
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.1, Problem 1fT
The mask used in parts C-E is replaced by one that has a triangular hole as shown.
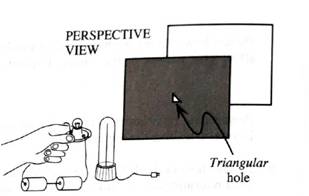
Predict what you would see on the screen when a small bulb is held next to the top of a long-filament bulb as shown. Sketch your prediction below.
Compare sour prediction with those of your partners. After you and your partners have come to an agreement, check your prediction. Resolve any inconsistencies.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
For each of the actions depicted, determine the direction (right, left, or zero) of the current induced to flow through the resistor in the circuit containing the secondary coil. The coils are wrapped around a plastic core. Immediately after the switch is closed, as shown in the figure, (Figure 1) in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? If the switch is then opened, as shown in the figure, in which direction does the current flow through the resistor? I have the answers to the question, but would like to understand the logic behind the answers. Please show steps.
When violet light of wavelength 415 nm falls on a single slit, it creates a central diffraction peak that is 8.60
cm wide on a screen that is 2.80 m away.
Part A
How wide is the slit?
ΟΙ ΑΣΦ
?
D= 2.7.10-8
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining
m
Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values.
Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all steps
Chapter 10 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 1aTCh. 10.1 - Predict how each of the following changes would...Ch. 10.1 - A mask with a circular hole is placed between a...Ch. 10.1 - What do your observations suggest about the path...Ch. 10.1 - Imagine that you held a string of closely spaced...Ch. 10.1 - The mask used in parts C-E is replaced by one that...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 1gTCh. 10.1 - Predict what you would see on the screen when an...Ch. 10.1 - Predict the size of the lit region on the screen...Ch. 10.1 - Suppose that the bulb were replaced by a long...
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 2cTCh. 10.1 - Predict what you would see on the screen at the...Ch. 10.1 - Suppose that the light from the top bulb in the...Ch. 10.1 - Predict what you would see on the screen in the...Ch. 10.2 - Close one eye and lean down so that your open eye...Ch. 10.2 - Suppose that you placed your finger behind the...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 1cTCh. 10.2 - Prob. 1dTCh. 10.2 - Place your head so that you can see the image of...Ch. 10.2 - Move the nail off w the right side of the mirror...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 3aTCh. 10.2 - Turn the large sheet of paper over (or obtain a...Ch. 10.2 - Remove the mirror and the object nail. For each...Ch. 10.2 - On the diagram at right, draw one ray from the pin...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 4bTCh. 10.2 - Determine the image location using the method of...Ch. 10.3 - A pin is placed In front of a cylindrical mirror...Ch. 10.3 - Could you use any two rays (even those that do not...Ch. 10.3 - Observers at M and N arc looking at an image of...Ch. 10.3 - Stick a pin into a piece of cardboard and place...Ch. 10.3 - Gradually decrease the angle between the mirrors...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 1bTCh. 10.4 - Three students are discussing their results from...Ch. 10.4 - For each case shown below, determine and label the...Ch. 10.4 - In each of the previous cases, predict what would...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 2cTCh. 10.4 - Explain how you can use a screen to determine the...Ch. 10.5 - Look at very distant object through a convex lens....Ch. 10.5 - Consider a point on the distant object that is...Ch. 10.5 - Suppose that you placed a very small bulb at the...Ch. 10.5 - Consider the ray chai is parallel to the principal...Ch. 10.5 - Consider the ray that goes through the focal point...Ch. 10.5 - How can you use these two rays to determine the...Ch. 10.5 - Consider the ray from the easer that strikes the...Ch. 10.5 - Draw the continuation of the two remaining rays...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 2fTCh. 10.5 - The diagram below shows a small object placed near...Ch. 10.5 - A lens, a bulb, and a screen are arranged as shown...Ch. 10.5 - Obtain the necessary equipment and check your...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 3cTCh. 10.6 - The diagram at right illustrates what an observer...Ch. 10.6 - Obtain two soda cans and a cardboard tube that has...Ch. 10.6 - Could an observer at each of the labeled points...Ch. 10.6 - Use the above diagram to answer the following...Ch. 10.6 - Obtain convex lens. Use the lens as a magnifying...Ch. 10.6 - Draw a ray diagram that shows how to determine the...Ch. 10.6 - The lateral magnification, m1 , is defined as...Ch. 10.6 - The angular magnification, m , is defined as m= ,...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
10.71 Identify each of the following as an acid or a base: (10.1)
H2SO4
RbOH
Ca(OH)2
HI
...
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculate the center of mass of the hollow cone shown below. Clearly specify the origin and the coordinate system you are using. Z r Y h Xarrow_forward12. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which will cause more damage? (think about which collision has a larger amount of kinetic energy dissipated/lost to the environment? I m II III A. I B. II C. III m m v brick wall ע ע 0.5v 2v 0.5m D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them) 2marrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question teach me step by step and draw for mearrow_forward
- From this question and answer can you explain how get (0,0,5) and (5,0,,0) and can you teach me how to solve thisarrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question and teach me using ( engineer method formula)arrow_forward11. If all three collisions in the figure below are totally inelastic, which brings the car of mass (m) on the left to a halt? I m II III m m ע ע ע brick wall 0.5v 2m 2v 0.5m A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. II and III F. I and III G. I, II and III (all of them)arrow_forward
- How can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?arrow_forwardYou want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the process to form the inlet and outlet. Square Cross Sectionarrow_forward1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device. 2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use. High Aspect Ratio Trenches Undoped Si Wafer P-doped Si 3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you use and why? 4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful. 5. You are given a composite…arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardAnother worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY