
We are only beginning to learn about the long-term effects of space travel on human health. A study published in 2016 (Nature Scientific Reports 6, Article number: 29901, nature.com/articles/srep29901, July 28, 2016, retrieved May 6, 2017) found that by 2014, seven of the U.S. astronauts who traveled to the moon during Apollo lunar missions of the 1960s and 1970s had died, and that three of these (3/7 = 43%) had died from cardiovascular disease (CVD). The overall U.S. death rate due to CVD for adults age 55 to 64 in 2013 was 27%. Do the data for lunar astronauts indicate that, as a group, they are at increased risk of death caused by CVD? Assume that it is reasonable to regard this sample as representative of the population of past, present, and future U.S. lunar astronauts.
- a. Explain why the data in this example should not be analyzed using a large-sample hypothesis test for a population proportion.
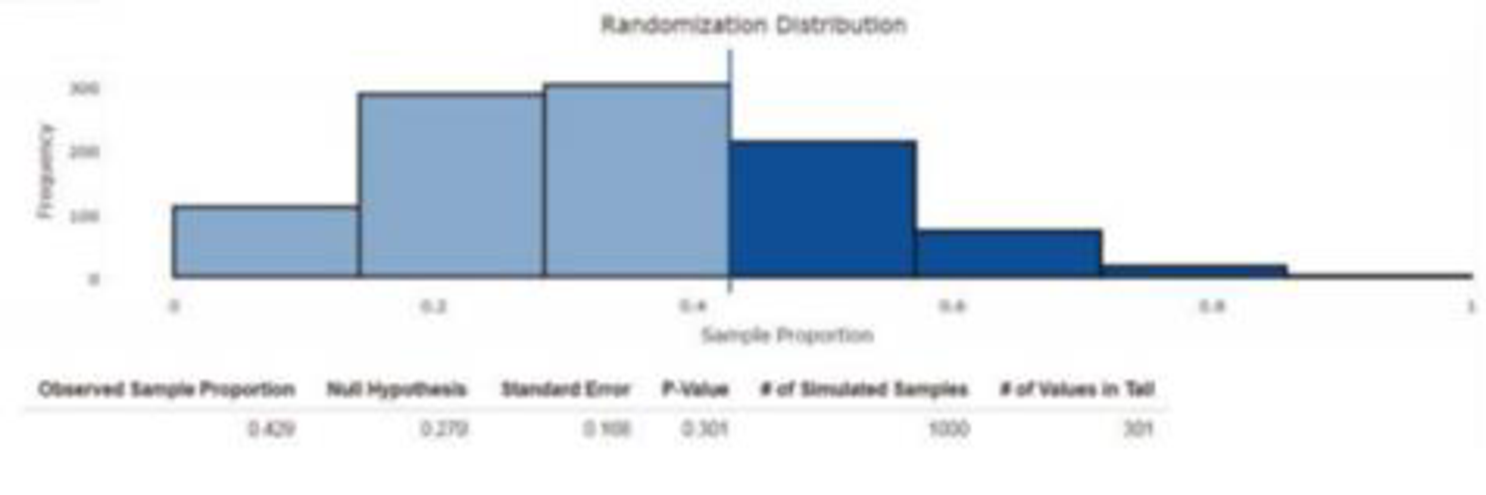
- b. Use the output at the top of the next page from the Shiny app “Randomization Test for One Proportion” to complete an appropriate hypothesis test.
