
a)
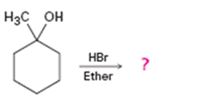
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols gets converted into the corresponding bromides on treatment with HBr in ether solution.
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction shown is
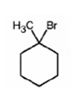
Explanation of Solution
When 1-methylcyclohexanol is treated with HBr, the OH group in it is replaced by the bromine to yield 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane and water as products.
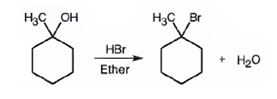
The product of the reaction shown is
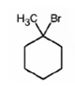
b)
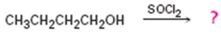
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols when treated with SOCl2 yield the corresponding alkyl chlorides along with SO2 and HCl.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 .
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 is 1-chlorobutane.
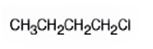
Explanation of Solution
When 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2, the OH group in is replaced by chlorine to yield 1-chlorobutane. SO2 and HCl are obtained as other products.
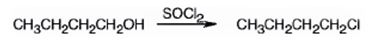
The product of the reaction in which 1-butanol reacts with SOCl2 is 1-chlorobutane.
c)
Interpretation:
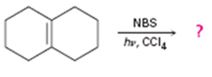
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Cycloalkenes on treatment with NBS in CCl4 in the presence of light undergo bromination at the allyl position.
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The products of the reaction shown are
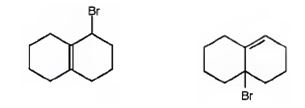
Explanation of Solution
NBS is normally used for allylic bromination. The reaction occurs through a radical mechanism. The radical produced by the homolytic cleavage of the C-H bond in the allyl position gets delocalized with the π electrons of the double bond to yield another radical with an odd electron at the junction of the rings. The attack of bromine radical hence leads to two different products as shown.
The products of the reaction shown are

d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
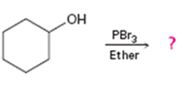
Alcohols give the corresponding bromides as products on treatment with PBr3 in ether solution.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3.
Answer to Problem 26AP
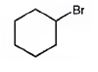
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3is
Explanation of Solution
When cyclohexanol is treated with PBr3, the OH group in it is replaced by the bromine to yield bromocyclohexane.
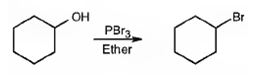
The product of the reaction in which cyclohexanol reacts with PBr3 is

e)
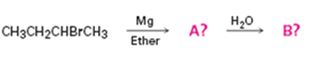
Interpretation:
The products of the reactions shown are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl bromides react with Mg in ether to give Grignard reagents. Grignard reagents when treated with water yield the corresponding
To predict:
The products of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The products of the reaction shown are sec-butyl magnesium bromide (A) and n-butane (B).
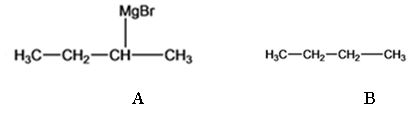
Explanation of Solution
sec-butyl bromide when reacted with Mg in ether yields sec-butyl magnesium bromide, a Grignard reagent. The sec-butyl magnesium bromide reacts with water to yield n-butane.
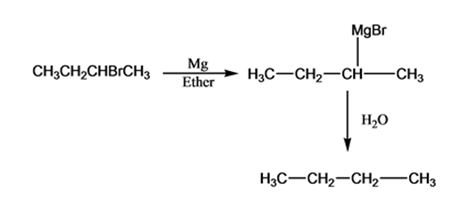
The products of the reaction shown are sec-butyl magnesium bromide (A) and n-butane (B).
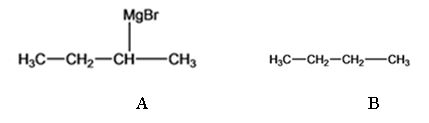
f)
Interpretation:
The products of the reaction shown are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
To predict:
The product of the reaction shown.
Answer to Problem 26AP
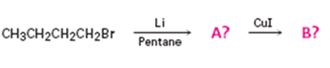
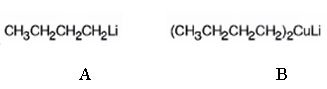
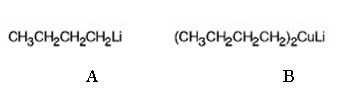
The products of the reaction shown are N-butyllithium (A) and Lithium n-dibutyl copper (B).
Explanation of Solution
n-Butyl bromide reacts with Li to yield n-butyl lithium and lithium bromide. The n-butyl lithium produced when reacted with CuI yields Lithium n-dibutyl copper as the product.
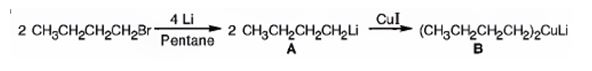
The products of the reaction shown are N-butyllithium (A) and Lithium n-dibutyl
g)
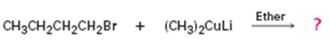
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction shown is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
When alkyl halides are treated with lithium dimethyl copper, the halogens are displaced by an alkyl group and a higher alkane is produced as the product.
To predict:
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper.
Answer to Problem 26AP
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper is n-pentane.
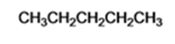
Explanation of Solution
When n-butyl bromide is treated with lithium dimethylcopper, the bromine is replaced by a methyl group to yield n-pentane as the product.
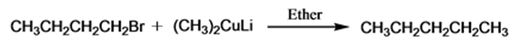
The product of the reaction in which n-butyl bromide reacts with lithium dimethylcopper is n-pentane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/OWL
- What will the enolate for this be using LDA, THF, and cold temperatures? What will it be using NaOEt at rt?arrow_forwardHelp me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forward
- CHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forwardCan anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

