
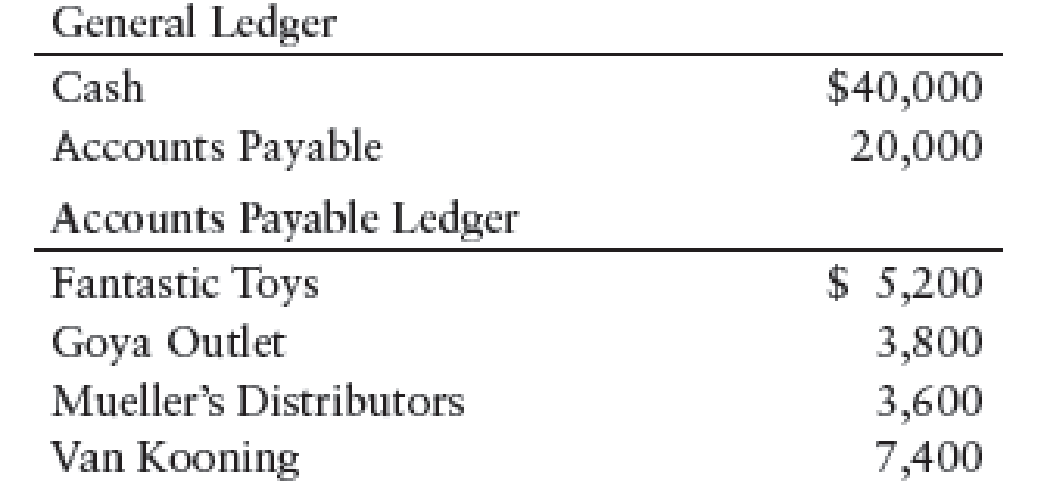
CASH PAYMENTS TR ANS ACTIONS Sam Santiago operates a retail variety store. The books include a general journal and an accounts payable ledger. Selected account balances on May 1 are as follows:
The following are the transactions related to cash payments for the month of May:
May 1 Issued Check No. 426 in payment of May rent (Rent Expense), $2,400.
3 Issued Check No. 427 to Mueller’s Distributors in payment of merchandise purchased on account, $3,600, less a 3% discount. Check was written for $3,492.
7 Issued Check No. 428 to Van Kooning in partial payment of merchandise purchased on account, $5,500. A cash discount was not allowed.
12 Issued Check No. 429 to Fantastic Toys for merchandise purchased on account, $5,200, less a 1% discount. Check was written for $5,148.
15 Issued Check No. 430 to City Power and Light (Utilities Expense), $1,720.
18 Issued Check No. 431 to A-1 Warehouse for a cash purchase of merchandise, $4,800.
26 Issued Check No. 432 to Goya Outlet for merchandise purchased on account, $3,800, less a 2% discount. Check was written for $3,724.
30 Issued Check No. 433 to Mercury Transit Company for freight charges on merchandise purchased (Freight-In), $1,200.
31 Issued Check No. 434 to Town Merchants for a cash purchase of merchandise, $3,000.
Required
- 1. Enter the transactions starting with page 9 of a general journal.
- 2. Post from the general journal to the general ledger and the accounts payable ledger. Use general ledger account numbers as shown in the chapter.
1.
Journalize the cash payment transactions for the month of May.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Journalize the cash payment transactions for the month of May.
Transaction on May 1:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 1 | Rent Expense | 521 | 2,400 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 2,400 | ||||
| (Record payment of rent expense) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Rent Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on May 3:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 3 | Accounts Payable, M Distributors | 202/✓ | 3,600 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 3,492 | ||||
| Purchases Discounts | 501.2 | 108 | ||||
| (Record cash paid for purchases on account) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Accounts Payable, M Distributors is a liability account. Since the payable decreased, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Purchases Discounts is a contra-purchases or contra-costs account, and contra-purchases accounts increase the equity value, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Note 1:
Compute purchases discount value.
Transaction on May 7:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 7 | Accounts Payable, VK | 202/✓ | 5,500 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 5,500 | ||||
| (Record cash paid for purchases on account) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Accounts Payable, VK is a liability account. Since the payable decreased, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on May 12:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 12 | Accounts Payable, F Toys | 202/✓ | 5,200 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 5,148 | ||||
| Purchases Discounts | 501.2 | 52 | ||||
| (Record cash paid for purchases on account) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Accounts Payable, F Toys is a liability account. Since the payable decreased, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Purchases Discounts is a contra-purchases or contra-costs account, and contra-purchases accounts increase the equity value, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Note 2:
Compute purchases discount value.
Transaction on May 15:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 15 | Utilities Expense | 533 | 1,720 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 1,720 | ||||
| (Record payment of utilities expense) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Utilities Expense is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on May 18:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 18 | Purchases | 501 | 4,800 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 4,800 | ||||
| (Record purchase of inventory) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Purchases is an expense account which records the cost of inventory purchased. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on May 26:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 26 | Accounts Payable, G Outlet | 202/✓ | 3,800 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 3,724 | ||||
| Purchases Discounts | 501.2 | 76 | ||||
| (Record cash paid for purchases on account) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Accounts Payable, G Outlet is a liability account. Since the payable decreased, the liability decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
- Purchases Discounts is a contra-purchases or contra-costs account, and contra-purchases accounts increase the equity value, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Note 3:
Compute purchases discount value.
Transaction on May 30:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 30 | Freight-In | 502 | 1,200 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 1,200 | ||||
| (Record payment of freight charges) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Freight-In is an expense account. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Transaction on May 31:
| Page: 9 | ||||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May | 31 | Purchases | 501 | 3,000 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 3,000 | ||||
| (Record purchase of inventory) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Purchases is an expense account which records the cost of inventory purchased. An increase in expense reduces the equity value, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
2.
Post the given transactions into the accounts of the general ledger, and the suppliers account in accounts payable ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Posting transactions: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting the transactions.
Post the given transactions into the accounts of the general ledger.
| ACCOUNT Cash ACCOUNT NO. 101 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 40,000 | |||
| 1 | J9 | 2,400 | 37,600 | ||||
| 3 | J9 | 3,492 | 34,108 | ||||
| 7 | J9 | 5,500 | 28,608 | ||||
| 12 | J9 | 5,148 | 23,460 | ||||
| 15 | J9 | 1,720 | 21,740 | ||||
| 18 | J9 | 4,800 | 16,940 | ||||
| 26 | J9 | 3,724 | 13,216 | ||||
| 30 | J9 | 1,200 | 12,016 | ||||
| 31 | J9 | 3,000 | 9,016 | ||||
Table (10)
| ACCOUNT Accounts Payable ACCOUNT NO. 202 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 20,000 | |||
| 3 | J9 | 3,600 | 16,400 | ||||
| 7 | J9 | 5,500 | 10,900 | ||||
| 12 | J9 | 5,200 | 5,700 | ||||
| 28 | J9 | 3,800 | 1,900 | ||||
Table (11)
| ACCOUNT Purchases ACCOUNT NO. 501 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 18 | J9 | 4,800 | 4,800 | |||
| 31 | J9 | 3,000 | 7,800 | ||||
Table (12)
| ACCOUNT Purchases Discounts ACCOUNT NO. 501.2 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 3 | J9 | 108 | 108 | |||
| 12 | J9 | 52 | 160 | ||||
| 26 | J9 | 76 | 236 | ||||
Table (13)
| ACCOUNT Freight-In ACCOUNT NO. 502 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 30 | J9 | 1,200 | 1,200 | |||
Table (14)
| ACCOUNT Rent Expense ACCOUNT NO. 521 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 1 | J9 | 2,400 | 2,400 | |||
Table (15)
| ACCOUNT Utilities Expense ACCOUNT NO. 533 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| May | 15 | J9 | 1,720 | 1,720 | |||
Table (16)
Post the accounts payable balances of the suppliers to the supplier accounts in the accounts payable ledger.
| NAME F Toys | ||||||
| ADDRESS | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 5,200 | ||
| 12 | J9 | 5,200 | 0 | |||
Table (17)
| NAME G Outlet | ||||||
| ADDRESS | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,800 | ||
| 26 | J9 | 3,800 | 0 | |||
Table (18)
| NAME M Distributors | ||||||
| ADDRESS | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| May | 1 | Balance | ✓ | 3,600 | ||
| 3 | J9 | 3,600 | ||||
Table (19)
| NAME VK | ||||||
| ADDRESS | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| May | 18 | Balance | ✓ | 7,400 | ||
| 7 | J9 | 5,500 | 1,900 | |||
Table (20)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
College Accounting, Chapter 1-15 (Looseleaf)
- Please provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniques.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardProvide solution without Ai if give answer copy past or Ai i give dislikearrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