Output for Exercise 10.74
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Introduction To Statistics And Data Analysis
- Pls help asaparrow_forwardSolve the following LP problem using the Extreme Point Theorem: Subject to: Maximize Z-6+4y 2+y≤8 2x + y ≤10 2,y20 Solve it using the graphical method. Guidelines for preparation for the teacher's questions: Understand the basics of Linear Programming (LP) 1. Know how to formulate an LP model. 2. Be able to identify decision variables, objective functions, and constraints. Be comfortable with graphical solutions 3. Know how to plot feasible regions and find extreme points. 4. Understand how constraints affect the solution space. Understand the Extreme Point Theorem 5. Know why solutions always occur at extreme points. 6. Be able to explain how optimization changes with different constraints. Think about real-world implications 7. Consider how removing or modifying constraints affects the solution. 8. Be prepared to explain why LP problems are used in business, economics, and operations research.arrow_forwardged the variance for group 1) Different groups of male stalk-eyed flies were raised on different diets: a high nutrient corn diet vs. a low nutrient cotton wool diet. Investigators wanted to see if diet quality influenced eye-stalk length. They obtained the following data: d Diet Sample Mean Eye-stalk Length Variance in Eye-stalk d size, n (mm) Length (mm²) Corn (group 1) 21 2.05 0.0558 Cotton (group 2) 24 1.54 0.0812 =205-1.54-05T a) Construct a 95% confidence interval for the difference in mean eye-stalk length between the two diets (e.g., use group 1 - group 2).arrow_forward
- An article in Business Week discussed the large spread between the federal funds rate and the average credit card rate. The table below is a frequency distribution of the credit card rate charged by the top 100 issuers. Credit Card Rates Credit Card Rate Frequency 18% -23% 19 17% -17.9% 16 16% -16.9% 31 15% -15.9% 26 14% -14.9% Copy Data 8 Step 1 of 2: Calculate the average credit card rate charged by the top 100 issuers based on the frequency distribution. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardPlease could you check my answersarrow_forwardLet Y₁, Y2,, Yy be random variables from an Exponential distribution with unknown mean 0. Let Ô be the maximum likelihood estimates for 0. The probability density function of y; is given by P(Yi; 0) = 0, yi≥ 0. The maximum likelihood estimate is given as follows: Select one: = n Σ19 1 Σ19 n-1 Σ19: n² Σ1arrow_forward
- Please could you help me answer parts d and e. Thanksarrow_forwardWhen fitting the model E[Y] = Bo+B1x1,i + B2x2; to a set of n = 25 observations, the following results were obtained using the general linear model notation: and 25 219 10232 551 XTX = 219 10232 3055 133899 133899 6725688, XTY 7361 337051 (XX)-- 0.1132 -0.0044 -0.00008 -0.0044 0.0027 -0.00004 -0.00008 -0.00004 0.00000129, Construct a multiple linear regression model Yin terms of the explanatory variables 1,i, x2,i- a) What is the value of the least squares estimate of the regression coefficient for 1,+? Give your answer correct to 3 decimal places. B1 b) Given that SSR = 5550, and SST=5784. Calculate the value of the MSg correct to 2 decimal places. c) What is the F statistics for this model correct to 2 decimal places?arrow_forwardCalculate the sample mean and sample variance for the following frequency distribution of heart rates for a sample of American adults. If necessary, round to one more decimal place than the largest number of decimal places given in the data. Heart Rates in Beats per Minute Class Frequency 51-58 5 59-66 8 67-74 9 75-82 7 83-90 8arrow_forward
- can someone solvearrow_forwardQUAT6221wA1 Accessibility Mode Immersiv Q.1.2 Match the definition in column X with the correct term in column Y. Two marks will be awarded for each correct answer. (20) COLUMN X Q.1.2.1 COLUMN Y Condenses sample data into a few summary A. Statistics measures Q.1.2.2 The collection of all possible observations that exist for the random variable under study. B. Descriptive statistics Q.1.2.3 Describes a characteristic of a sample. C. Ordinal-scaled data Q.1.2.4 The actual values or outcomes are recorded on a random variable. D. Inferential statistics 0.1.2.5 Categorical data, where the categories have an implied ranking. E. Data Q.1.2.6 A set of mathematically based tools & techniques that transform raw data into F. Statistical modelling information to support effective decision- making. 45 Q Search 28 # 00 8 LO 1 f F10 Prise 11+arrow_forwardStudents - Term 1 - Def X W QUAT6221wA1.docx X C Chat - Learn with Chegg | Cheg X | + w:/r/sites/TertiaryStudents/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B2759DFAB-EA5E-4526-9991-9087A973B894% QUAT6221wA1 Accessibility Mode பg Immer The following table indicates the unit prices (in Rands) and quantities of three consumer products to be held in a supermarket warehouse in Lenasia over the time period from April to July 2025. APRIL 2025 JULY 2025 PRODUCT Unit Price (po) Quantity (q0)) Unit Price (p₁) Quantity (q1) Mineral Water R23.70 403 R25.70 423 H&S Shampoo R77.00 922 R79.40 899 Toilet Paper R106.50 725 R104.70 730 The Independent Institute of Education (Pty) Ltd 2025 Q Search L W f Page 7 of 9arrow_forward

 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning

