
Using & Understanding Mathematics, Books a la Carte edition (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134716015
Author: Jeffrey O. Bennett, William L. Briggs
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 10.C, Problem 27E
To determine
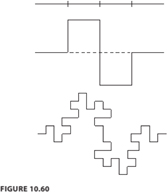
a. The relation between N and R for quadratic Koch curve.
b. The fractal dimension of quadratic coach curve and conclusion about the length of quadratic Koch curve with conclusions
c. Why the total area of quadratic Koch Island is the same as the area of the original square and the length of the Koch Island.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q3: Answer the following:
(i) Let f(z) is an analytic function in a simply connected domain S and y is a simple, closed, positively
oriented contour lying in S. Prove that f, f(z)dz = 0.
DO NOT GIVE THE WRONG ANSWER
SHOW ME ALL THE NEEDED STEPS
11: A rectangle has a base that is growing at a rate of 3 inches per second and a height that is shrinking at a rate of one inch per second. When the base is 12 inches and the height is 5 inches, at what rate is the area of the rectangle changing?
please answer by showing all the dfalowing necessary step
DO NOT GIVE ME THE WRONG ANSWER
The sides of a cube of ice are melting at a rate of 1 inch per hour. When its volume is 64 cubic inches, at what rate is its volume changing?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Using & Understanding Mathematics, Books a la Carte edition (7th Edition)
Ch. 10.A - Prob. 1QQCh. 10.A - Prob. 2QQCh. 10.A - An acute angle is a. less than 90°. b. exactly...Ch. 10.A - 4. A regular polygon always has
a. four sides. b....Ch. 10.A - 5. A right triangle always has
three equal-length...Ch. 10.A - 6. The circumference of a circle of radius r...Ch. 10.A - The volume of a sphere of radius r is a. \[\pi...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 8QQCh. 10.A - If you triple the radius of a sphere, the volume...Ch. 10.A - Suppose you cut a large stone block into four...
Ch. 10.A - What do we mean by Euclidean geometry?Ch. 10.A - Prob. 2ECh. 10.A - What do we mean by dimension? How is dimension...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 4ECh. 10.A - What is plane geometry? What does it mean for...Ch. 10.A - 6. What is a polygon? How do we measure the...Ch. 10.A - What are the formulas for the circumference and...Ch. 10.A - 8. Describe how we calculate the volumes and...Ch. 10.A - What are the scaling laws for area and volume?...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 10ECh. 10.A - Prob. 11ECh. 10.A - Prob. 12ECh. 10.A - My bedroom is a rectangular prism that measures 12...Ch. 10.A - walked around the circular pond to a point on the...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 15ECh. 10.A - 16. By building a fence across my rectangular...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 17ECh. 10.A - Prob. 18ECh. 10.A - Angles and Circles. Find the degree measure of the...Ch. 10.A - 17-22: Angles and Circles. Find the degree measure...Ch. 10.A - 17-22: Angles and Circles. Find the degree measure...Ch. 10.A - 17-22: Angles and Circles. Find the degree measure...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 23ECh. 10.A - Prob. 24ECh. 10.A - Prob. 25ECh. 10.A - Prob. 26ECh. 10.A - Prob. 27ECh. 10.A - Prob. 28ECh. 10.A - Prob. 29ECh. 10.A - Prob. 30ECh. 10.A - Circle Practice. Find the circumference and area...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 32ECh. 10.A - Circle Practice. Find the circumference and area...Ch. 10.A - 31-36: Circle Practice. Find the circumference and...Ch. 10.A - Circle Practice. Find the circumference and area...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 36ECh. 10.A - Prob. 37ECh. 10.A - Prob. 38ECh. 10.A - Perimeters and Areas. Use Table 10.2 to find the...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 40ECh. 10.A - Prob. 41ECh. 10.A - Prob. 42ECh. 10.A - Triangle Geometry. Find the perimeter and area of...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 44ECh. 10.A - 43-46: Triangle Geometry. Find the perimeter and...Ch. 10.A - 43-46: Triangle Geometry. Find the perimeter and...Ch. 10.A - Window Space. A picture window has a length of 8...Ch. 10.A - A Running Track. A running track has straight legs...Ch. 10.A - Building Stairs. Refer to Figure 10.14, showing...Ch. 10.A - No Calculation Required. The end views of two...Ch. 10.A - Parking Lot. A parking lot is shaped like a...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 52ECh. 10.A - Prob. 53ECh. 10.A - 53-57: Three-Dimensional Objects. Use the formulas...Ch. 10.A - Three-Dimensional Objects. Use the formulas in...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 56ECh. 10.A - Prob. 57ECh. 10.A - 58. Water Canal. A water canal has a rectangular...Ch. 10.A - 59. Water Reservoir. The water reservoir for a...Ch. 10.A - 60. Oil Drums. Which holds more: an oil drum with...Ch. 10.A - Tree Volumes. Is there more wood in a 40-foot-high...Ch. 10.A - Architectural Model. Suppose you build an...Ch. 10.A - Architectural Model: Suppose you build an...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 64ECh. 10.A - Architectural Model: Suppose you build an...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 66ECh. 10.A - Architectural Model: Suppose you build an...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 68ECh. 10.A - Quadrupling Your Size. Suppose you magically...Ch. 10.A - Quadrupling Your Size. Suppose you magically...Ch. 10.A - Quadrupling Your Size. Suppose you magically...Ch. 10.A - 72-74: Comparing People. Consider a person named...Ch. 10.A - 72-74: Comparing People. Consider a person named...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 74ECh. 10.A - Squirrels or People? Squirrels and humans are both...Ch. 10.A - 75-76: Squirrels or People? Squirrels and humans...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 77ECh. 10.A - Prob. 78ECh. 10.A - Comparing Balls. Consider a softball with a radius...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 80ECh. 10.A - Dimension. Examine a closed book. How many...Ch. 10.A - Perpendicular and Parallel. Suppose you mark a...Ch. 10.A - Perpendicular and Parallel. Suppose you draw two...Ch. 10.A - Backyard. Figure 10.25 shows the layout of a...Ch. 10.A - Human Lung. The human lung has approximately 300...Ch. 10.A - 86. Automobile Engine Capacity. The size of a car...Ch. 10.A - 87. The Chunnel. The English Channel Tunnel, or...Ch. 10.A - Prob. 88ECh. 10.A - Prob. 89ECh. 10.A - Prob. 90ECh. 10.A - The Geometry of Ancient Cultures. Research the use...Ch. 10.A - Surveying and GIS. Surveying is one of the oldest...Ch. 10.A - Platonic Solids. Why are there five and only five...Ch. 10.B - The number of minutes of are in a full circle is...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 2QQCh. 10.B - If you travel due east, you are traveling along a...Ch. 10.B - 4. If you are located at latitude 30°S and...Ch. 10.B - What would be different about the Sun if you...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 6QQCh. 10.B - If you are bicycling eastward up a hill with a 10%...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 8QQCh. 10.B - Prob. 9QQCh. 10.B - Prob. 10QQCh. 10.B - How do we describe fractions of a degree of angle?Ch. 10.B - Prob. 2ECh. 10.B - How is angular size related to physical size?Ch. 10.B - Prob. 4ECh. 10.B - Give at least two examples of ways in which the...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 6ECh. 10.B - Give an example of a practical problem that can be...Ch. 10.B - 8. What is an optimization problem? Give an...Ch. 10.B - 9. In December, it is winter at 70oW and 44oS.
Ch. 10.B - Prob. 10ECh. 10.B - Prob. 11ECh. 10.B - Prob. 12ECh. 10.B - Prob. 13ECh. 10.B - Prob. 14ECh. 10.B - Angle Conversions I. Convert the given degree...Ch. 10.B - 15-20: Angle Conversions I. Convert the given...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 17ECh. 10.B - Prob. 18ECh. 10.B - Prob. 19ECh. 10.B - Angle Conversions I. Convert the given degree...Ch. 10.B - 21-26: Angle Conversions II. Convert the given...Ch. 10.B - 21-26: Angle Conversions II. Convert the given...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 23ECh. 10.B - Prob. 24ECh. 10.B - Angle Conversions II. Convert the given angle...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 26ECh. 10.B - Prob. 27ECh. 10.B - Prob. 28ECh. 10.B - Prob. 29ECh. 10.B - Prob. 30ECh. 10.B - Prob. 31ECh. 10.B - Prob. 32ECh. 10.B - Prob. 33ECh. 10.B - Prob. 34ECh. 10.B - Prob. 35ECh. 10.B - Prob. 36ECh. 10.B - Angular Size. Use the formula relating angular...Ch. 10.B - Angular Size. Use the formula relating angular...Ch. 10.B - Angular Size. Use the formula relating angular...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 40ECh. 10.B - Prob. 41ECh. 10.B - Prob. 42ECh. 10.B - Prob. 43ECh. 10.B - Prob. 44ECh. 10.B - Prob. 45ECh. 10.B - 46. Grade of a Road. How much does a road with a...Ch. 10.B - 47. Pitch of a Roof. What is the angle (relative...Ch. 10.B - Grade of a Path. What is the approximate grade...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 49ECh. 10.B - Grade of a Trail. How much does a trail with a 22%...Ch. 10.B - Map Distances. Refer to the map in Figure 10.37....Ch. 10.B - Prob. 52ECh. 10.B - Prob. 53ECh. 10.B - Prob. 54ECh. 10.B - Prob. 55ECh. 10.B - Map Distances. Refer to the map in Figure 10.37....Ch. 10.B - Prob. 57ECh. 10.B - Prob. 58ECh. 10.B - 57-60: Acreage Problems. Refer to Figure 10.31,...Ch. 10.B - Acreage Problems. Refer to Figure 10.31, but use...Ch. 10.B - 61-64: Determining Similarity. Determine which...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 62ECh. 10.B - Prob. 63ECh. 10.B - Prob. 64ECh. 10.B - Prob. 65ECh. 10.B - Analyzing Similar Triangles. Determine the lengths...Ch. 10.B - Analyzing Similar Triangles. Determine the lengths...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 68ECh. 10.B - Solar Access. Assume that the policy given In...Ch. 10.B - Solar Access. Assume that the policy given In...Ch. 10.B - Solar Access. Assume that the policy given in...Ch. 10.B - Solar Access. Assume that the policy given in...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 73ECh. 10.B - Prob. 74ECh. 10.B - Prob. 75ECh. 10.B - Prob. 76ECh. 10.B - Prob. 77ECh. 10.B - Designing Plastic Buckets. A company manufactures...Ch. 10.B - Designing Cardboard Boxes. Suppose you are...Ch. 10.B - Designing Steel Safes. A large steel sale with a...Ch. 10.B - Blu-ray Geometry. The capacity of a single-sided,...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 82ECh. 10.B - Prob. 83ECh. 10.B - Prob. 84ECh. 10.B - Prob. 85ECh. 10.B - Prob. 86ECh. 10.B - Prob. 87ECh. 10.B - Filling a Pool. A spherical water tank has a...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 89ECh. 10.B - Prob. 90ECh. 10.B - Prob. 91ECh. 10.B - 92. Estimating Heights. In trying in estimate the...Ch. 10.B - 93. Soda Can Design. Standard soft drink cans hold...Ch. 10.B - 94. Melting Ice. A glaciers surface is...Ch. 10.B - Prob. 95ECh. 10.B - Prob. 96ECh. 10.B - Prob. 97ECh. 10.B - Prob. 98ECh. 10.B - Prob. 99ECh. 10.B - Prob. 100ECh. 10.C - Fractal geometry is useful because it is the only...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 2QQCh. 10.C - Prob. 3QQCh. 10.C - Which of the following is a general characteristic...Ch. 10.C - How do fractal dimensions differ from in Euclidean...Ch. 10.C - 6. An island coastline has a fractal dimension...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 7QQCh. 10.C - Prob. 8QQCh. 10.C - Prob. 9QQCh. 10.C - Prob. 10QQCh. 10.C - Prob. 1ECh. 10.C - Prob. 2ECh. 10.C - Explain the meaning of the factors R and N used in...Ch. 10.C - What is the snowflake curve? Explain why we cannot...