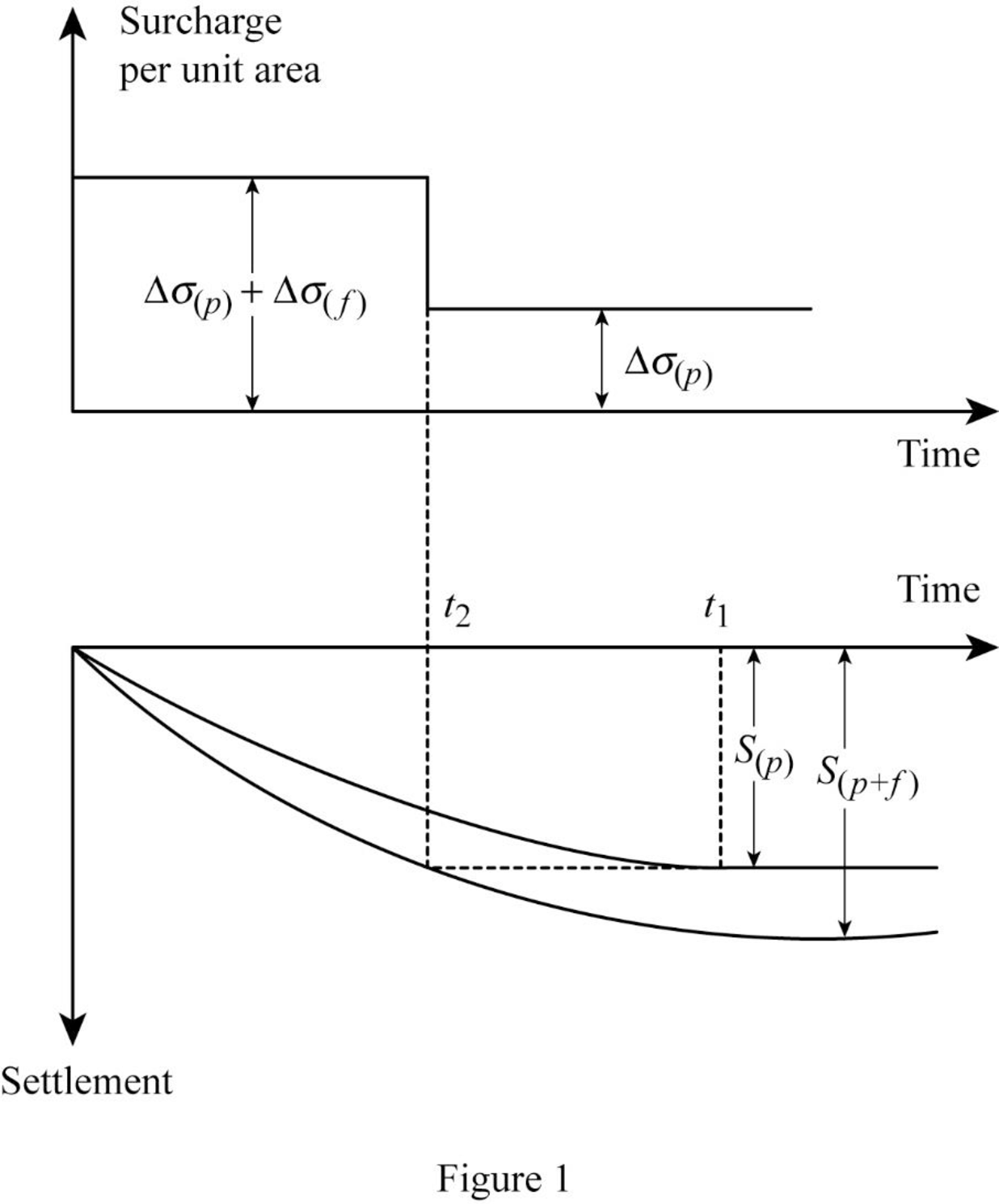
Figure 1 shows the settlement-time relationship under the surcharge load of
The settlement,
The settlement of the clay layer rises with increase in time in both the cases (settlement due to structural load and surcharge load). Thus, the surcharge increases with the increase in the settlement with respect to time.
Therefore, the given statement is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINE
- need helparrow_forwardNEED HELP.arrow_forwardnent 6-Transverse Shear & Deflection ↓ 2 of 2 -+ Automatic Zoom 4.) The built-up wooden beam shown is subjected to a vertical shear of 8 kN. Knowing the the nails are spaced longitudinally every 60 mm at A and every 25 mm at B, determine the shear force in the nails at A and B. (5 points) 50 300- 400 A 50 A C 150 B A 100 50 200 A B Dimensions in mm 5.) A 2.5 inch x 5.5 inch rectangular Southern pine section (E=1.8 x 103 ksi) is used in an 8 ft cantilever span subjected to the loads shown. Compute the deflections at point A. (4 points) Дarrow_forward
- E:/school%20pack/BENG%202/EG231/STATICS/LECTURE%20NOTES/PRACTICE%20QUESTIONS/EG%20231%20Chap-5%20Practice%20Que PDF 豆豆豆豆豆豆 aw V Aa | Ask Copilot - + 4 of 8 D 3. Calculate the y-coordinate of the centroid of the shaded area. 74 mm y 3232 mm mm DELL 32 mm -x F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 prt sc F10 home end F11 F 2 W E3 $ 4 € 95 % & 6 7 8 * 00 R T Y כ 9 O Parrow_forward*8-60. The 2-in.-diameter rod is subjected to the forces shown. Determine the state of stress at point B, and show the results on a differential element located at this point. Probs. 8-59/60 B 8 in. 600 lb 12 in. 500 lb 800 lbarrow_forwardfind SFD and BMD by using slope deflection methodarrow_forward
- The following relates to Problems 4 and 5. Christchurch, New Zealand experienced a major earthquake on February 22, 2011. It destroyed 100,000 homes. Data were collected on a sample of 300 damaged homes. These data are saved in the file called CIEG315 Homework 4 data.xlsx, which is available on Canvas under Files. A subset of the data is shown in the accompanying table. Two of the variables are qualitative in nature: Wall construction and roof construction. Two of the variables are quantitative: (1) Peak ground acceleration (PGA), a measure of the intensity of ground shaking that the home experienced in the earthquake (in units of acceleration of gravity, g); (2) Damage, which indicates the amount of damage experienced in the earthquake in New Zealand dollars; and (3) Building value, the pre-earthquake value of the home in New Zealand dollars. PGA (g) Damage (NZ$) Building Value (NZ$) Wall Construction Roof Construction Property ID 1 0.645 2 0.101 141,416 2,826 253,000 B 305,000 B T 3…arrow_forwardfind SFD and BMDarrow_forwardThe data needed to answer this question is given by this link: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1vzb03U7Uvzm7X-by3OchQNwYeREzbP6Z-xzZMP2tzNw/edit?usp=sharing if it is easier to make a copy of the data because it is on view only then feel free to do so.arrow_forward
- The data needed to answer this question is given in the following link (file is on view only so if you would like to make a copy to make it easier for yourself feel free to do so) https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1aV5rsxdNjHnkeTkm5VqHzBXZgW-Ptbs3vqwk0SYiQPo/edit?usp=sharingarrow_forwardA k 000 6 ft A kips Bl D ft C C kips 10 ft 12 ft E B k/ft D E ft tarrow_forwardH.W: show that the equations 1. (x+y)dy+(x-y)dx = 0 2. x²dy+(y²-xy)dx = 0 are homogeneous and solve:arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning