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 5ECh. 10.C - Prob. 6ECh. 10.C - Briefly describe what we mean by the process of...Ch. 10.C - 8. What is random iteration? Why do objects...Ch. 10.C - 9. I can use a yardstick to find the area of my...Ch. 10.C - I can use a yardstick to measure the length of the...Ch. 10.C - The area of the snowflake island is given by its...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 12ECh. 10.C - The edge of this leaf has a fractal dimension of...Ch. 10.C - This entire leaf, riddled with holes, has a...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 15ECh. 10.C - Prob. 16ECh. 10.C - Prob. 17ECh. 10.C - Prob. 18ECh. 10.C - Prob. 19ECh. 10.C - Prob. 20ECh. 10.C - 15-26: Ordinary and Fractal Dimensions. Find the...Ch. 10.C - 15-26: Ordinary and Fractal Dimensions. Find the...Ch. 10.C - 15-26: Ordinary and Fractal Dimensions. Find the...Ch. 10.C - Prob. 24ECh. 10.C - Prob. 25ECh. 10.C - Prob. 26ECh. 10.C - Prob. 27ECh. 10.C - Prob. 28ECh. 10.C - Prob. 29ECh. 10.C - Prob. 30ECh. 10.C - Prob. 31ECh. 10.C - Prob. 32ECh. 10.C - Prob. 33ECh. 10.C - Fractal Research. Locate at least two websites...Ch. 10.C - 35. Fractal Art. Visit a website that features...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Wendy is looking over some data regarding the strength, measured in Pascals (Pa), of some rope and how the strength relates to the number of woven strands in the rope. The data are represented by the exponential function f(x) = 2x, where x is the number of woven strands. Explain how she can convert this equation to a logarithmic function when strength is 256 Pascals. Please type out answerarrow_forwardName: Date: Bell: Unit 11: Volume & Surface Area Homework 2: Area of Sectors Directions: Find the area of each shaded sector. Round to the hundredths place. 1. GH 11 in 2. KL 20 ft H F 64 G L 119 M K 3. BA 6.5 cm 4. YZ 14.2 m B 23 X 87° Y Z 5. KL = 27.1 mm J 32 L X:360-32.1 K A-3 360 7. BD 18 cm E 136 B X=32.8 127.0 (271) A: 069.13 Amm² 19=2102.13 A-136 360.16912 A:300cm² A=96.13 6. PQ = 2.8 in P R 311° 8. WZ 5.3 km V = Z 108 W D 9. HK = 25 ft G H KO 26 X 10. SR 26 m = S 73 T R Gina Wilson (All Things Algebarrow_forwardHarrison and Sherrie are making decisions about their bank accounts. Harrison wants to deposit $200 as a principal amount, with an interest of 2% compounded quarterly. Sherrie wants to deposit $200 as the principal amount, with an interest of 4% compounded monthly. Explain which method results in more money after 2 years. Show all work. Please type out answerarrow_forward
- Mike is working on solving the exponential equation 37x = 12; however, he is not quite sure where to start. Solve the equation and use complete sentences to describe the steps to solve. Hint: Use the change of base formula: log y = log y log barrow_forwardUsing logarithmic properties, what is the solution to log3(y + 5) + log36 = log366? Show all necessary steps.arrow_forward4.2 Comparing Linear and Exponential Change 7) Money is added to (and never removed from) two different savings accounts (Account A and Account B) at the start of each month according to different mathematical rules. Each savings account had $500 in it last month and has $540 in it this month. (a) Assume the money in Account A is growing linearly: How much money will be in the account next month? How much money was in the account two months ago? How long will it take for the account to have at least $2500? Write an equation relating the amount of money in the account and the number of months from now. Clearly define the meaning of each variable in your equation, and interpret the meaning of each constant in your equation. (b) Assume the money in Account B is growing exponentially. How much money will be in the account next month? How much money was in the account two months ago? How long will it take for the account to have at least $2500? Write an equation relating the amount of money…arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the solution to the equation 25(z − 2) = 125? - Oz = 5.5 Oz = 3.5 Oz = -2.5 z = -0.5arrow_forwardAnalyze the graph below to identify the key features of the logarithmic function. 2 0 2 6 8 10 12 2 The x-intercept is y = 7, and the graph approaches a vertical asymptote at y = 6. The x-intercept is x = 7, and the graph approaches a vertical asymptote at x = 6. The x-intercept is y = -7, and the graph approaches a vertical asymptote at y = −6. The x-intercept is x = -7, and the graph approaches a vertical asymptote at x = −6.arrow_forwardCompare the graphs below of the logarithmic functions. Write the equation to represent g(x). 2 f(x) = log(x) 2 g(x) -6 -4 -2 ° 2 0 4 6 8 -2 - 4 g(x) = log(x) - g(x) = log(x) + 4 g(x) = log(x+4) g(x) = log(x-4) -2 -4 -6arrow_forward
- Which of the following represents the graph of f(x)=3x-2? 3 2 • 6 3 2 0- 0- • 3 2 0 -2 3arrow_forward2) Suppose you start with $60 and increase this amount by 15%. Since 15% of $60 is $9, that means you increase your $60 by $9, so you now have $69. Notice that we did this calculation in two steps: first we multiplied $60 by 0.15 to find 15% of $60, then we added this amount to our original $60. Explain why it makes sense that increasing $60 by 15% can also be accomplished in one step by multiplying $60 times 1.15. 3) Suppose you have $60 and want to decrease this amount by 15%. Since 15% of $60 is $9, that means you will decrease your $60 by $9, so you now have $51. Notice that we did this calculation in two steps: first we multiplied $60 by 0.15 to find 15% of $60, then we subtracted this amount from our original $60. Explain why it makes sense that decreasing $60 by 15% can also be accomplished in one step by multiplying $60 times 0.85. 4) In the Read and Study section, we noted that the population in Colony B is increasing each year by 25%. Which other colony in the Class Activity…arrow_forwardSuppose an experiment was conducted to compare the mileage(km) per litre obtained by competing brands of petrol I,II,III. Three new Mazda, three new Toyota and three new Nissan cars were available for experimentation. During the experiment the cars would operate under same conditions in order to eliminate the effect of external variables on the distance travelled per litre on the assigned brand of petrol. The data is given as below: Brands of Petrol Mazda Toyota Nissan I 10.6 12.0 11.0 II 9.0 15.0 12.0 III 12.0 17.4 13.0 (a) Test at the 5% level of significance whether there are signi cant differences among the brands of fuels and also among the cars. [10] (b) Compute the standard error for comparing any two fuel brands means. Hence compare, at the 5% level of significance, each of fuel brands II, and III with the standard fuel brand I. [10] �arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...
Math
ISBN:9781259676512
Author:Kenneth H Rosen
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...
Math
ISBN:9780134392790
Author:Beckmann, Sybilla
Publisher:PEARSON


Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)
Math
ISBN:9780134683713
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:PEARSON

Discrete Mathematics With Applications
Math
ISBN:9781337694193
Author:EPP, Susanna S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Math
ISBN:9781259985607
Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. Mercer
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Points, Lines, Planes, Segments, & Rays - Collinear vs Coplanar Points - Geometry; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dDWjhRfBsKM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Naming Points, Lines, and Planes; Author: Florida PASS Program;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F-LxiLSSaLg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY